
Fermentation Chemicals Market Size, Share, & Industry Analysis Report
: By Product (Alcohols, Enzymes, Organic Acids, and Other Products), By Application, and By Region – Market Forecast, 2025–2034
- Published Date:Aug-2025
- Pages: 120
- Format: PDF
- Report ID: PM3313
- Base Year: 2024
- Historical Data: 2020-2023
Market Overview
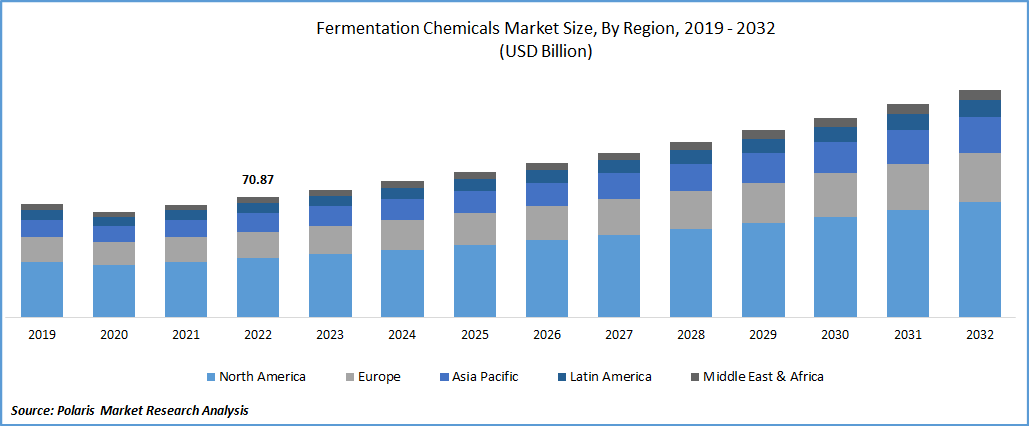
The fermentation chemicals market size was valued at USD 80.48 billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 6.9% between 2025 and 2034. The rising demand for bio-based products and the increasing use of fermentation chemicals in the development of essential medicines are a few of the key factors driving market growth.
Key Insights
- The alcohols segment dominates the market, primarily driven by its high versatility and strong bonding capabilities across various substrate types.
- The nutritional & pharmaceutical segment is projected to register the highest growth rate during the projection period, owing to the rising usage of fermentation-derived products across the health and wellness sectors.
- Asia Pacific leads the market. The regional market dominance is attributed to its robust manufacturing base, especially in emerging economies such as India and China.
- Asia Pacific is also anticipated to register the highest growth rate during the projection period. Rising disposable incomes have led to increased consumption of processed food and beverages in the region.
Industry Dynamics
- The growing emphasis on the usage of sustainable and eco-friendly alternatives is driving the demand for fermentation chemicals.
- The expanding food and beverage industry, where fermentation is widely utilized for the production of various products, drives market growth.
- Technological advancements in fermentation are expected to provide several market opportunities in the coming years.
- Environmental concerns and regulatory hurdles may present market challenges.
Market Statistics
2024 Market Size: USD 80.48 billion
2034 Projected Market Size: USD 156.47 billion
CAGR (2025-2034): 6.9%
Asia Pacific: Largest Market in 2024
To Understand More About this Research: Request a Free Sample Report
The rising demand for enzymes in various industrial applications, such as food processing, and the increasing consumption of fermented foods and beverages boost the market growth.
The fermentation chemicals market focuses on the production of chemicals through the biological process of fermentation, where microorganisms break down complex compounds. This process yields various substances utilized across diverse industries, including food and beverages, pharmaceuticals, and biofuels. The market's expansion is significantly influenced by the increasing demand for bio-based products, as consumers and industries seek sustainable alternatives to traditional chemical processes. This shift is further propelled by the growing application of fermentation chemicals in the food and beverage industry, where they enhance flavor, texture, and nutritional value.
