
Cell and Gene Therapy Clinical Trials Market Size, Share, Trends, Industry Analysis Report
By Phase (Phase I, Phase II, Phase III, Phase IV), By Indication, By Region – Market Forecast, 2025–2034
- Published Date:Aug-2025
- Pages: 129
- Format: PDF
- Report ID: PM6185
- Base Year: 2024
- Historical Data: 2020 - 2023
Overview
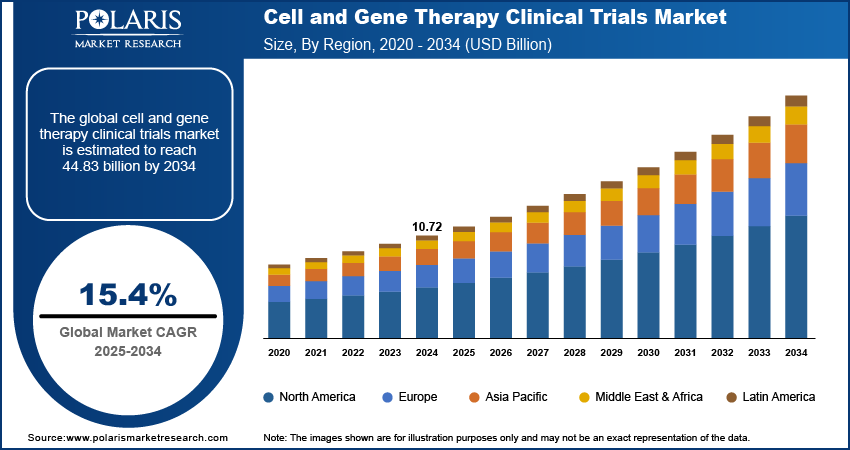
The global cell and gene therapy clinical trials market size was valued at USD 10.72 billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 15.4% from 2025 to 2034. Increased funding from pharmaceutical companies, venture capitalists, and governments is accelerating innovation in cell and gene therapies. Substantial capital is directed toward scaling clinical-stage pipelines, supporting early-phase trials, and expanding infrastructure, fueling demand for trial-specific services and platforms.
Key Insights
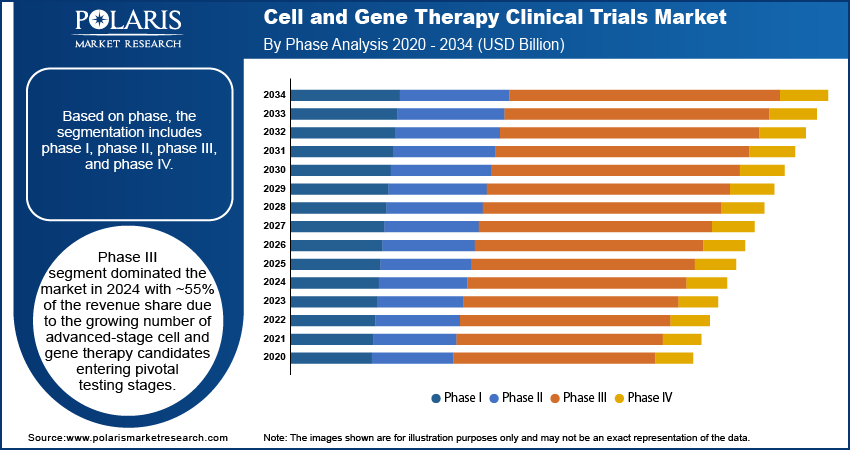
- The phase III segment held ~55% revenue share in 2024, driven by the rising numbers of cell and gene therapy candidates in late-stage clinical trials.
- The oncology segment led in 2024 due to high demand for therapies targeting cancer through advanced clinical trials.
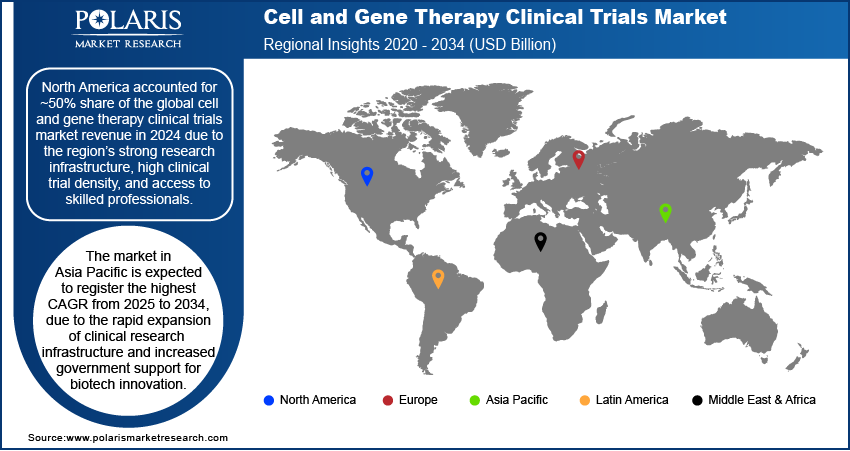
- North America captured ~50% of the market in 2024, supported by strong research infrastructure and a high concentration of clinical trials.
