
Rare Earth Metals Market Size, Share, Trend, Industry Analysis Report
By Product (Cerium, Dysprosium, Gadolinium, Lutetium, Neodymium, Praseodymium, Yttrium, Others), By Application, By Region – Market Forecast, 2025–2034
- Published Date:Jul-2025
- Pages: 129
- Format: PDF
- Report ID: PM6093
- Base Year: 2024
- Historical Data: 2020-2023
Overview
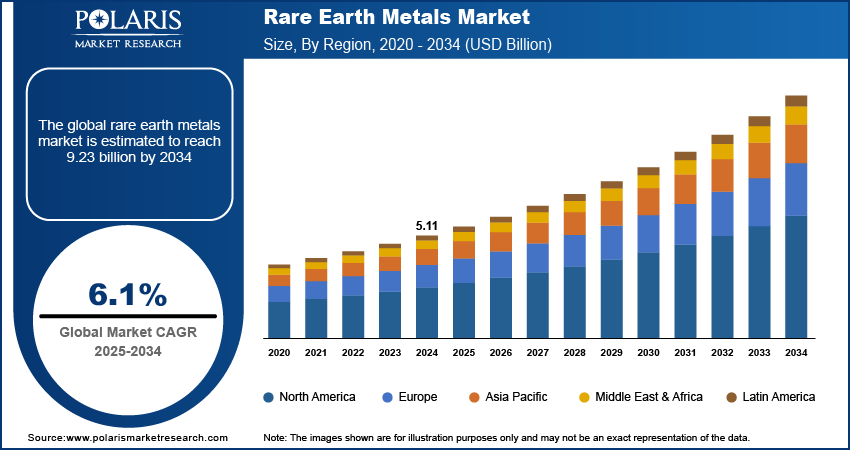
The global rare earth metals market size was valued at USD 5.11 billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 6.1% from 2025 to 2034. Rising global demand for electric vehicles is driving the consumption of rare earth magnets such as neodymium and dysprosium, in permanent magnet motors. Automakers are increasingly reliant on these materials to meet efficiency, torque, and range requirements in next-generation EVs.
Key Insights
- The neodymium segment accounted for ~31% of the revenue share in 2024 due to its essential role in high-performance permanent magnets used in electric vehicles, robotics, and renewable energy systems.
- The magnet segment held the largest revenue share of ~41% in 2024 due to the critical importance of rare earth magnets in modern technologies.
- North America is gradually strengthening its rare earth metals market through increased exploration activities and policy support aimed at reducing dependency on overseas supply chains.
- The U.S. rare earth metals market is witnessing strong momentum, supported by aggressive policy frameworks targeting mineral independence.
- In 2024, Asia Pacific accounted for the largest revenue share of ~85% due to dominant production volumes, extensive refining capacity, and presence of leading rare earth processors.
- The market in China is showing strong growth due to its vast resource base, well-developed separation technologies, and strategic focus on value-added applications.
Industry Dynamics
- Continued innovation and rising consumption of electronic devices globally are strengthening the market’s demand foundation.
- Rising global demand for electric vehicles is driving the consumption of rare earth magnets such as neodymium and dysprosium, in permanent magnet motors.
- Global decarbonization policies are increasing the adoption of rare earth metals across energy storage and emission control systems.
- High extraction and processing costs restrain the affordability and widespread adoption of rare earth metals
Market Statistics
- 2024 Market Size: USD 5.11 billion
- 2034 Projected Market Size: USD 9.23 billion
- CAGR (2025–2034): 6.1%
- Asia Pacific: Largest market in 2024
To Understand More About this Research: Request a Free Sample Report
The rare earth metals market refers to the global trade and consumption of a group of 17 chemically similar metallic elements, including lanthanides, scandium, and yttrium. These metals are critical in manufacturing advanced technologies such as electric vehicles, wind turbines, smartphones, defense systems, and catalysts, due to their magnetic, luminescent, and electrochemical properties. The market spans mining, refining, and end-use applications across electronics, energy, and industrial sectors. Continued innovation and rising consumption of electronic devices globally are strengthening the market’s demand. Smartphones, laptops, and wearables require rare earth elements for miniaturized speakers, batteries, and screens.
