
Human Papillomavirus Testing Market Size, Share, Trends, Industry Analysis Report
: By Product (Instruments, Consumables, Services), By Application, By Technology, By End-use, and Region– Market Forecast, 2025–2034
- Published Date:Jun-2025
- Pages: 130
- Format: PDF
- Report ID: PM5744
- Base Year: 2024
- Historical Data: 2020-2023
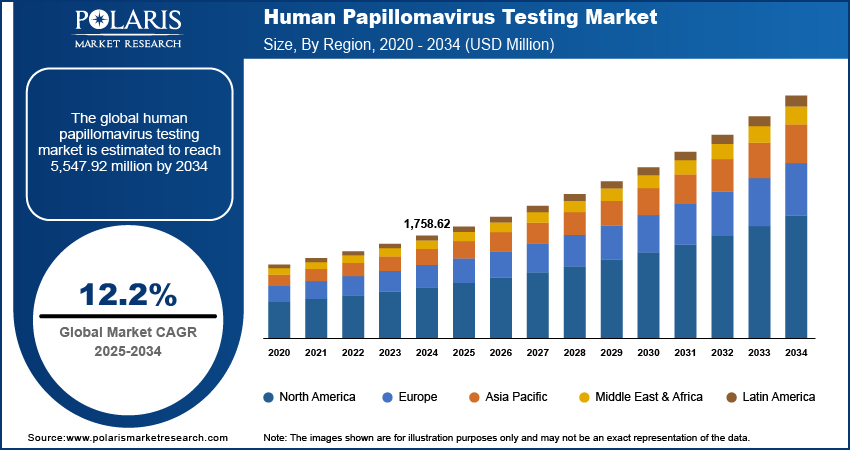
The human papillomavirus testing market size was valued at USD 1,758.62 million in 2024, exhibiting a CAGR of 12.2% during 2025–2034. The Human Papillomavirus (HPV) testing market is driven by rising HPV infection rates, growing awareness of cervical cancer prevention, technological advancements, and increased government support for early screening programs.
Market Overview:
The human papillomavirus (HPV) testing market is centered around the analysis of samples to detect the presence of the HPV virus, a common sexually transmitted infection. These STD diagnostic tests are primarily employed in screening for cervical cancer, as certain high-risk HPV strains are known to cause this disease. The increasing global emphasis on preventive healthcare and the rising awareness regarding the link between HPV and cervical cancer are significant driver factors. Furthermore, the implementation of national cervical cancer screening programs in various regions contributes substantially to the demand. Technological advancements in diagnostic techniques, such as the development of more sensitive and specific molecular tests, are also fueling the development by offering improved accuracy in identifying high-risk HPV infections.
The growing adoption of HPV testing as a primary screening tool, either independently or in conjunction with traditional Pap tests (co-testing), is a notable market trend. Additionally, the introduction of self-sampling HPV test kits is enhancing penetration by improving accessibility and convenience for women, particularly in underserved areas. Government initiatives and funding aimed at promoting cervical cancer screening and HPV vaccination programs further bolster the growth factors. The increasing prevalence of HPV-related diseases and the continuous advancements in molecular infectious disease diagnostics are expected to sustain a robust forecast for HPV testing in the coming years, indicating strong potential.
To Understand More About this Research: Request a Free Sample Report
Industry Dynamics:
Rising Awareness and Screening Programs
Increased public awareness regarding the strong correlation between persistent human papillomavirus (HPV) infections and the development of cervical cancer serves as a significant driver. Educational campaigns by government health organizations and non-profit entities have effectively communicated the importance of regular screening for early detection and prevention. For instance, the National Cancer Institute (NCI) highlights that cervical cancer was once the leading cause of cancer deaths for women in the United States. Still, the death rate has decreased significantly in the past 40 years, largely due to the increased use of the Pap test and HPV test for screening. Furthermore, the implementation of organized cervical cancer screening programs by governments worldwide has led to a substantial increase in the demand for HPV testing. These programs often recommend or include HPV testing as a primary or secondary screening method. This heightened awareness and the establishment of systematic screening initiatives are collectively propelling the growth.
Technological Advancements in Testing Methods
Continuous technological advancements significantly influence the human papillomavirus testing market in diagnostic methodologies. The evolution from traditional cytology-based Pap tests to highly sensitive and specific molecular assays for HPV detection has revolutionized cervical cancer screening. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR)--based assays, for example, offer enhanced accuracy in identifying high-risk HPV genotypes. The National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) published research indicating the superior sensitivity of HPV DNA testing compared to cytology in detecting high-grade cervical lesions. Moreover, the development of point-of-care HPV testing and self-sampling kits is improving accessibility, particularly in low-resource settings and for women who face barriers to traditional clinic-based screening. These technological innovations, leading to more accurate, efficient, and accessible testing options, are a key development factor driving the expansion.