The pharmaceutical sector also contributes substantially to growth, as fermentation chemicals are increasingly used in the production of essential medicines, including antibiotics and vaccines. The sector’s reliance on fermentation for drug production, coupled with the overall expansion of the pharmaceutical, further fuels the demand for fermentation chemicals. Additionally, the inherent advantages of fermentation chemicals, such as their cost-effectiveness and eco-friendliness compared to petroleum-derived chemicals, contribute to their increasing adoption across multiple sectors.
Market Dynamics
Rising Demand for Bio-based Products
The increasing consumer and industrial preference for sustainable and eco-friendly alternatives propels the fermentation chemicals market growth. Fermentation processes utilize renewable chemicals and raw materials and often have a lower environmental impact compared to traditional chemical synthesis. This aligns with the global movement toward a bio-based economy, where industrial processes and products rely on renewable biological resources. The International Energy Agency (IEA) consistently reports on the growth of biofuels. Their Renewables 2023 report noted that global biofuel production increased by 6% in 2023, reaching 2.1 million barrels per day of oil equivalent, with a projected increase of 38% by 2028. This substantial growth in biofuel production utilizes fermentation processes for creating ethanol and other bio-based components, requiring fermentation chemicals. This shift in focus toward sustainable solutions is directly increasing the demand for fermentation chemicals across applications such as bioplastics, biofuels, and green chemicals.
Expansion of Food and Beverage Industry
The food and beverage industry has long utilized fermentation for producing various products, and its continued expansion acts as a major driver. Fermentation chemicals, such as enzymes, organic acids, and alcohols, play crucial roles in enhancing the flavor, texture, nutritional value, and shelf life of food and beverage products. A report by the International Organisation of Vine and Wine (OIV) in 2022 highlighted that the global wine production amounted to approximately 258 million hectoliters, indicating a substantial demand for precision fermentation processes and related chemicals. Similarly, the rising consumption of fermented foods such as yogurt, cheese, and sauerkraut, driven by their perceived health benefits, further boosts the demand for fermentation chemicals. The continuous innovation in food processing techniques utilizing fermentation and the growing global population's demand for diverse and processed food products are significant factors propelling the growth.
Expansion of Pharmaceutical Industry
The pharmaceutical industry is a significant end user of fermentation chemicals. Fermentation is employed in the production of a wide array of pharmaceuticals, including antibiotics, vaccines, vitamins, and other bioactive compounds. The World Health Organization (WHO) regularly reports on the increasing global burden of chronic diseases. For instance, the WHO estimates that cancer cases are anticipated to grow from 20 million in 2024 to 30 million by 2040, which will drastically increase the need for targeted therapies. The increasing global healthcare expenditure, the rising prevalence of chronic diseases, and the continuous research and development in novel drug formulations that often rely on fermentation processes are key factors contributing to the pharmaceutical industry's growth. As the pharmaceutical sector expands and develops new therapeutics, the demand for high-quality fermentation chemicals as crucial intermediates and active fermented ingredients will continue to rise, thereby driving the growth.
Segment Insights
Market Assessment – By Product
The fermentation chemicals market, by product, is segmented into alcohols, enzymes, organic acids, and other products. Among these, the alcohols segment currently accounts for the largest share. This dominance is due to its exceptional versatility, cost-effectiveness, and strong bonding capabilities across a wide range of substrates, including metals, plastics, and composites. Alcohol-based adhesives are widely used in construction, automotive, and electronics industries for both temporary and permanent bonding. Their quick drying time, ease of application, and compatibility with other formulation ingredients further contribute to their dominance. Additionally, the growing demand for sustainable and low-VOC adhesives has driven manufacturers to favor alcohol-based formulations, reinforcing their leading market position.
The enzymes segment is anticipated to exhibit the highest growth rate during the forecast period. This rapid expansion is fueled by the increasing application of industrial enzymes across a multitude of sectors, such as food and beverage processing, detergents, animal feed, and pharmaceuticals. The growing demand for sustainable and efficient industrial processes, coupled with advancements in enzyme engineering and production technologies, is driving significant development in this area. The versatility and specificity of enzymes in catalyzing various biochemical reactions make them increasingly attractive for a wide range of industrial applications, positioning the enzymes segment for substantial growth in the coming years.