Military-grade technologies such as missile guidance systems, satellites, and stealth aircraft depend on rare earth elements for precision, durability, and performance. Government spending on defense modernization is contributing to sustained demand. Moreover, emerging clean technologies, including hydrogen fuel cells and advanced batteries, depend on rare earths for efficiency improvements. Global decarbonization policies are increasing the adoption of these materials across energy storage and emission control systems.
Drivers and Opportunities
Surge in Electric Vehicle Production: Electric vehicle manufacturers are increasing their use of high-performance rare earth magnets, especially neodymium and dysprosium, to power compact and energy-efficient motors. According to the International Energy Agency, in 2024, global production of electric vehicles reached 17.3 million units, marking a roughly 25% increase over the previous year's figures. These magnets play a key role in enhancing motor strength, improving vehicle acceleration, and increasing battery range. The shift from internal combustion engines to electric drivetrains is making these materials essential in automotive design. Leading EV makers are also developing in-house supply chains or forming alliances to secure consistent access to these critical inputs. Growing consumer preference for zero-emission vehicles, supported by government subsidies and stricter emissions regulations, is accelerating EV adoption and fueling the demand for rare earth metals globally.
Expansion of Wind Energy Installations: Wind turbines, especially in offshore installations, depend heavily on rare earth magnets for reliable and efficient energy conversion. According to World Economic Forum, in 2023, the global wind industry demonstrated significant growth, installing 50% more capacity compared to the previous year. Permanent magnet generators use neodymium and praseodymium to reduce mechanical wear and improve performance in harsh environments. These materials help turbines generate electricity with lower maintenance needs and higher durability, even in fluctuating weather. The push for decarbonization is leading to increased investments in wind energy infrastructure by both public and private sectors. Countries are setting ambitious targets for renewable energy, prompting large-scale projects that rely on these advanced materials. This shift is driving stable and long-term growth in rare earth metals consumption.
Segmental Insights
Product Analysis
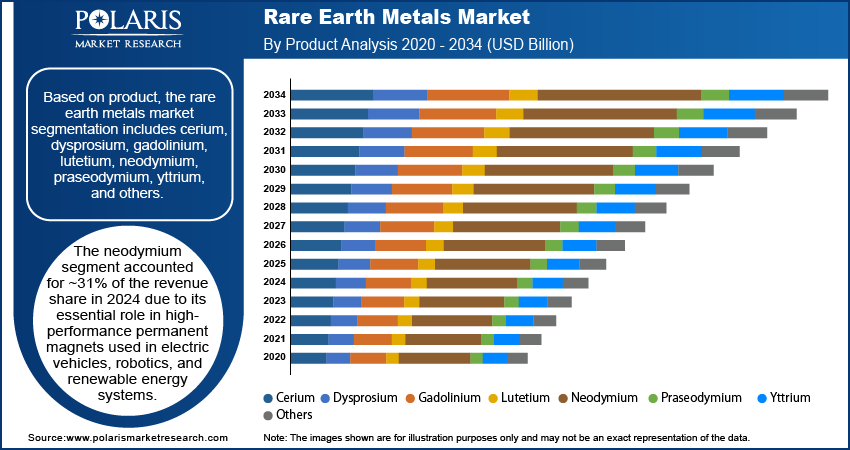
Based on product, the segmentation includes cerium, dysprosium, gadolinium, lutetium, neodymium, praseodymium, yttrium, and others. The neodymium segment accounted for ~31% of the revenue share in 2024 due to its essential role in high-performance permanent magnets used in electric vehicles, robotics, and renewable energy systems. Demand from the automotive and electronics sectors has driven consistent procurement of neodymium due to its unmatched magnetic strength-to-size ratio. Neodymium-based magnets offer superior torque and energy efficiency, making them critical for lightweight, compact motor designs in next-generation EVs and wind turbines. Industrial users also value the material for miniaturizing components in headphones, hard drives, and industrial automation systems. The growing reliance on advanced motion control and energy-efficient motors across industries has further solidified its dominance.
