
Fabry Disease Treatment Market Size, Share, & Industry Analysis Report
By Route of Administration (Intravenous Route and Oral Route), By Therapy, By Distribution Channel, By Region – Market Forecast, 2025–2034
- Published Date:Jun-2025
- Pages: 129
- Format: PDF
- Report ID: PM5760
- Base Year: 2024
- Historical Data: 2020-2023
Market Overview
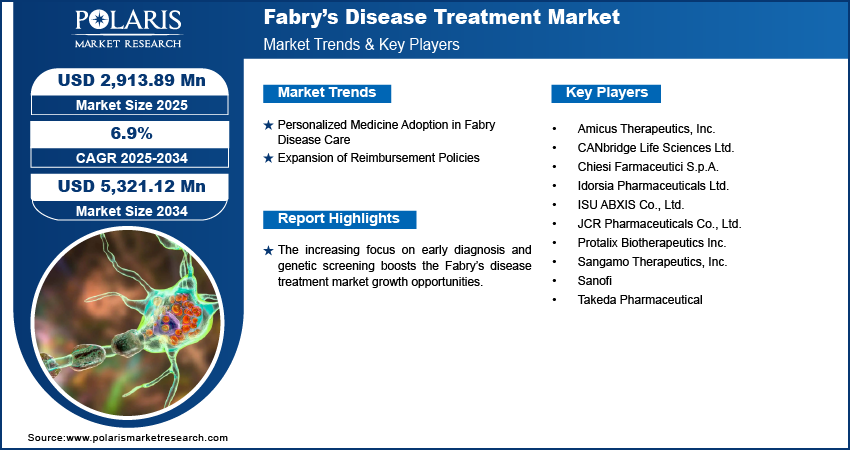
The global Fabry disease treatment market size was valued at USD 2,727.85 million in 2024 and is projected to register a CAGR of 6.9% during 2025–2034. The increasing focus on early diagnosis and genetic screening further boosts the market opportunities. Early identification of Fabry disease allows timely intervention, preventing severe damage to vital organs.
Fabry disease is a rare genetic disorder that affects the body's ability to break down specific fatty substances, leading to their expansion in various organs. The market for Fabry disease treatment has grown in response to the need for managing and slowing the progression of this lifelong condition. The market contains therapies that target the root cause of the disease as well as those that manage its symptoms, such as enzyme replacement therapy, Chaperone Therapy, and others. These treatments aim to improve the quality of life for patients and reduce complications that arise from damage to the heart, kidneys, and nervous system. According to a September 2023 report by EURORDIS-Rare Diseases Europe, approximately 300 million people worldwide have rare diseases, including around 30 million in Europe. The increasing prevalence of rare diseases, such as Fabry disease, is contributing to the market growth.
The rising investments in research and development for rare diseases further contribute to the market expansion. In July 2023, the UKRI launched the USD 18 million Rare Disease Research Platform to improve diagnosis and treatment by uniting 11 research nodes due to the rare diseases affecting 1 in 17 UK citizens, with over 30% of affected children dying before age five. Additionally, pharmaceutical companies are increasing their focus on niche therapeutic areas such as Fabry disease due to the unmet clinical needs and the potential for innovative solutions.
To Understand More About this Research: Request a Free Sample Report
Market Dynamics
Personalized Medicine Adoption in Fabry Disease Care
The growing adoption of personalized medicine shows a transformative role in the treatment of Fabry disease. Personalized medicine involves tailoring medical treatment to an individual genetic profile and disease characteristics. This shift toward individualized care is improving diagnosis, allowing targeted intervention, and supporting better disease management across diverse patient subgroups. The core challenges in treating Fabry disease are its variability in symptoms and severity among different patients. Personalized medicine addresses this by incorporating genetic testing and biomarker analysis in the treatment process, helping clinicians make more informed decisions about therapy types, dosage, and timing. For instance, a May 2025 report by the NIH stated that they have successfully treated an infant with CPS1 deficiency using personalized CRISPR gene editing, marking the first human application of this approach. The six-month process from diagnosis to treatment demonstrates the potential for rapid, customized therapies for rare genetic disorders. As a result, patients are more likely to receive treatments that are effective for their specific condition, leading to improved outcomes and reduced adverse effects.