Increasing Prevalence of HPV Infections
The widespread prevalence of human papillomavirus (HPV) infections globally is a fundamental driver for HPV testing. HPV is the most common sexually transmitted infection. While many infections are transient and resolve spontaneously, persistent infections with high-risk genotypes can lead to cervical cancer and other anogenital cancers. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), nearly all sexually active people will get HPV at some point in their lives, and about 43 million people in the United States had HPV in 2018. This high prevalence necessitates widespread screening to identify individuals at risk of developing HPV-related cancers. The significant size is directly correlated with the need for regular testing to manage and monitor the burden of HPV infections, thereby fueling the demand trends.
Segmental Insights:
Market Assessment By Application
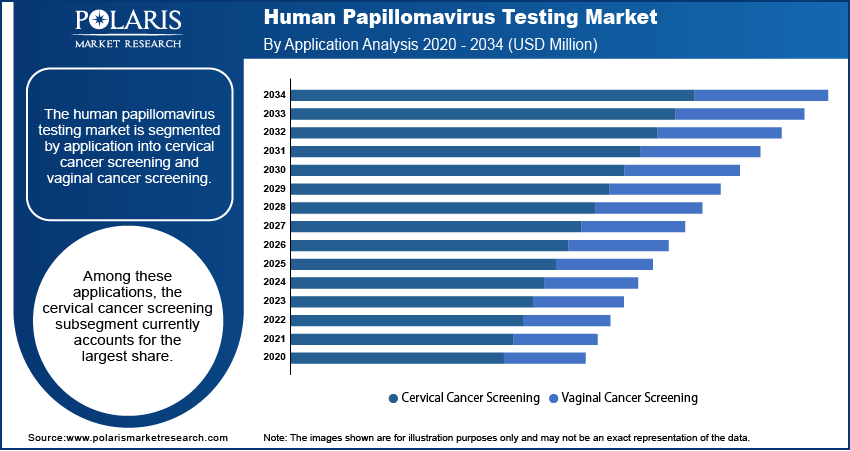
The market is segmented by application into cervical cancer screening and vaginal cancer screening. Among these applications, the cervical cancer screening subsegment currently accounts for the largest share. This dominance is primarily attributed to the well-established role of HPV testing in routine cervical cancer screening programs globally. The strong emphasis on early detection of precancerous lesions and the widespread adoption of HPV testing, either as a primary screening method or in conjunction with cytology, contribute significantly to the substantial demand within this subsegment. The well-defined clinical guidelines and the extensive infrastructure supporting cervical cancer screening programs further solidify its leading position.
The vaginal cancer screening subsegment is anticipated to exhibit the highest growth rate in the foreseeable future. This growth is driven by an increasing recognition of the role of HPV in vaginal cancer development and a growing emphasis on comprehensive gynecological health. While the current utilization of HPV testing for vaginal cancer screening is lower compared to cervical cancer, rising awareness among healthcare professionals and the development of more specific testing protocols for vaginal abnormalities are expected to fuel development in this area. Furthermore, the potential for integrating HPV testing into broader gynecological screening practices suggests a significant potential and an accelerated growth rate for the vaginal cancer screening subsegment.
Market Evaluation By Product
The market is segmented by product into instruments, consumables, and services. Currently, the consumables subsegment holds the largest share. This is primarily due to the recurring nature of HPV testing procedures, which necessitates the continuous procurement of reagents, assay kits, and other disposable materials used in the testing process. The high volume of HPV tests conducted globally, driven by widespread screening programs and increasing demand, directly translates to a substantial and consistent demand for these consumables, thereby establishing its dominance.
The services subsegment is projected to experience the highest growth rate in the coming years. This growth is fueled by the increasing demand for specialized laboratory services, including HPV testing and analysis, as well as the growing trend of outsourcing diagnostic testing to specialized service providers. The need for advanced testing methodologies, coupled with the increasing focus on efficient and timely reporting of results, is driving the expansion of the services subsegment. Furthermore, the development of integrated service offerings that include sample collection, testing, and interpretation is expected to further accelerate the development and contribute to the highest growth rate.
Market Assessment By Technology
The market is segmented by technology into PCR, immunodiagnostics, and other technologies. Among these, the PCR subsegment currently commands the largest share. This is primarily because PCR-based assays offer high sensitivity and specificity in detecting HPV DNA, making them the preferred technology for cervical cancer screening and diagnosis globally. The robust adoption of molecular diagnostic techniques and the established clinical utility of digital PCR in identifying high-risk HPV genotypes contribute significantly to its dominant position.