The praseodymium segment is expected to register the highest CAGR due to its increasing usage in combination with neodymium to enhance magnet corrosion resistance and thermal stability. Praseodymium is also gaining demand in alloy manufacturing and aerospace applications, particularly for producing high-strength metals required in jet engines and aircraft turbines. Consumer electronics manufacturers are incorporating praseodymium to improve color performance in display technologies. The material's versatility in green energy systems and advanced electronics makes it increasingly attractive amid technological transitions across sectors. Market participants are ramping up production and sourcing strategies to meet the growing requirements, especially in lightweight alloys and magnetic materials.
The demand for gadolinium is growing due to its expanding application in medical imaging and nuclear reactor components. Gadolinium’s unique magnetic properties make it a valuable contrast agent in MRI procedures, where it enhances image clarity and diagnostic accuracy. In the energy sector, gadolinium is being utilized in control rods for nuclear reactors because of its high neutron absorption capacity. It also plays a role in magneto-caloric refrigeration systems and specialty alloys designed for high-temperature environments. Ongoing medical advancements and research into clean nuclear energy are propelling the usage of gadolinium across research institutions, hospitals, and energy utilities. Its growing relevance in healthcare and power sectors is supporting its rising adoption.
Application Analysis
In terms of application, the segmentation includes magnet, catalysts, metallurgy, polishing, glass, phosphors, ceramics, and others. The magnet segment held the largest revenue share of ~41% in 2024 due to the critical importance of rare earth magnets in modern technologies such as electric vehicle drivetrains, wind turbine generators, and high-performance consumer electronics. These magnets provide high magnetic strength and durability, enabling energy-efficient motors and compact designs. The shift toward electrification in transport and infrastructure has led to massive procurement of neodymium, samarium, and praseodymium-based magnets. Manufacturers prefer these materials to meet evolving performance standards, reduce carbon emissions, and comply with stringent environmental regulations. Strong investments in renewable energy projects and automotive electrification continue to fuel demand for rare earth magnets globally.
The catalyst segment is growing due to the increasing use of rare earth metals in refining and chemical processing industries. Cerium and lanthanum are extensively used as fluid catalytic cracking (FCC) catalysts to improve fuel yield and efficiency in oil refineries. These materials enhance chemical reactivity and stability under extreme temperatures, making them indispensable for petroleum and emission control applications. The automotive sector also uses rare earth catalysts in vehicle exhaust treatment systems to lower harmful emissions. Growing environmental regulation and push for cleaner fuel production are strengthening the need for advanced catalytic materials, positioning rare earths as vital to sustainable chemical and industrial operations.
Regional Analysis
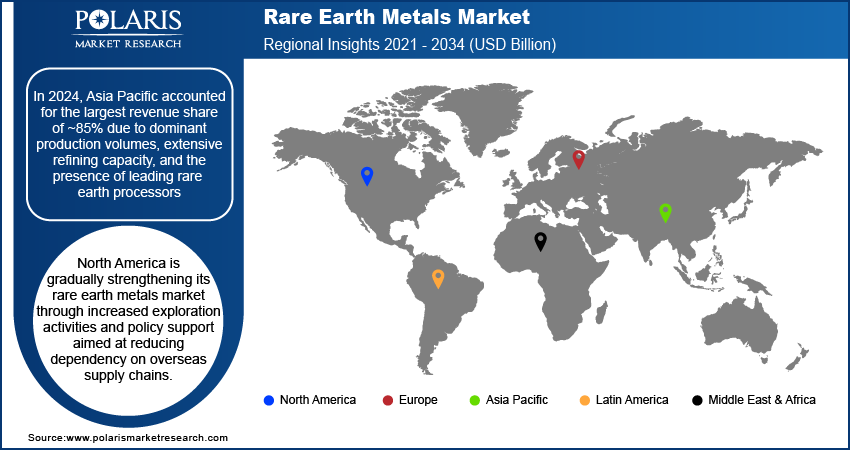
North America is gradually strengthening its rare earth metals market through increased exploration activities and policy support aimed at reducing dependency on overseas supply chains. Manufacturers are focusing on diversifying sourcing and boosting domestic extraction, particularly for critical elements such as neodymium and dysprosium used in EVs and defense technologies. Investments in rare earth separation and processing facilities are increasing to address downstream value chain gaps. Government-backed incentives for critical mineral security and strategic collaborations between private players and research institutions are driving regional innovation. The region’s push to support electrification, clean energy, and national security is creating a robust environment for the North America rare earth elements market.
