
Biomarkers Market Size, Share, Trends, & Industry Analysis By Type, (Safety Biomarkers, Efficacy Biomarkers, and Validation Biomarkers), By Research Area, By Technology, By Disease Indication, By Application, and By Region – Market Forecast, 2025–2034
- Published Date:Jul-2025
- Pages: 129
- Format: pdf
- Report ID: PM5934
- Base Year: 2024
- Historical Data: 2020-2023
Market Overview
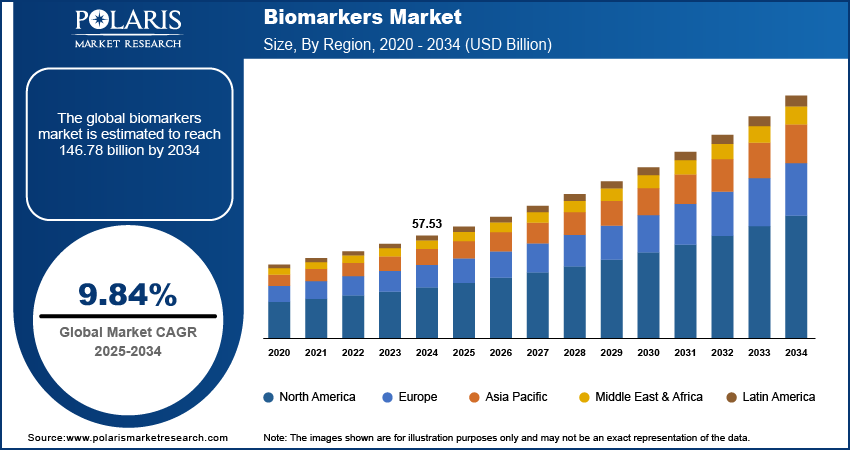
The biomarkers market size was valued at USD 57.53 billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 9.84% from 2025–2034. Rising prevalence of chronic diseases coupled with advancements in genomics and proteomics is driving the market growth.
Biomarkers refer to measurable indicators of a biological state or condition that are used to detect or monitor disease progression, evaluate therapeutic responses, or assess health status. These indicators such as genes, proteins, or metabolites are collected from body fluids or tissues and serve as essential tools in clinical diagnostics and pharmaceutical research. Biomarkers support early diagnosis, prognosis, and stratification of patients, thereby enabling the development of targeted therapies and improving treatment outcomes.
In clinical diagnostics, biomarkers assist in disease identification and classification, while in research environments, they aid in understanding pathophysiology and evaluating therapeutic efficacy. Biomarkers may be found in various biological samples such as blood, urine, tissue, and cerebrospinal fluid, depending on the disease and intended application. The integration of biomarkers into modern healthcare is transforming traditional medical approaches by enabling more individualized, data-driven care, and expanding their relevance in chronic disease management, early detection, and therapeutic development.
Pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies are increasingly investing in research and development to accelerate drug discovery services and improve clinical outcomes, driving the demand for biomarker-based solutions. For instance, in April 2025, Roche committed USD 50 billion to expand manufacturing and R&D facilities across six U.S. states over the next five years. The investment aimed to strengthen drug discovery in gene therapy, metabolic diseases, and AI-driven research. Biomarkers are considered as an essential tool in enhancing clinical trial efficiency, selecting appropriate patient populations, and predicting drug delivery response and safety profiles. Biomarkers enable early identification of treatment responders and non-responders, reducing trial costs and improve approval success rates. This is pushing more companies to adopt biomarker strategies across all stages of drug development, from preclinical research to post-marketing surveillance.
In addition, regulatory authorities across major markets are actively accelerating the adoption of biomarker-based diagnostics and therapeutics, propelling the market growth. Agencies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) established policies that facilitate the integration of biomarkers into drug development and clinical decision-making. These regulatory efforts include fast-track designations, breakthrough therapy approvals, and collaborative qualification procedures aimed at validating new biomarkers for specific indications.