The immunodiagnostics subsegment is anticipated to demonstrate the highest growth rate in the near future. This growth is driven by the increasing development and adoption of rapid and cost-effective point-of-care testing solutions for HPV detection. While currently holding a smaller share compared to PCR, the advantages of immunodiagnostic assays, such as ease of use and potential for decentralized testing, are expected to fuel their market development. The growing emphasis on accessible and timely screening, particularly in resource-limited settings, positions immunodiagnostics and immunoassays for significant penetration and the highest growth rate.
Market Assessment By End-Use
The market is segmented by end-use into hospitals & clinics, laboratories, and others. Currently, the hospitals & clinics subsegment accounts for the largest share. This is attributed to the fact that hospitals and clinics serve as primary points of care for a significant proportion of the population undergoing routine cervical cancer screening and diagnostic procedures. The established infrastructure within these healthcare settings and the integration of HPV testing into standard clinical practice contribute substantially to the high demand and the leading position of this end-use segment.
The laboratories subsegment is expected to exhibit the highest growth rate in the coming years. This growth is driven by the increasing trend of outsourcing diagnostic testing services, including HPV testing, to specialized clinical laboratories. The ability of laboratories to handle a high volume of samples, provide advanced testing capabilities, and ensure efficient turnaround times makes them an increasingly preferred choice for healthcare providers and screening programs. The growing demand for specialized HPV testing services and the continuous advancements in laboratory automation are anticipated to fuel significant development and the highest growth rate.
Regional Analysis
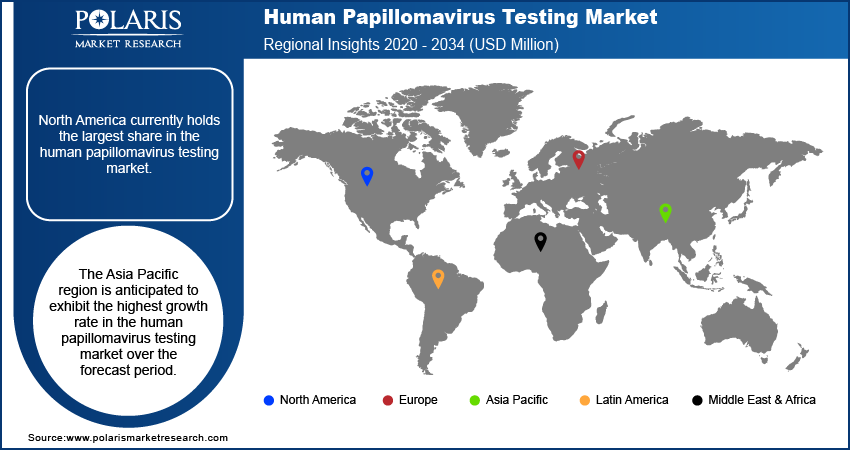
North America human papillomavirus testing market currently holds the largest share. This dominance can be attributed to well-established cervical cancer screening programs, high awareness levels regarding HPV, and the presence of advanced healthcare infrastructure. The widespread adoption of HPV testing as a primary or adjunctive screening tool, coupled with favorable reimbursement policies and the availability of sophisticated diagnostic technologies, contributes significantly to the substantial size in this region. Furthermore, the presence of key players and ongoing research and development activities further solidify North America's leading position.
The Asia Pacific human papillomavirus testing market is anticipated to exhibit the highest growth rate over the forecast period. This rapid development is driven by increasing government initiatives to implement cervical cancer screening programs, rising awareness about HPV and its link to cancer, and a growing healthcare expenditure in several countries within the region. The increasing penetration of advanced diagnostic technologies and the large population base are also significant growth factors. As screening programs expand and access to healthcare improves, the Asia Pacific region presents substantial potential and is expected to witness the fastest demand trends.
Key Players and Competitive Insights
Some of the major players in the human papillomavirus testing market include QIAGEN N.V., F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG, Hologic, Inc., Abbott Laboratories, Becton, Dickinson and Company (BD), Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Danaher Corporation (Cepheid), bioMérieux S.A., GenMark Diagnostics, Inc. (acquired by Roche), Agilent Technologies, Inc., and Luminex Corporation (DiaSorin S.p.A.). These entities are engaged in the development, manufacturing, and distribution of a range of HPV testing products, including instruments, consumables, and services, catering to the global demand for cervical cancer screening and other HPV-related diagnostics.