- The U.S. dominated the market in North America in 2024, driven by leading biotech firms and specialized clinical research networks.
- The industry in Asia Pacific is expected to grow fastest from 2025 to 2034, fueled by expanding clinical infrastructure and government support for biotech.
- China led in Asia Pacific in 2024 due to a surge in domestic biotech companies, rising investments, and growth in GMP-compliant manufacturing facilities.
Industry Dynamics
- Increasing number of cell and gene therapy candidates entering clinical trials is driving demand for specialized trial management and monitoring services.
- Strong government funding and regulatory support in the U.S. and EU are accelerating trial approvals and development timelines for advanced therapies.
- Expansion of decentralized and hybrid trial models improves patient access and enrollment in complex cell and gene therapy studies.
- High costs and complex logistics for handling live cell products limit scalability and participation in global clinical trial networks.
Market Statistics
- 2024 Market Size: USD 10.72 billion
- 2034 Projected Market Size: USD 44.83 billion
- CAGR (2025–2034): 15.4%
- North America: Largest market in 2024
To Understand More About this Research: Request a Free Sample Report
The cell and gene therapy clinical trials market refers to the ecosystem that supports research, development, and regulatory evaluation of therapies that use cellular modification or genetic engineering to treat or cure diseases. This includes infrastructure, services, and technologies required to conduct preclinical and clinical trials for such therapies, involving patient recruitment, biomarker analysis, vector delivery systems, regulatory compliance, and advanced manufacturing. The market plays a critical role in enabling biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies to bring next-generation therapies for oncology, rare diseases, and genetic disorders through phased clinical testing.
Biotech firms are increasingly relying on contract research organizations for trial design, site management, regulatory strategy, and patient recruitment. These strategic alliances enable faster trial execution, reduce costs, and scale resources across multiple geographies. Moreover, shifts toward virtual and hybrid clinical trials improve accessibility and patient retention. Adaptive trial designs allow real-time adjustments, improving trial efficiency and increasing the likelihood of success, especially for personalized therapies targeting small populations.
Drivers & Opportunities
High Prevalence of Rare and Genetic Disorders: The growing number of individuals affected by rare and genetic disorders is creating strong demand for innovative treatments, including cell and gene therapies. According to the Rare Diseases International, more than 300 million people worldwide are suffering from a rare disease, with over 6,000 identified. These conditions affect 3.5% – 5.9% of the global population. Many of these conditions have no existing cure or have limited treatment options, making them a priority for research and clinical development. This unmet need encourages quicker patient recruitment and higher participation in clinical trials, especially when supported by patient advocacy groups and nonprofit organizations. The emotional and medical urgency behind these disorders also draws attention from regulatory bodies and funding agencies, which helps push trials forward and increases their overall success potential.
Rising R&D Investments in Advanced Therapies: The market for cell and gene therapy clinical trials is seeing strong momentum due to increased investments in research and development (R&D). Pharmaceutical companies, biotechnology firms, and public organizations are allocating significant funds to develop next-generation treatments. These investments are focused on expanding clinical-stage pipelines, improving laboratory and manufacturing infrastructure, and supporting early-stage exploratory studies. The push for innovation is also encouraging partnerships between research institutes and industry players, allowing them to share knowledge and resources. This growing capital flow supports a higher volume of trials and improves their quality, speed, and efficiency.
Segmental Insights
Phase Analysis
Based on phase, the segmentation includes phase I, phase II, phase III, and phase IV. The phase III segment dominated the market in 2024 with ~55% of the revenue share due to the growing number of advanced-stage cell and gene therapy candidates entering pivotal testing stages. These trials often require larger patient populations and longer durations, leading to higher trial budgets and increased demand for specialized services. Regulatory bodies demand comprehensive safety and efficacy data before approval, pushing companies to prioritize this phase. Many therapies have shown strong promise in earlier stages, prompting sponsors to scale up late-phase trials. The complexity and resource intensity of Phase III trials significantly contribute to their higher share in the overall market.