Industry Dynamics
Rising Prevalence of Chronic Diseases
The growing incidence of chronic diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular disorders, diabetes, and neurodegenerative conditions is boosting the demand for biomarkers in clinical diagnostics and disease management. According to the World Health Organization, chronic diseases including cardiovascular conditions, cancer, diabetes, and respiratory disorders are projected to be responsible for 86% of the 90 million annual deaths by 2050. These conditions require early and accurate detection to initiate timely interventions and improve patient outcomes. Biomarkers offer a reliable means of identifying disease onset, progression, and response to treatment, which is crucial in chronic illnesses. The global shift toward preventive healthcare is driving the use of biomarkers for risk stratification and early screening as a standard part of clinical workflows.
In addition, the expanding application of biomarkers in infectious disease management including real-time monitoring of disease outbreaks and response to antimicrobial therapies is fueling the market growth. Health systems are increasingly relying on biomarkers for rapid diagnostics during epidemics and pandemics, improving containment strategies and public health response. This growing reliance is increasing the need for reliable and scalable diagnostic solutions, to meet the rising global health crises.
Advancements in Genomics and Proteomics
The rising advancements in molecular biology in genomics and proteomics, are fueling the discovery, validation, and deployment of increasingly precise and disease-specific biomarkers. For example, in October 2024, Illumina introduced the MiSeq i100 Series, offering faster, more user-friendly, and cost-effective next-generation sequencing (NGS) solutions. The MiSeq i100 Series features rapid run times of just four hours and room-temperature reagent storage, making it well-suited for applications such as microbiology, infectious diseases, and oncology. High-throughput sequencing technologies, mass spectrometry, and advanced bioinformatics platforms are evolving rapidly, providing researchers powerful tools to explore complex biological systems. These advancements are accelerating the identification of new biomarker candidates with strong diagnostic and prognostic potential.
Additionally, the growing integration of omics data into clinical applications is transforming the landscape of personalized medicine. Researchers and clinicians utilize multi-omics approaches to analyze interactions between genes, proteins, and metabolites, leading to a deeper understanding of disease pathways and more accurate patient profiling. This multidisciplinary adoption is fueling the use of biomarkers in diagnostics along with development of targeted therapeutics and companion diagnostics.
Segmental Insights
Type Analysis
The segmentation, based on type includes, safety biomarkers, efficacy biomarkers, and validation biomarkers. The efficacy biomarkers segment is projected to grow at a robust pace by 2034. This dominance is attributed to the increasing use of efficacy biomarkers in evaluating drug responses during clinical trials and monitoring therapeutic outcomes in real-world settings. These biomarkers are particularly valuable in oncology and immunology, determining treatment effectiveness, guiding dose adjustments, and minimizing adverse effects. Pharmaceutical companies are incorporating efficacy biomarkers to enhance clinical trial design, reduce attrition rates, and improve regulatory submission outcomes, making it a central component in drug development strategies.
The validation biomarkers segment is projected to grow at the fastest pace during the forecast period. This growth is driven by the need for reproducible, accurate, and standardized biomarker data in clinical and regulatory settings. Growing importance on data reliability from healthcare providers and regulatory agencies is boosting increased demand for validated biomarkers in areas such as oncology, cardiology, and rare diseases. Validation biomarkers help in confirming the consistency and accuracy of diagnostic results, ensuring to meet clinical and regulatory requirements, thus expanding the adoption across global healthcare markets.