The competitive landscape is characterized by the presence of both well-established multinational corporations and specialized diagnostic companies. Competition is driven by factors such as product innovation, technological advancements, test accuracy, ease of use, and the breadth of testing portfolios. Companies are focused on developing more sensitive and specific assays, point-of-care solutions, and automated platforms to enhance penetration and address the evolving needs of healthcare providers and screening programs. Strategic collaborations, partnerships, and acquisitions also play a role in shaping the competitive dynamics and development within the human papillomavirus testing market.
List of Key Companies in Human Papillomavirus Testing Industry:
- Abbott Laboratories
- Agilent Technologies, Inc.
- Becton, Dickinson and Company (BD)
- bioMérieux S.A.
- Danaher Corporation (Cepheid)
- F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG
- GenMark Diagnostics, Inc. (acquired by Roche)
- Hologic, Inc.
- Luminex Corporation (DiaSorin S.p. A.)
- QIAGEN N.V.
- Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
Human Papillomavirus Testing Industry Developments
- February 2025: Metropolis Healthcare and Roche Diagnostics introduced a WHO-endorsed self-sampling HPV DNA test in India, targeting early cervical cancer detection and improved access, especially in underserved regions.
- February 2024: Hologic announced that its new Genius Digital Diagnostics System with the Genius Cervical AI algorithm received clearance from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
Human Papillomavirus Testing Market Segmentation
By Application Outlook (Revenue – USD Million, 2020–2034)
- Cervical Cancer Screening
- Vaginal Cancer Screening
By Product Outlook (Revenue – USD Million, 2020–2034)
- Instruments
- Consumables
- Services
By Technology Outlook (Revenue – USD Million, 2020–2034)
- PCR
- Immunodiagnostics
- Other Technologies
By End-Use Outlook (Revenue – USD Million, 2020–2034)
- Hospitals & Clinics
- Laboratories
- Others
By Regional Outlook (Revenue-USD Million, 2020–2034)
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Mexico
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- UK
- Italy
- Spain
- Netherlands
- Russia
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- Malaysia
- South Korea
- Indonesia
- Australia
- Vietnam
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Middle East & Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Israel
- South Africa
- Rest of Middle East & Africa
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
Human Papillomavirus Testing Market Report Scope:
|
Report Attributes |
Details |
|
Market Size Value in 2024 |
USD 1,758.62 million |
|
Market Size Value in 2025 |
USD 1,968.78 million |
|
Revenue Forecast by 2034 |
USD 5,547.92 million |
|
CAGR |
12.2% from 2025 to 2034 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Historical Data |
2020–2023 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025–2034 |
|
Quantitative Units |
Revenue in USD million and CAGR from 2025 to 2034 |
|
Report Coverage |
Revenue Forecast, Market Competitive Landscape, Growth Factors, and Industry Insights |
|
Segments Covered |
|
|
Regional Scope |
|
|
Competitive Landscape |
|
|
Report Format |
|
|
Customization |
Report customization as per your requirements with respect to countries, regions, and segmentation. |
FAQ's
The global market size was valued at USD 1,758.62 million in 2024 and is projected to grow to USD 5,547.92 million by 2034.
The market is projected to register a CAGR of 12.2% during the forecast period, 2024-2034.
North America had the largest share of the market.
Some of the major players include QIAGEN N.V., F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG, Hologic, Inc., Abbott Laboratories, Becton, Dickinson and Company (BD), Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Danaher Corporation (Cepheid), bioMérieux S.A., GenMark Diagnostics, Inc. (acquired by Roche), Agilent Technologies, Inc., and Luminex Corporation (DiaSorin S.p.A.).
The cervical cancer screening segment accounted for the larger share of the market in 2024.
Following are some of the trends: ? Increasing Adoption of HPV Testing as Primary Screening Tool: There is a growing shift towards using HPV testing as the first-line screening method for cervical cancer, either alone or in combination with cytology (co-testing), driven by its higher sensitivity for detecting precancerous lesions. ? Development of Point-of-Care (POC) HPV Testing: The emergence of rapid and user-friendly POC HPV tests is improving accessibility, particularly in low-resource settings and for immediate results during consultations.
Human papillomavirus (HPV) testing is a medical analysis performed to detect the presence of the human papillomavirus, a common sexually transmitted infection. These tests typically analyze samples collected from the cervix in women to identify high-risk HPV types that are known to cause changes in cervical cells, potentially leading to cervical cancer. HPV testing can be done alongside a Pap test (which looks for abnormal cervical cells) or as a primary screening method for women over a certain age. The primary goal of HPV testing is to identify individuals at higher risk of developing cervical cancer so that appropriate monitoring or intervention can be implemented.