Expansion of Reimbursement Policies
The evolution of reimbursement frameworks is significantly elevating the demand for therapies targeting rare diseases. The financial implications of treatment, often involving prolonged or lifelong administration, impose considerable challenges on both patients and healthcare systems. In response, governmental bodies, insurers, and policymakers are increasingly adopting comprehensive models that account for the distinct economic dynamics of rare diseases, exemplified by initiatives such as the Operational Description of Rare Diseases, the International Rare Diseases Research Consortium (IRDiRC), and methodologies established by the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE). These developments are facilitating a structured approach to reimbursement for Fabry disease interventions. Furthermore, contemporary reimbursement strategies frequently incorporate value-based care models that incentivize enhanced health outcomes. This shift is prompting manufacturers to focus on developing more precise, effective therapies that align treatment objectives with payer expectations. As the policy landscape evolves, all stakeholders, including payers, providers, developers, and advocacy organizations, stand to gain from a more predictable and sustainable reimbursement system. Thus, the expansion of reimbursement policies boosts the industry expansion.
Segment Insights
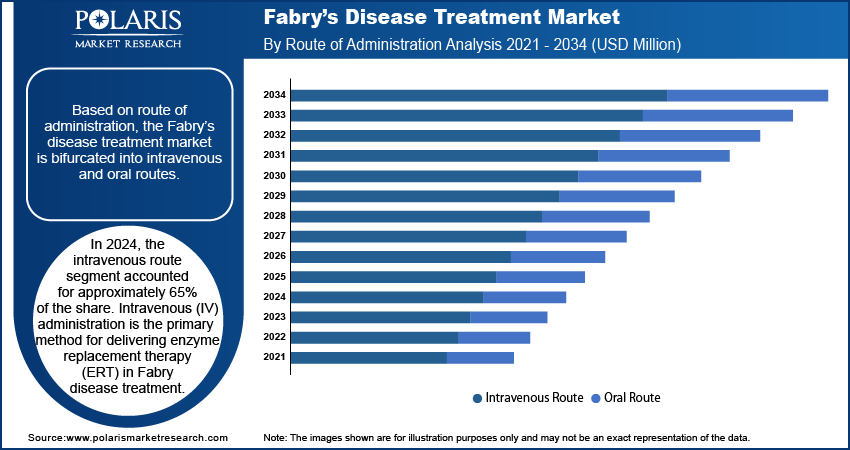
Market Assessment by Route of Administration
In 2024, the intravenous route segment accounted for approximately 65% of the share. Intravenous (IV) administration is the primary method for delivering enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) in Fabry disease treatment. ERT involves infusing synthetic enzymes directly into the bloodstream, compensating for the deficient alpha-galactosidase A enzyme in patients. This approach ensures efficient distribution of the therapeutic enzyme to affected organs, such as the kidneys, heart, and nervous system, thereby mitigating disease progression and alleviating symptoms. This dominance of the IV route in Fabry disease management is attributed to its proven efficacy in stabilizing critical organ functions. Clinical studies have consistently demonstrated that regular IV infusions slow the progression of renal and cardiac complications, which are prevalent in Fabry patients. Moreover, the controlled environment of IV administration allows healthcare providers to monitor patients closely for any adverse reactions, ensuring timely interventions when necessary.
The oral route segment is projected to register a CAGR of 7.0% from 2025 to 2034. This treatment approach is suited for patients with amenable mutations of the GLA gene and works by stabilizing the misfolded alpha-galactosidase A enzyme, allowing it to function correctly inside lysosomes. Unlike enzyme replacement therapy (ERT), which requires hospital visits for intravenous administration, oral therapies are taken at home, offering a significant improvement in convenience, treatment adherence, and overall patient quality of life. Additionally, several governments across Asia Pacific are investing in genomic research and rare disease diagnostics, which supports early identification of Fabry disease and facilitates the use of mutation-specific treatments such as migalastat.
Market Assessment by Therapy
In 2024, the enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) segment accounted for approximately 60% of the share. ERT involves intravenous infusions of synthetic enzymes such as agalsidase alfa or beta, which help break down Gb3, slowing disease progression and alleviating symptoms such as neuropathic pain, gastrointestinal issues, and organ dysfunction. Early intervention with ERT is essential to prevent irreversible damage, particularly in vital organs. The increasing prevalence of Fabry disease programs for high-cost therapies is driving demand for enzyme replacement and expanding reimbursement therapy (ERT). Governments are implementing rare disease policies to enhance treatment access, though disparities persist due to economic constraints. For instance, Brazil public health system provides partial ERT coverage, whereas Saudi Arabia Ministry of Health includes it in its essential treatments. Regional initiatives, such as national rare disease plans and partnerships with biopharmaceutical firms, are accelerating ERT accessibility, though gaps remain in low-resource settings.