Market Evaluation – By Application
The fermentation chemicals market, by application, is segmented into industrial application, food & beverages, nutritional & pharmaceutical, plastic & fibers, and other applications. Currently, the industrial application segment represents the largest share, driven by the extensive utilization of fermentation-derived chemicals in various industrial processes. These chemicals serve as crucial components in the manufacturing of a wide array of products, including solvents, detergents, and other industrial intermediates, leading to substantial demand and a dominant share for this application segment.
The nutritional & pharmaceutical segment is projected to experience the highest growth rate during the forecast period. This rapid growth is fueled by the increasing demand for fermentation-derived products in the health and wellness sectors. The rising consumer awareness regarding health and nutrition, coupled with the growing pharmaceutical industry's reliance on fermentation for producing vital drugs, vitamins, and other nutritional supplements, is significantly boosting the demand. The continuous advancements in biotechnology and the increasing focus on preventive healthcare are expected to further accelerate the growth of the nutritional & pharmaceutical application segment.
Regional Analysis
The fermentation chemicals market demonstrates a significant global presence, with key regions exhibiting distinct dynamics and growth patterns. North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East & Africa represent the major geographical segments influencing the overall landscape. Each region's market size, growth trajectory, and key drivers are shaped by factors such as industrial development, consumer preferences, regulatory frameworks, and the prevalence of end-use industries within their respective economies. Understanding these regional nuances is crucial for comprehending the global outlook and identifying potential entry opportunities.
Asia Pacific currently holds the largest share, owing to the presence of a large manufacturing base, particularly in countries such as China and India, which are significant consumers and producers of fermentation chemicals. The growing food and beverage industry, coupled with increasing investments in industrial biotechnology and biopharmaceuticals in this region, further contributes to its leading position. The sheer scale of industrial activities and the burgeoning population in Asia Pacific create a substantial demand for a wide range of fermentation-derived products.
Asia Pacific is also projected to exhibit the highest growth rate over the forecast period. This rapid expansion is driven by a confluence of factors, including increasing industrialization, rising disposable incomes leading to higher consumption of processed foods and beverages, and growing investments in the pharmaceutical and biotechnology sectors. Furthermore, supportive government initiatives promoting bio-based industries and the increasing adoption of sustainable practices across various applications are fueling development in this region. The dynamic economic growth and expanding end-use industries within Asia Pacific position it as a high-potential region.
Key Players and Competitive Insights
A few key players active in the fermentation chemicals market include Cargill, Incorporated; Evonik Industries AG; BASF SE; Koninklijke DSM N.V.; DuPont de Nemours, Inc.; Ajinomoto Co., Inc.; Archer-Daniels-Midland Company; Lonza Group AG; Novozymes A/S; Chr. Hansen Holding A/S; Corbion N.V.; and Kerry Group plc.
The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of well-established multinational corporations and smaller, specialized companies. Competition is driven by factors such as product innovation, cost efficiency, application-specific solutions, and strategic partnerships. Players are increasingly focusing on developing sustainable and bio-based production methods to cater to the growing demand for environmentally friendly products. Furthermore, collaborations and acquisitions are observed as companies aim to expand their product portfolios and geographical reach.
Cargill, Incorporated, headquartered in Minneapolis, Minnesota, USA, offers a diverse range of fermentation-derived products, including organic acids, ethanol, and specialty ingredients for the food & beverage and industrial sectors. Their extensive global network and strong focus on agricultural processing provide a robust foundation for their involvement.
Evonik Industries AG, based in Essen, Germany, provides a variety of fermentation products, such as amino acids, feed additives, and biocatalysts, catering to the animal nutrition, pharmaceutical, and specialty chemicals industries. Their expertise in biotechnology and focus on developing high-performance products solidify their position as a significant participant.
List of Key Companies
- Ajinomoto Co., Inc.
- Archer-Daniels-Midland Company
- BASF SE
- Cargill, Incorporated
- Chr. Hansen Holding A/S
- Corbion N.V.
- DuPont de Nemours, Inc.
- Evonik Industries AG
- Kerry Group plc
- Koninklijke DSM N.V.
