
U.S. Microgrid Market Size, Share, Trends, Industry Analysis Report
By Power Source (Natural Gas, CHP, Solar PV, Diesel, Fuel Cell, Others), By Product, By Application– Market Forecast, 2025–2034
- Published Date:Aug-2025
- Pages: 129
- Format: PDF
- Report ID: PM6143
- Base Year: 2024
- Historical Data: 2020 - 2023
Overview
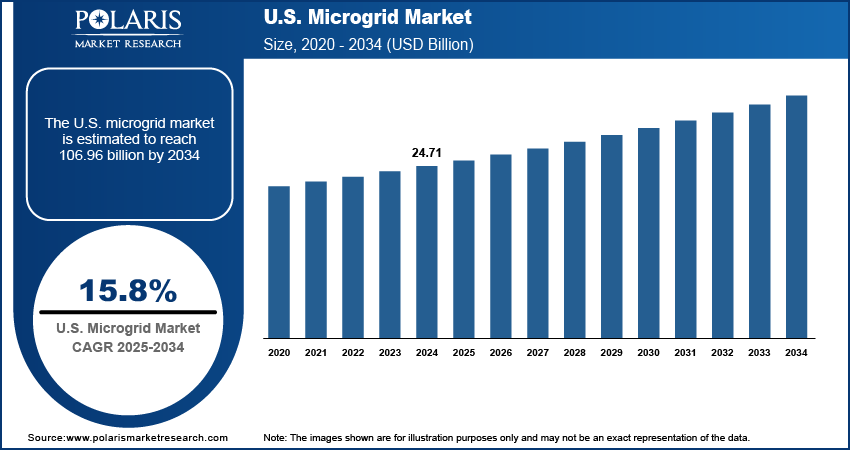
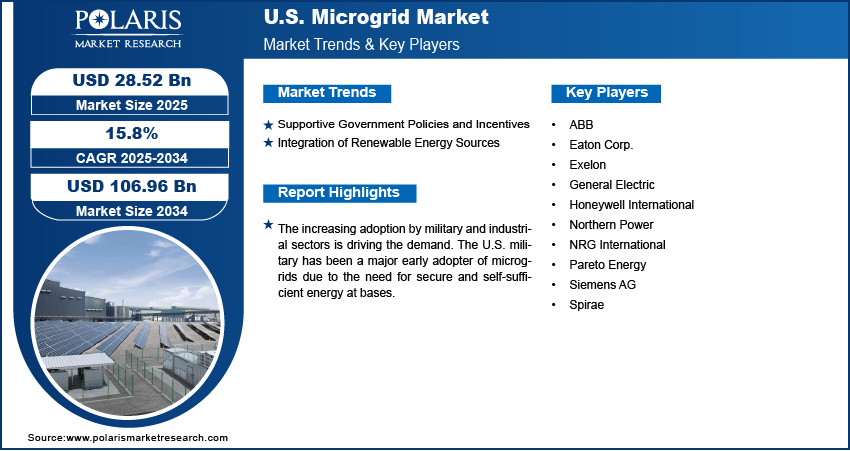
The U.S. microgrid market size was valued at USD 24.71 billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 15.8% from 2025 to 2034. The market growth is driven by supportive government policies and incentives and the integration of renewable energy sources.
Key Insights
- In 2024, the CHP segment dominated with the largest share. CHP is favored as it simultaneously produces electricity and useful thermal energy from a single fuel source, making it highly efficient.
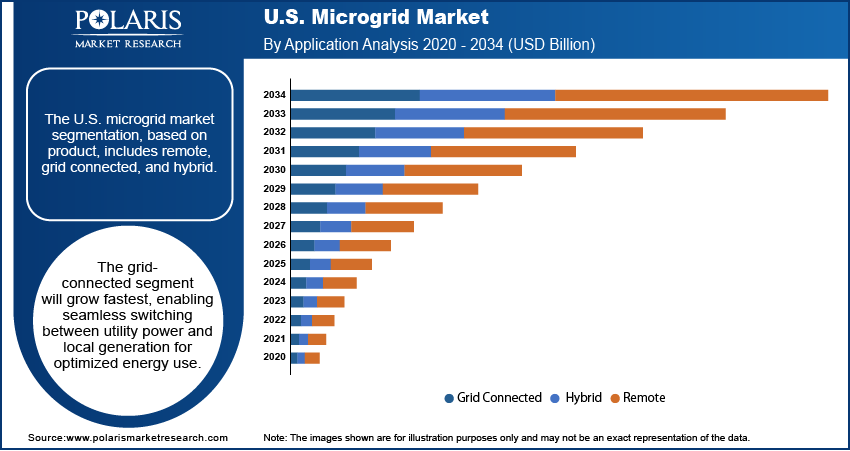
- The grid connected segment is expected to experience the fastest growth during the forecast period, as these systems operate in connection with the main utility grid, allowing users to switch between grid power and local generation as needed.