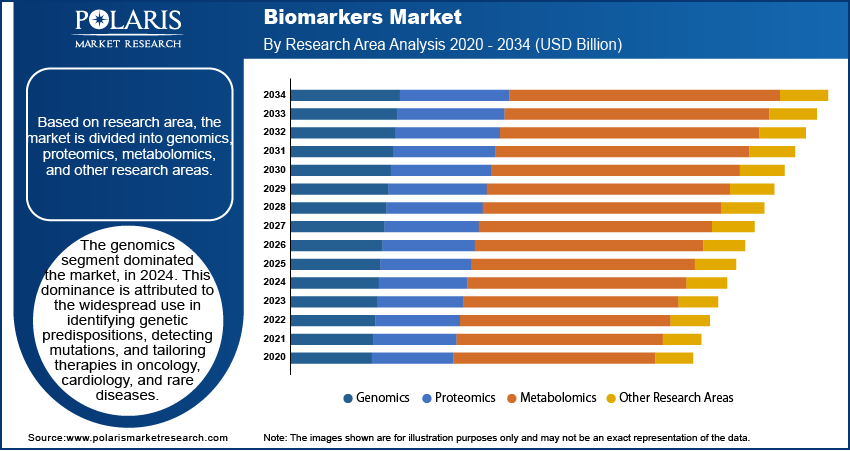
Research Area Analysis
The segmentation, based on research area includes, genomics, proteomics, metabolomics, and other research areas. The genomics segment dominated the market, in 2024. This dominance is attributed to the widespread use in identifying genetic predispositions, detecting mutations, and tailoring therapies in oncology, cardiology, and rare diseases. Genomic biomarkers are integral to precision medicine for guiding clinicians in making data-driven treatment decisions. The increasing use of gene panels, next-generation sequencing, and genome-wide association studies propelled the adoption of genomics in disease risk stratification and targeted therapeutic approaches. For instance, in March 2025, Bio‑Techne launched the AmplideX Nanopore Carrier Plus Kit, a nanopore-based gene panel that resolves 11 carrier screening genes previously difficult to analyze via short-read sequencing.
The proteomics segment is expected to exhibit the fastest growth rate during the forecast period. This rapid expansion is due to the rising adoption of protein-based biomarkers in clinical diagnostics and therapeutic monitoring. Advances in technologies such as mass spectrometry and protein microarrays enabled deeper insights into protein expression, structure, and interactions, which are vital for understanding disease mechanisms. Proteomic biomarkers are increasingly explored for diseases with complex pathophysiology, such as Alzheimer’s, autoimmune disorders, and cancers, driving new developments for diagnostic innovation.
Technology Analysis
The segmentation, based on technology includes, immunoassays, next-generation sequencing (NGS), polymerase chain reaction (PCR), mass spectrometry, chromatography, other technologies. The immunoassays segment accounted for substantial share in 2024 due to the it’s high sensitivity, ease of implementation, and cost-effectiveness position immunoassays as the preferred technology for detecting specific proteins and antibodies in clinical settings. Immunoassays are widely applied in the diagnosis of infectious diseases, cancer, cardiovascular conditions, and autoimmune disorders. The technology is well-suited for point-of-care diagnostics and scalable for large population health programs, maintaining a strong presence in hospital laboratories and decentralized testing settings.
The next-generation sequencing (NGS) segment is projected to witness the fastest growth during the assessment period. The rapid adoption of NGS is driven by its ability to generate detailed genomic data, enabling identification of novel biomarkers and comprehensive disease profiling. NGS is transformative in oncology, rare diseases, and pharmacogenomics, where it supports personalized treatment planning. Its integration into clinical workflows is accelerated by falling sequencing costs, expanding genomic databases, and increasing awareness among healthcare providers of its diagnostic potential.
Disease Indication Analysis
The segmentation, based on disease indication includes, cancer, infectious disease, immunological disorders, neurological disorders, cardiovascular disorders, and other disease indications. The cancer segment dominated the market, in 2024. This dominance is attributed to the high global incidence of cancer and the increasing reliance on biomarker-guided diagnosis and therapy selection. Biomarkers are now essential in stratifying cancer patients, predicting responses to immunotherapies, and monitoring minimal residual disease. In clinical practice, cancer biomarkers such as HER2, BRCA1/2, and PD-L1 become standard tools for treatment planning. The expanding role in companion diagnostics is boosting the importance in delivering personalized oncology care.