The substrate reduction therapy segment is expected to register a CAGR of 7.1% from 2025 to 2034. Substrate reduction therapy is an alternative treatment strategy for Fabry disease, offering a different mechanism of action compared to traditional enzyme replacement therapy. While ERT addresses the enzyme deficiency by providing exogenous enzyme infusions, SRT takes a complementary approach by reducing the production of glycosphingolipids, the substrates that accumulate abnormally in this disorder. This oral therapy option provides greater convenience for patients and may benefit those who cannot tolerate or respond inadequately to ERT. The development of SRT reflects advances in understanding Fabry disease pathology and the growing emphasis on personalized treatment approaches tailored to patients' specific genetic mutations and disease manifestations. Moreover, the potential for SRT to address central nervous system symptoms, as some investigational SRTs are designed to cross the blood-brain barrier, an area where ERT falls short.
Market Evaluation by Distribution Channel
In 2024, the hospitals segment accounted for approximately 42% of the share due to its role in managing rare and complex therapies. The centralized administration and monitoring capabilities provided by hospital pharmacies are essential for therapies such as ERT requiring specialized handling, storage, and intravenous infusion. Hospital settings ensure the presence of trained personnel and infrastructure for managing infusion-related adverse events, making them the preferred distribution and administration channel. Hospitals often serve as diagnostic and treatment hubs for rare diseases, facilitating early diagnosis and initiation of therapy through coordinated efforts between pharmacists, geneticists, and specialists. This collaborative approach improves treatment adherence and outcomes.
The retail pharmacies segment is expected to register a CAGR of 7.0% from 2025 to 2034 due to the expansion of specialty pharmacy services within retail settings. Major pharmacy chains are increasingly integrating specialty drug programs to dispense complex therapies such as enzyme replacement therapies (ERTs) and pharmacological chaperones, supported by dedicated pharmacist counseling and patient monitoring services. The growing trend of home-based care is also influencing the role of retail pharmacies. As more patients shift to at-home infusions and oral therapies, retail pharmacies are being relied upon to coordinate delivery logistics, provide training support, and monitor adherence, further embedding them in the treatment process.
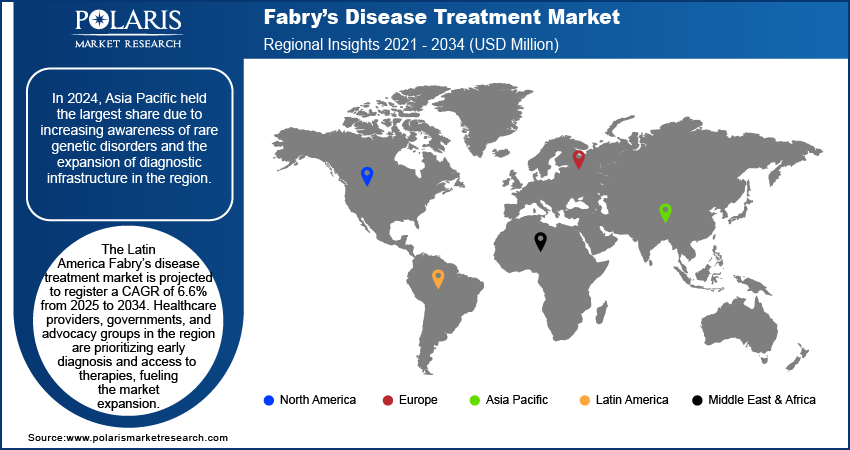
Regional Analysis
Asia Pacific Fabry Disease Treatment Market In 2024, the Asia Pacific Fabry disease treatment market was valued at USD 540 million due to increasing awareness of rare genetic disorders and the expansion of diagnostic infrastructure in the region. Initiatives by healthcare authorities, governments, and rare disease advocacy groups have boosted the adoption of life-saving drugs for the treatment of Fabry disease in the region, particularly in developed regions such as Japan, South Korea, and Australia. The government of Australia, through the Life Saving Drugs Program (LSDP), subsidized access for eligible Fabry disease patients to expensive life-saving drugs. These initiatives are creating a favorable environment for pharmaceutical companies offering enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) and chaperone therapies for Fabry disease treatment to expand their footprint in the region. Pharmaceutical companies are also responding to the growing demand for Fabry drugs by increasing investments in regional research and clinical development. Multinational firms, including Takeda and Sanofi, are introducing local clinical trials and partnering with regional healthcare providers to ensure the development of drugs for Fabry disease treatment. For instance, Sanofi initiated global clinical trials, including Asia Pacific, for Fabry disease, specifically focusing on the investigational drug venglustat, which is a substrate reduction therapy.