The phase I segment is expected to register the highest CAGR from 2025 to 2034 due to the influx of new investigational products entering the clinical pipeline. Advancements in genome editing technologies and vector engineering are enabling more novel candidates to move into early testing. Biotech startups and academic research centers are actively initiating exploratory trials, encouraged by early preclinical success and funding support. Growth in personalized medicine and rare disease research is driving demand for initial safety assessments in small patient groups. As the field expands, more sponsors are accelerating entry into human trials, leading to a surge in Phase I activity.
Indication Analysis
In terms of indication, the segmentation includes oncology, cardiology, CNS, musculoskeletal, infectious diseases, dermatology, endocrine, metabolic, genetic, immunology & inflammation, ophthalmology, hematology, gastroenterology, and others. The oncology segment held the largest revenue share in 2024 due to the high number of active cell and gene therapy trials targeting various cancer types. Cancer remains a top therapeutic focus due to the complexity of the disease and unmet clinical needs. CAR-T therapies and other engineered cell-based approaches have shown breakthrough responses in hematologic and solid tumors, attracting robust investments and regulatory priority. Trial sponsors are increasingly concentrating on cancers with specific genetic mutations, enhancing the precision and impact of investigational therapies. Strong clinical momentum and favorable regulatory frameworks helped oncology secure the largest share of total market revenue.
The cardiology segment is expected to register the highest CAGR from 2025 to 2034, driven by increasing focus on regenerative therapies for chronic heart conditions. Gene therapies aiming to repair or regenerate cardiac tissue have gained traction due to limitations in current pharmacological treatments. Recent advances in delivering genetic payloads directly to cardiac cells are accelerating clinical innovation in heart failure, myocardial infarction, and inherited cardiovascular disorders. Rising burden of heart disease globally and growing interest in disease-modifying interventions are encouraging early- and mid-stage trials in this area. Collaborations between biotech firms and cardiology research institutes are further expanding this high-growth segment.
Regional Analysis
The North America cell and gene therapy clinical trials market accounted for ~50% of the global revenue share in 2024 due to the region’s strong research infrastructure, high clinical trial density, and access to skilled professionals. Leading academic centers, contract research organizations, and biopharmaceutical companies operate extensive early- and late-phase trials across the U.S. and Canada. In 2025, Novartis announced that it will enhance its manufacturing and research and development capabilities in the U.S., committing an investment of USD 23 billion over the next five years. This expansion aims to boost its operational presence and innovation pipeline within the U.S. market. The region also benefits from a favorable regulatory environment that encourages accelerated approvals and early patient access programs for advanced therapies. Significant government and private sector funding further supports clinical innovation, enabling continuous trial initiation and expansion. High disease prevalence and proactive trial recruitment strategies solidify North America's dominant market position.
U.S. Cell and Gene Therapy Clinical Trials Market Insights
The U.S. dominated the market in 2024 due to its concentration of top-tier biotech companies and specialized clinical research networks. Regulatory initiatives such as the FDA's Regenerative Medicine Advanced Therapy (RMAT) designation continue to attract global sponsors to launch trials in the country. The U.S.-based institutions frequently pioneer first-in-human and pivotal studies, driven by deep capital reserves and streamlined regulatory coordination. Patient recruitment is further supported through large treatment centers and disease-specific registries. A mature reimbursement ecosystem and strong intellectual property protection create a favorable setting for long-term trial activity, helping the U.S. remain a preferred destination for cell and gene therapy development.
Asia Pacific Cell and Gene Therapy Clinical Trials Market Trends
Asia Pacific is expected to register the highest CAGR from 2025 to 2034, due to the rapid expansion of clinical research infrastructure and increased government support for biotech innovation. For instance, India aims to establish a USD 1 trillion biotechnology economy by 2047, supported by significant government initiatives. Countries such as China, South Korea, and Singapore are making strategic investments to attract global and local sponsors. Large patient populations and relatively lower trial costs are prompting sponsors to expand early- and mid-stage trials in the region. Regulatory agencies across Asia Pacific are also modernizing approval pathways, enabling faster trial initiation. Multinational companies are forming regional alliances with hospitals and research institutions, which is accelerating the scale and frequency of gene and cell therapy trials.
China Cell and Gene Therapy Clinical Trials Market Overview
China led the Asia Pacific market in 2024 due to its surge in homegrown biotech firms, increased capital investments, and expansion of GMP-certified manufacturing sites. Clinical trial approvals have become more efficient under the National Medical Products Administration (NMPA), boosting the volume of ongoing studies. Chinese researchers are actively developing CAR-T, gene editing, and stem cell platforms tailored to local disease profiles. Additionally, China’s large pool of treatment-naïve patients facilitates rapid enrollment, making it an attractive location for sponsors seeking faster data readouts. Significant funding through government programs and local venture capital has positioned China as a regional leader in trial volume.