The neurological disorders segment is projected to expand at the fastest CAGR during the forecast period. Growing prevalence of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, along with increasing research into early diagnostic strategies, is driving demand for reliable neurological biomarkers. According to the Alzheimer’s Association, more than 7 million Americans are currently living with Alzheimer’s disease, a figure expected to approach 13 million by 2050. These biomarkers offer significant promise in tracking disease progression and predicting therapeutic response, particularly through cerebrospinal fluid analysis, neuroimaging, and blood-based assays. Rising global investment in brain health and neuro-research is further accelerating the segment growth.
Application Analysis
The segmentation, based on application includes, clinical diagnostics, drug discovery & development, personalized medicine, clinical research, and other application. The clinical diagnostics segment accounted for significant share in 2024. This dominance is attributed to the growing incorporation of biomarkers into routine diagnostics for conditions such as cardiovascular diseases, infectious diseases, and cancer. Clinicians are increasingly utilizing biomarker-based tests to guide diagnostic accuracy, enable early detection, and support risk assessment. The shift toward proactive and preventive care models is expanding the use of biomarkers in diagnostics across hospital and outpatient settings.
The personalized medicine segment is expected to witness the fastest growth over the forecast period. The rise of precision healthcare approaches and targeted therapy protocols is fueling demand for biomarkers that match treatments to individual patient profiles. In oncology, biomarkers are essential in determining eligibility for immunotherapy and molecular-targeted drugs. The growth is further fueled by strong regulatory backing, rising patient awareness, and the expanding portfolio of biomarker-based companion diagnostics that enable more tailored clinical decisions.
Regional Analysis
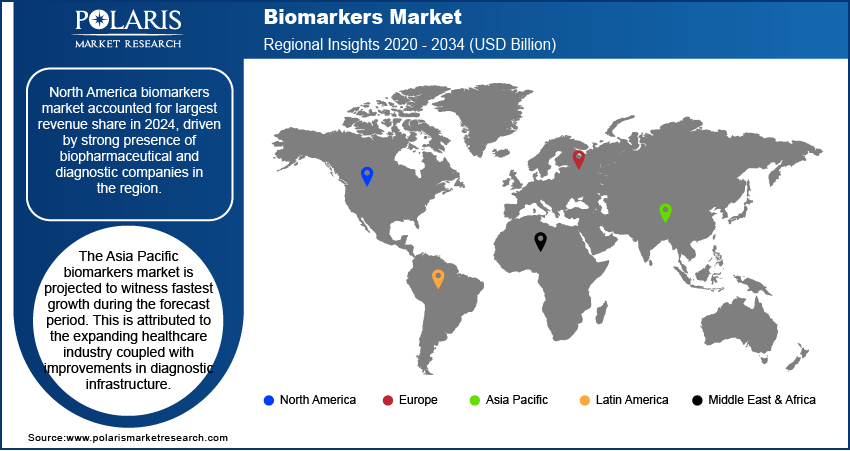
North America biomarkers market accounted for largest revenue share in 2024, driven by strong presence of biopharmaceutical and diagnostic companies in the region. The region hosts some of the world’s leading drug developers and molecular diagnostic firms that are heavily investing in biomarker discovery and validation. These companies are actively leveraging biomarkers to support clinical trial optimization, companion diagnostic development, and personalized therapeutic interventions. Also, high healthcare expenditure and advanced clinical infrastructure are further propelling biomarker adoption. North America is home to a wide network of technologically advanced clinical laboratories, hospitals, and academic research centers that facilitate large-scale biomarker implementation. These facilities are equipped with state-of-the-art diagnostic platforms, bioinformatics tools, and biobanks that enable real-time biomarker analysis, patient stratification, and data integration.