- Lonza Group AG
- Novozymes A/S
Fermentation Chemicals Industry Developments
- September 2024: Evonik Coating Additives introduced two new biosurfactants, TEGO Wet 570 Terra and TEGO Wet 580 Terra, specifically designed for waterborne coatings and inks. These biosurfactants are produced through a unique fermentation process using renewable corn feedstock.
- October 2023: BASF announced its investment in a new fermentation plant in Ludwigshafen, Germany, for the production of biological and biotechnology-based crop protection chemicals and products. The plant will manufacture biological fungicides and seed treatment products. It is also planned to produce the main building block of Inscalis®, a novel insecticide.
Fermentation Chemicals Market Segmentation
By Product Outlook (Revenue – USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- Alcohols
- Enzymes
- Organic Acids
- Other Products
By Application Outlook (Revenue – USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- Industrial Application
- Food & Beverages
- Nutritional & Pharmaceutical
- Plastic & Fibers
- Other Applications
By Regional Outlook (Revenue – USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- UK
- Italy
- Spain
- Netherlands
- Russia
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- Malaysia
- South Korea
- Indonesia
- Australia
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Middle East & Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Israel
- South Africa
- Rest of Middle East & Africa
- Latin America
- Mexico
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
Fermentation Chemicals Market Report Scope
|
Report Attributes |
Details |
|
Market Size Value in 2024 |
USD 80.48 billion |
|
Market Size Value in 2025 |
USD 85.83 billion |
|
Revenue Forecast by 2034 |
USD 156.47 billion |
|
CAGR |
6.9% from 2025 to 2034 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Historical Data |
2020–2023 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025–2034 |
|
Quantitative Units |
Revenue in USD billion and CAGR from 2025 to 2034 |
|
Report Coverage |
Revenue Forecast, Market Competitive Landscape, Growth Factors, and Industry Insights |
|
Segments Covered |
|
|
Regional Scope |
|
|
Competitive Landscape |
|
|
Report Format |
|
|
Customization |
Report customization as per your requirements with respect to countries, regions, and segmentation. |
How is the report valuable for an organization?
Workflow/Innovation Strategy
The fermentation chemicals market has been segmented into detailed segments of product and application. Moreover, the study provides the reader with a detailed understanding of the different segments at both the global and regional levels.
Market Entry Strategies
The market presents significant growth opportunities driven by the increasing demand for sustainable and bio-based products across various industries. A key marketing strategy involves highlighting the environmental benefits and cost-effectiveness of fermentation-derived chemicals compared to traditional alternatives. Emphasizing application-specific solutions and collaborating with end-use industries, such as food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and plastics, can enhance market penetration. Furthermore, investing in research and development to expand the range of fermentable chemicals and improving production efficiencies will be crucial for maintaining a competitive edge and capitalizing on the evolving market trends.
FAQ's
The market size was valued at USD 80.48 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow to USD 156.47 billion by 2034.
The market is projected to register a CAGR of 6.9% during the forecast period.
Asia Pacific held the largest share of the market in 2024.
A few key players include Cargill, Incorporated; Evonik Industries AG; BASF SE; Koninklijke DSM N.V.; DuPont de Nemours, Inc.; Ajinomoto Co., Inc.; Archer-Daniels-Midland Company; Lonza Group AG; Novozymes A/S; Chr. Hansen Holding A/S; Corbion N.V.; and Kerry Group plc.
The industrial application segment accounted for the largest share of the market in 2024.
Following are a few of the trends: ? Growing Demand for Bio-based Alternatives: There is an increasing shift toward sustainable and eco-friendly products, driving the demand for fermentation chemicals as alternatives to petrochemical-based chemicals. ? Expansion in Food and Beverage Industry: The rising consumer preference for natural ingredients, clean-label products, and functional foods is leading to increased use of fermentation-based additives, preservatives, and flavor enhancers. The growing consumption of alcoholic and non-alcoholic beverages also contributes significantly.
Fermentation chemicals refer to a wide range of chemical compounds produced through the metabolic process of fermentation, primarily by microorganisms such as bacteria, yeasts, and fungi. This biochemical process occurs in the absence of oxygen (anaerobically) and involves the breakdown of organic substances, such as sugars and starches, into simpler molecules.