U.S. Rare Earth Metals Market Insights
The U.S. industry is witnessing strong momentum, supported by aggressive policy frameworks targeting mineral independence. Major focus lies in establishing vertically integrated rare earth supply chains to serve growing demand from electric vehicle manufacturing, renewable energy systems, and defense sectors. The U.S. Department of Energy's annual reports highlight that wind power is among the fastest-growing and lowest-cost electricity sources in America. In 2022, it accounted for 22% of new electricity capacity, with USD 12 billion in investments. Companies are expanding domestic mining operations and forming strategic partnerships for refining capabilities to counter supply vulnerabilities. Federal funding initiatives and critical minerals legislation are propelling private sector involvement. The country’s shift toward clean technology adoption and digital infrastructure upgrades is reinforcing the importance of rare earth elements in permanent magnets, electronics, and optical devices, further stimulating long-term market demand.
Asia Pacific Rare Earth Metals Market Trends
In 2024, Asia Pacific accounted for the largest revenue share of ~85% due to dominant production volumes, extensive refining capacity, and presence of leading rare earth processors. Countries such as China, Myanmar, and Australia are central to the global supply of rare earth elements, particularly those required for magnets and batteries. Regional players benefit from cost-effective extraction, favorable geology, and well-established logistics. Asia Pacific’s integration of rare earths into its booming electronics, automotive, and renewable sectors keeps demand consistent across the value chain. According to the International Trade Administration (ITA), India ranks as the third-largest energy consumer globally. The Ministry of Power reported that the country's peak electricity demand hit a remarkable 223 gigawatts (GW) in June 2023, reflecting a 3.4% increase from its previous record in 2022. Strong R&D initiatives in material science and government support for export-oriented production enhance the region’s leadership in rare earth processing and application innovation.
China Rare Earth Metals Market Overview
China is showing strong growth due to its vast resource base, well-developed separation technologies, and strategic focus on value-added applications. State-driven efforts to consolidate mining operations and control pricing structures enable long-term market dominance. Domestic demand for rare earth metals remains high, driven by expanding EV production, green energy projects, and 5G telecommunications. China’s rare earth policies promote technological self-sufficiency while enhancing export value through magnet and battery manufacturing. Environmental regulations have encouraged more sustainable mining practices, which improve both capacity and global competitiveness. The country’s continued investments in strategic reserves and downstream innovation further boosts its influence in the global markets.
Europe Rare Earth Metals Market Assessment
The market in Europe is witnessing a steady increase in rare earth production, with efforts concentrated on establishing secure and sustainable supply chains. Key mining projects across nations such as Sweden and Greenland are being developed to reduce dependency on Asian imports. Policy directives from the European Union prioritize rare earths as strategic resources essential for climate goals and digital transformation. Investments are being directed toward recycling technologies and extraction from industrial waste to increase self-sufficiency. The push for domestic processing capabilities and green manufacturing has brought attention to rare earth applications in wind turbines, electric mobility, and electronics, contributing to regional production expansion and innovation.