The US Biomarkers Market Insight
The US, in particular, dominated the market, capturing largest regional market share. This growth is due to supportive government initiatives coupled with robust regulatory framework for drug development and deployment across the country. Programs such as the Precision Medicine Initiative laid the foundation for nationwide integration of biomarkers into clinical practice by supporting data-driven approaches to individualized care. Federal agencies such as the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) are actively funding biomarker research, issuing guidance documents, and creating qualification programs that streamline biomarker validation for diagnostics and drug development. For instance, U.S. Food and Drug Administration’s (FDA) the Fit-for-Purpose (FFP) Initiative serves as a regulatory pathway to support the use of evolving drug development tools (DDTs) in specific contexts within drug development programs. This strong regulatory support along with increasing collaboration between government, academia, and industry to advance biomarker-driven healthcare, is boosting the market growth.
Asia Pacific Biomarkers Market
The Asia Pacific biomarkers market is projected to witness fastest growth during the forecast period. This is attributed to the expanding healthcare industry coupled with improvements in diagnostic infrastructure. Countries such as India and China are investing in new hospitals, pathology labs, and molecular diagnostic centers to address rising healthcare demands and improve disease detection. For example, in the Union Budget 2025–26, the Indian government allocated USD 11.50 billion to strengthen, maintain, and improve the nation’s healthcare infrastructure and services. These infrastructure upgrades are creating a favorable environment for the integration of biomarker-based screening and diagnostic services. Furthermore, the rising number of chronic diseases in the region is pushing healthcare providers to adopt early detection tools, making biomarkers a crucial component of disease prevention and management strategies.
Also, the rising investments in genomics and biotechnology across the region is further propelling the market growth. Governments in countries such as China, India, Japan, and South Korea are supporting national genomics programs, biobank initiatives, and personalized medicine projects to accelerate molecular research and innovation. These government-led efforts are supported by growing private-sector R&D investments aimed at developing biomarker-based diagnostics and targeted therapeutics. Thus, growing investment in scientific and technical advancement is accelerating biomarker discovery is the region.
Europe In Biomarkers Market Overview
Europe biomarkers market growth is driven by supportive regulatory and funding mechanisms in the region. Programs such as Horizon Europe are offering substantial financial support for research initiatives focused on biomarker discovery, validation, and clinical translation. The European Commission announced a significant investment of approximately USD 7.9 billion under the 2025 Horizon Europe work program, aimed at advancing the region’s leadership in global research, innovation, and sustainability. These funding initiatives aim to strengthen diagnostic capabilities, promote personalized healthcare, and support industry-academia collaborations across member states. In addition, the European Medicines Agency (EMA) implemented frameworks that boosting the integration of biomarkers into clinical trials and facilitate their qualification for use in drug development, contributing to regulatory clarity and market expansion.
Furthermore, the region’s strong foundation in academic research and cross-sector collaboration further accelerates market the growth of the market. High-quality research institutions across countries such as Germany, France, and the Netherlands are partnering with pharmaceutical and biotech companies to accelerate translational research and biomarker commercialization. These collaborations are pushing innovative diagnostic platforms, digital health tools, and precision therapies tailored to disease-specific biomarker profiles. Therefore, the growing focus on policy alignment, research leadership, and targeted funding is propelling the market growth.
Key Players & Competitive Analysis Report
The global biomarkers market is characterized by high competition, driven by rapid technological advancements, growing demand for precision diagnostics, and a continuous push for innovation across clinical and research applications. Leading players are focusing on expanding biomarker portfolios through strategic collaborations, new product development, acquisitions, and investments in next-generation platforms. The competitive landscape is shaped by companies that are integrating multi-omics technologies, digital tools, and AI-driven analytics to support more accurate, real-time, and personalized biomarker solutions. Rising demand for early disease detection and personalized treatment is pushing companies to focus on developing diagnostics that support the growing use of targeted therapies.