Japan Fabry Disease Treatment Market
The Fabry disease treatment market in Japan was valued at approximately USD 130 million in 2024. Regulatory bodies such as the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) have implemented fast-track regulatory initiatives, such as the sakigake designation and the conditional early approval System, to accelerate the approval of innovative treatments for serious and rare diseases, including orphan drugs such as those for Fabry disease. These initiatives are thereby propelling the market growth in the region.
North America Fabry Disease Treatment Market
The Fabry disease treatment market in North America is driven by robust clinical infrastructure, favorable regulatory frameworks, and a well-established reimbursement ecosystem that supports access to high-cost rare disease therapies. Significant adoption of enzyme replacement therapies is evident due to early diagnosis initiatives and specialist availability across major healthcare centers. The region shows strong uptake of oral chaperone therapies, particularly in patients with amenable mutations, backed by comprehensive genetic screening programs. Advanced clinical research in the US and Canada is fueling the development of gene therapy candidates, supported by public-private funding collaborations and fast-track regulatory designations. Payer models in North America increasingly recognize the value of long-term disease management and are evolving to include outcomes-based contracts, thereby enhancing patient access to innovative therapies.
Latin America Disease Treatment Market
The Latin America Fabry disease treatment market is projected to register a CAGR of 6.6% from 2025 to 2034. Healthcare providers, governments, and advocacy groups in LATAM are prioritizing early diagnosis and access to therapies, which is fueling the overall expansion. Countries such as Brazil and Argentina are implementing screening programs for early disease detection, with the rising awareness of the condition symptoms, such as chronic pain, kidney dysfunction, and cardiovascular complications. This proactive approach is creating a strong foundation for Fabry disease treatment adoption and improved patient outcomes. The growing investments in healthcare in countries such as Brazil and Argentina are also fueling the market in the region by expanding access to diagnostics, therapies, and specialized care. For instance, Brazil is the largest healthcare industry in Latin America and spends 9.47% of its GDP on healthcare, which represents USD 161 billion. Additionally, Argentina and Brazil expanding reimbursement policies are reducing personal costs for patients, making Fabry disease treatments more affordable. These investments further support medical training programs, ensuring more physicians can accurately diagnose and manage the disease, ultimately improving patient outcomes across the region.
Middle East & Africa Disease Treatment Market
The Fabry disease treatment market in the Middle East & Africa was valued at USD 170 million in 2024. Pharmaceutical companies are actively expanding their presence in the MENA to meet the emerging demand for rare disease treatments, including Fabry drugs. Global firms such as Sanofi and Takeda are intensifying regional presence through local partnerships, regulatory initiatives, and educational campaigns aimed at a sustainable disease management ecosystem, with an emphasis on rare diseases, including Fabry disease. For instance, in October 2023, King Abdullah International Medical Research Center (KAIMRC), Saudi Arabia major institution in biomedical and clinical research, signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with Sanofi to establish a sustainable disease management ecosystem powered by artificial intelligence (AI) and real-world evidence (RWE), with an emphasis on rare diseases, oncology, and rare blood disorders. These developments are thereby propelling the overall growth in the MENA. Moreover, the growing healthcare sector in countries such as Qatar and Bahrain propels the growth in MENA by enhancing access, diagnostics, and funding for rare disease therapies. Both nations are expanding and modernizing their healthcare infrastructure, enabling earlier and more accurate diagnosis of genetic and metabolic disorders such as Fabry disease.
Key Players & Competitive Analysis Report
The Fabry disease treatment market demonstrates a dynamic and competitive landscape shaped by continuous advancements in therapeutic approaches. Pharmaceutical companies compete by developing enzyme replacement therapies (ERTs), chaperone therapies, and gene therapies that target the underlying deficiency of alpha-galactosidase A. Firms prioritize expanding their treatment portfolios to include therapies that offer improved efficacy, reduced immunogenicity, and more convenient administration routes, such as oral or less frequent intravenous infusions. Participants intensify R&D investments to innovate novel therapies, including second-generation ERTs and investigational gene therapies, which aim to achieve sustained enzyme expression and address the limitations of traditional treatments.