Europe Cell and Gene Therapy Clinical Trials Market Outlook
The market for cell and gene therapy in Europe is expanding steadily due to its growing pipeline of advanced therapy medicinal products (ATMPs) and improved harmonization in clinical trial regulations. The European Medicines Agency (EMA) and local authorities are offering incentives such as PRIME designation and scientific advice, which encourage sponsors to initiate early-phase trials across multiple EU nations. Various countries such as Germany, the UK, and the Netherlands are witnessing growth in academic and commercial trial activity, especially in rare diseases and oncology. Rising patient advocacy and broader access to trial networks are supporting faster enrollment. Strategic partnerships between European biotech companies and global sponsors are also enhancing trial execution capacity.
Key Players & Competitive Analysis
The competitive landscape of the cell and gene therapy clinical trials market is characterized by robust industry analysis, with stakeholders focusing on accelerating innovation and expanding their therapeutic pipelines. Companies are employing strategic market expansion strategies to enter untapped geographies and broaden patient access to clinical studies. Joint ventures and strategic alliances with research institutes and hospitals are enhancing trial efficiency and patient recruitment. Mergers and acquisitions are reshaping the competitive dynamics, enabling firms to consolidate capabilities in vector manufacturing, clinical operations, and regulatory navigation. Post-merger integration efforts are aimed at harmonizing R&D functions and trial governance across international operations.
Technological advancements, including AI-driven trial design and real-time patient monitoring, are becoming central to competitive differentiation. Sponsors are prioritizing decentralized and adaptive trial models to streamline data collection and reduce time-to-market. The competitive environment remains dynamic, with firms leveraging strategic partnerships and digital innovations to accelerate the development of next-generation therapies.
Key Players
- Charles River Laboratories
- ICON Plc
- IQVIA
- LabCorp
- Medpace
- Novotech
- PAREXEL International Corp.
- Syneos Health
- Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.
- Veristat, LLC
Cell and Gene Therapy Clinical Trials Industry Developments
May 2025: Thales enhanced its naval cybersecurity systems by integrating AI-driven threat detection and secure digital architectures to improve cyber resilience in modern maritime operations.
June 2024: Speedcast integrated Cydome’s AI-powered threat analytics, real-time monitoring, vulnerability scanning, and SIEM capabilities into its SIGMA platform, enabling fleet-wide cybersecurity monitoring and compliance with IMO, IACS E26, and NIS2 regulations.
Cell and Gene Therapy Clinical Trials Market Segmentation
By Phase Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- Phase I
- Phase II
- Phase III
- Phase IV
By Indication Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- Oncology
- Cardiology
- CNS
- Musculoskeletal
- Infectious Diseases
- Dermatology
- Endocrine, Metabolic, Genetic
- Immunology & Inflammation
- Ophthalmology
- Hematology
- Gastroenterology
- Others
By Regional Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- North America
- U.S.
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- UK
- Italy
- Spain
- Netherlands
- Russia
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- Malaysia
- South Korea
- Indonesia
- Australia
- Vietnam
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Middle East & Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Israel
- South Africa
- Rest of Middle East & Africa
- Latin America
- Mexico
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
Cell and Gene Therapy Clinical Trials Market Report Scope
|
Report Attributes |
Details |
|
Market Size in 2024 |
USD 10.72 billion |
|
Market Size in 2025 |
USD 12.35 billion |
|
Revenue Forecast by 2034 |
USD 44.83 billion |
|
CAGR |
15.4% from 2025 to 2034 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Historical Data |
2020–2023 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025–2034 |
|
Quantitative Units |
Revenue in USD billion and CAGR from 2025 to 2034 |
|
Report Coverage |
Revenue Forecast, Competitive Landscape, Growth Factors, and Industry Trends |
|
Segments Covered |
|
|
Regional Scope |
|
|
Competitive Landscape |
|
|
Report Format |
|
|
Customization |
Report customization as per your requirements with respect to countries, regions, and segmentation. |
FAQ's
The global market size was valued at USD 10.72 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow to USD 44.83 billion by 2034.
The global market is projected to register a CAGR of 15.4% during the forecast period.
North America accounted for ~50% of the revenue share in 2024 due to the region’s strong research infrastructure, high clinical trial density, and access to skilled professionals.
A few of the key players in the market are Charles River Laboratories; ICON Plc; IQVIA; LabCorp; Medpace; Novotech; PAREXEL International Corp.; Syneos Health; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.; and Veristat, LLC.
Phase III segment dominated the market with ~55% of the revenue share in 2024 due to the growing number of advanced-stage cell and gene therapy candidates entering pivotal testing stages.
The oncology segment held the largest revenue share in 2024 due to the high number of active cell and gene therapy trials targeting various cancer types.