Prominent players operating in the biomarkers market include Abbott Laboratories, Agilent Technologies, Inc., BioMérieux SA, Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc., Charles River Laboratories International, Inc., Eurofins Scientific SE, F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Guardant Health, Inc., Illumina, Inc., Merck KGaA, QIAGEN N.V., Revvity, Inc., Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc., Quanterix Corporation, and Siemens Healthineers AG.
Key Players
- Abbott Laboratories
- Agilent Technologies, Inc.
- BioMérieux SA
- Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.
- Charles River Laboratories International, Inc.
- Eurofins Scientific SE
- F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd
- Guardant Health, Inc.
- Illumina, Inc.
- Merck KGaA
- QIAGEN N.V.
- Revvity, Inc.
- Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.
- Quanterix Corporation
- Siemens Healthineers AG
Industry Developments
May 2025: The University of Houston received a USD 3 million CPRIT grant to establish a cancer immunotherapy biomarker core facility focused on advanced proteomic screening technologies. This expansion boosted the biomarkers industry by enabling faster discovery of protein biomarkers for cancer immunotherapy.
April 2025: The Viromarkers project launched in Rome, as a cross-sectoral public-private partnership, aiming to develop and validate virus-related biomarkers for HIV, Hepatitis D, and CMV in immunocompromised individuals. The project also intended to support early detection and improve long-term health outcomes in vulnerable patient populations.
April 2025: The LuNGS Alliance, led by the Cancer Research and Statistic Foundation and supported by AstraZeneca, Pfizer, Roche, and 4baseCare, launched free lung NGS biomarker testing in India. The TARGT first solid assay analyzed 72 actionable genes to guide personalized lung cancer treatment plans.
Biomarkers Market Segmentation
By Type Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- Safety Biomarkers
- Efficacy Biomarkers
- Validation Biomarkers
By Research Area Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- Genomics
- Proteomics
- Metabolomics
- Other Research Areas
By Technology Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- Immunoassays
- Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS)
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
- Mass Spectrometry
- Chromatography
- Other Technologies
By Disease Indication Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- Cancer
- Infectious Disease
- Immunological Disorders
- Neurological Disorders
- Cardiovascular Disorders
- Other Disease Indications
By Application Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- Clinical Diagnostics
- Drug Discovery & Development
- Personalized Medicine
- Clinical Research
- Other Application
By Regional Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- UK
- Italy
- Spain
- Netherlands
- Russia
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- Malaysia
- South Korea
- Indonesia
- Australia
- Vietnam
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Middle East & Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Israel
- South Africa
- Rest of Middle East & Africa
- Latin America
- Mexico
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
Biomarkers Market Report Scope
|
Report Attributes |
Details |
|
Market Size in 2024 |
USD 57.53 Billion |
|
Market Size in 2025 |
USD 63.07 Billion |
|
Revenue Forecast by 2034 |
USD 146.78 Billion |
|
CAGR |
9.84% from 2025 to 2034 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Historical Data |
2020–2023 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025–2034 |
|
Quantitative Units |
Revenue in USD Billion and CAGR from 2025 to 2034 |
|
Report Coverage |
Revenue Forecast, Competitive Landscape, Growth Factors, and Industry Trends |
|
Segments Covered |
|
|
Regional Scope |
|
|
Competitive Landscape |
|
|
Report Format |
|
|
Customization |
Report customization as per your requirements with respect to countries, regions, and segmentation. |
FAQ's
The global market size was valued at USD 57.53 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow to USD 146.78 billion by 2034.
The global market is projected to register a CAGR of 9.84% during the forecast period.
North America dominated the market share in 2024.
A few of the key players in the market are Abbott Laboratories, Agilent Technologies, Inc., BioMérieux SA, Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc., Charles River Laboratories International, Inc., Eurofins Scientific SE, F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Guardant Health, Inc., Illumina, Inc., Merck KGaA, QIAGEN N.V., Revvity, Inc.
The genomics segment dominated the market, in 2024.
The next-generation sequencing (NGS) segment is projected to witness the fastest growth during the assessment period.