Clinical trial activity remains robust, with several candidates in various phases targeting both treatment-naïve patients and those switching from standard care. Companies engage in strategic collaborations with academic institutions and biotech firms to access novel platforms and accelerate product development timelines. In addition, licensing deals and partnerships enable access to advanced gene-editing and vector-delivery technologies that enhance competitiveness in the evolving gene therapy segment.
List of Key Companies
- Amicus Therapeutics, Inc.
- CANbridge Life Sciences Ltd.
- Chiesi Farmaceutici S.p.A.
- Idorsia Pharmaceuticals Ltd.
- ISU ABXIS Co., Ltd.
- JCR Pharmaceuticals Co., Ltd.
- Protalix Biotherapeutics Inc.
- Sangamo Therapeutics, Inc.
- Sanofi
- Takeda Pharmaceutical
Fabry Disease Treatment Industry Developments
In March 2024, CENTOGENE extended its collaboration with Takeda to improve access to genetic testing for lysosomal storage disorders (LSDs) patients. This partnership aims to advance genetic diagnostics, ensuring timely and accurate testing for effective disease management.
In March 2022, JCR and Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma formed a partnership for marketing alliance for the Agalsidase Beta BS I.V. infusion to treat Fabry disease in Japan.
In January 2022, ISU ABXIS entered into a licensing agreement with NPO Petrovax Pharm in Russia for "Fabagal," a therapeutic agent indicated for the treatment of Fabry disease
Fabry Disease Treatment Market Segmentation
By Route of Administration Outlook (Revenue USD Million, 2020–2034)
- Intravenous Route
- Oral Route
By Therapy Outlook (Revenue USD Million, 2020–2034)
- Enzyme Replacement Therapy (ERT)
- Substrate Reduction Therapy (SRT)
- Others
By Distribution Channel Outlook (Revenue USD Million, 2020–2034)
- Hospital Pharmacies
- Retail Pharmacies
- Online Pharmacies
By Regional Outlook (Revenue USD Million, 2020–2034)
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Mexico
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- UK
- Italy
- Spain
- Netherlands
- Russia
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- Malaysia
- South Korea
- Indonesia
- Australia
- Vietnam
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Middle East & Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Israel
- South Africa
- Rest of Middle East & Africa
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
Fabry Disease Treatment Market Report Scope
|
Report Attributes |
Details |
|
Market Size Value in 2024 |
USD 2,727.85 million |
|
Market Size Value in 2025 |
USD 2,913.89 million |
|
Revenue Forecast by 2034 |
USD 5,321.12 million |
|
CAGR |
6.9% from 2025 to 2034 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Historical Data |
2020–2023 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025–2034 |
|
Quantitative Units |
Revenue in USD million and CAGR from 2025 to 2034 |
|
Report Coverage |
Revenue Forecast, Competitive Landscape, Growth Factors, and Industry Trends |
|
Segments Covered |
|
|
Regional Scope |
|
|
Competitive Landscape |
|
|
Report Format |
|
|
Customization |
Report customization as per your requirements with respect to countries, regions, and segmentation. |
FAQ's
The global market size was valued at USD 2,727.85 million in 2024 and is projected to grow to USD 5,321.12 million by 2034.
The global market is projected to register a CAGR of 6.9% during the forecast period.
In 2024, the Asia Pacific held the largest share due to increasing awareness of rare genetic disorders and the expansion of diagnostic infrastructure in the region.
A few of the key players are Amicus Therapeutics, Inc.; CANbridge Life Sciences Ltd.; Chiesi Farmaceutici S.p.A.; Idorsia Pharmaceuticals Ltd.; ISU ABXIS Co., Ltd.; JCR Pharmaceuticals Co., Ltd.; Protalix Biotherapeutics Inc.; Sangamo Therapeutics, Inc.; Sanofi; and Takeda Pharmaceutical.
In 2024, the intravenous route segment accounted for the largest share. Intravenous (IV) administration is the primary method for delivering enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) in Fabry disease treatment.
In 2024, the enzyme replacement therapy (ERT) segment accounted for approximately 60% of the share. ERT helps break down Gb3, slowing disease progression and alleviating symptoms such as neuropathic pain, gastrointestinal issues, and organ dysfunction.