Key Players and Competitive Analysis
The competitive landscape of the rare earth metals market is defined by strategic shifts toward supply chain diversification, downstream integration, and value-added processing capabilities. Industry analysis highlights a growing focus on market expansion strategies such as establishing refining plants outside traditional production hubs and securing long-term raw material access through mining rights and exploration projects. Companies are increasingly pursuing joint ventures and strategic alliances to develop end-to-end rare earth ecosystems, particularly in regions seeking reduced import reliance. Mergers and acquisitions are accelerating as players look to consolidate resources, leverage technological synergies, and strengthen their presence across key application markets such as electric mobility, wind energy, and electronics. Post-merger integration initiatives are aligning supply logistics, production technologies, and customer outreach for better market penetration. Technological advancements in solvent extraction, separation, and magnet manufacturing are improving operational efficiency and reducing environmental impact, creating competitive advantages. Policy incentives and government-backed collaborations are further intensifying R&D investments and fostering innovation in sustainable mining and recycling. Overall, the rare earth metals market remains dynamic, with participants striving for geopolitical resilience, functional material specialization, and strategic control over the critical mineral value chain.
Key Players
- Alkane Resources Ltd
- Arafura Resources Ltd
- Avalon Advanced Materials Inc.
- China Northern Rare Earth (Group) High-Tech Co., Ltd.
- Greenland Minerals Ltd
- Hitachi Metals Ltd.
- Iluka Resources Limited
- Indian Rare Earth Limited
- Lynas Corporation Ltd
- Northern Minerals Ltd
- Rare Element Resources Ltd.
- Shin-Etsu Chemical Co., Ltd.
- Ucore Rare Metals Inc.
Industry Developments
July 2025: Apple invested USD 500 million to strengthen its U.S. supply chain for rare earth magnets through a partnership with MP Materials. The company will establish a recycling facility to process rare earth elements from recycled sources, promoting sustainable manufacturing practices.
Rare Earth Metals Market Segmentation
By Product Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- Cerium
- Dysprosium
- Gadolinium
- Lutetium
- Neodymium
- Praseodymium
- Yttrium
- Others
By Application Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- Magnets
- Catalysts
- Metallurgy
- Polishing
- Glass
- Phosphors
- Ceramics
- Others
By Regional Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- North America
- U.S.
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- UK
- Italy
- Spain
- Netherlands
- Russia
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- Malaysia
- South Korea
- Indonesia
- Australia
- Vietnam
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Middle East & Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Israel
- South Africa
- Rest of Middle East & Africa
- Latin America
- Mexico
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
Rare Earth Metals Market Report Scope
|
Report Attributes |
Details |
|
Market Size in 2024 |
USD 5.11 billion |
|
Market Size in 2025 |
USD 5.42 billion |
|
Revenue Forecast by 2034 |
USD 9.23 billion |
|
CAGR |
6.1% from 2025 to 2034 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Historical Data |
2020–2023 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025–2034 |
|
Quantitative Units |
Revenue in USD billion and CAGR from 2025 to 2034 |
|
Report Coverage |
Revenue Forecast, Competitive Landscape, Growth Factors, and Industry Trends |
|
Segments Covered |
|
|
Regional Scope |
|
|
Competitive Landscape |
|
|
Report Format |
|
|
Customization |
Report customization as per your requirements with respect to countries, regions, and segmentation. |
FAQ's
The global market size was valued at USD 5.11 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow to USD 9.23 billion by 2034.
The global market is projected to register a CAGR of 6.1% during the forecast period.
In 2024, Asia Pacific accounted for the largest revenue share of ~85% due to dominant production volumes, extensive refining capacity, and presence of leading rare earth processors.
A few of the key players in the market are Alkane Resources Ltd; Arafura Resources Ltd; Avalon Advanced Materials Inc.; China Northern Rare Earth (Group) High-Tech Co., Ltd.; Greenland Minerals Ltd; Hitachi Metals Ltd.; Iluka Resources Limited; Indian Rare Earth Limited; Lynas Corporation Ltd; Northern Minerals Ltd; Rare Element Resources Ltd.; Shin-Etsu Chemical Co., Ltd.; and Ucore Rare Metals Inc.
The neodymium segment accounted for ~31% of the revenue share in 2024 due to its essential role in high-performance permanent magnets used in electric vehicles, robotics, and renewable energy systems.
The magnet segment held the largest revenue share of ~41% in 2024 due to the critical importance of rare earth magnets in modern technologies such as electric vehicle drivetrains, wind turbine generators, and high-performance consumer electronics.