Industry Dynamics
- The supportive government policies and incentives drive the adoption of microgrids across the U.S.
- The integration of renewable energy sources is fueling the industry growth.
- The increasing adoption by the military and industrial sectors is driving the demand for microgrid systems.
- High initial investment costs and complex regulatory approvals restrain the widespread adoption of microgrid systems.
Market Statistics
- 2024 Market Size: USD 24.71 billion
- 2034 Projected Market Size: USD 106.96 billion
- CAGR (2025–2034): 15.8%
To Understand More About this Research: Request a Free Sample Report
A microgrid is a localized energy system that can operate independently or in coordination with the main power grid. It typically includes distributed energy resources such as solar panels, batteries, generators, and control systems to produce, store, and manage electricity. Microgrids enhance energy reliability, reduce dependence on centralized grids, and support sustainability by integrating renewable energy sources.
Major factors driving the demand for microgrid systems in the U.S. are the growing need for energy resilience. There is a greater risk of power outages as extreme weather events and natural disasters become more frequent. Microgrids offer a reliable backup power source during grid failures, making them ideal for hospitals, data centers, and military facilities. These systems operate independently from the main grid, ensuring uninterrupted power supply. This increased focus on reliability is pushing public institutions, private enterprises, and municipalities to invest in microgrids to safeguard critical operations during emergencies.
The increasing adoption by the military and industrial sectors is driving the demand microgrid systems. The U.S. military has been a major early adopter of microgrids due to the need for secure and self-sufficient energy at bases. These systems allow facilities to continue operations without relying on external power sources. Similarly, industries that require constant uptime such as manufacturing, healthcare, and data centers are investing in microgrids to reduce operational risks. This demand for energy independence and reliability in mission-critical sectors is driving growth, especially as these organizations seek to minimize disruptions and improve energy control.
Drivers and Opportunities
Supportive Government Policies and Incentives: Federal and state-level policies in the U.S. are actively promoting microgrid development. Programs such as the Department of Energy’s microgrid initiatives and state-level resilience grants provide funding and technical support for microgrid projects. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, in June 2025, the government funded USD 8 million to accelerate microgrid innovation through the Community Microgrid Assistance Partnership (C-MAP) program. Additionally, incentives such as investment tax credits for battery energy storage and solar systems make microgrids more affordable. These supportive regulations lower the financial and regulatory barriers for implementation, encouraging utilities, businesses, and communities to explore microgrid deployment. Consequently, fueling the industry growth.
Integration of Renewable Energy Sources: The push toward cleaner energy is accelerating microgrid adoption in the U.S. Microgrids easily integrate renewable sources such as solar and wind, along with battery energy storage, to create sustainable energy systems. This is particularly valuable as federal and state governments set aggressive carbon reduction targets. Microgrids help reduce dependence on fossil fuels and support the transition to a low-carbon economy. They further offer grid support by balancing renewable energy variability, making them a practical solution for improving grid stability while meeting environmental goals, thereby driving the U.S. microgrid market development.
Segmental Insights
Power Source Analysis
The U.S. microgrid market segmentation, based on power source, includes natural gas, CHP, solar PV, diesel, fuel cell, and others. In 2024, the CHP segment dominated with the largest share. CHP is favored as it simultaneously produces electricity and useful thermal energy from a single fuel source, making it highly efficient. It is commonly used in universities, hospitals, military bases, and industrial facilities where both heat and electricity are needed. The ability to reduce energy waste and cut costs has made CHP a preferred power source in microgrids. Moreover, its reliability during grid outages and efficiency benefits further drives the segment growth.
Product Analysis
Based on product, the U.S. microgrid market is segmented into remote, grid connected, and hybrid. The grid connected segment is expected to experience the fastest growth during the forecast period as these systems operate in connection with the main utility grid, allowing users to switch between grid power and local generation as needed. They offer the flexibility of selling excess power back to the grid while ensuring backup power during outages. Grid-connected microgrids are becoming attractive for commercial buildings, campuses, and municipalities with growing focus on renewable integration and cost savings through demand-side management. Additionally, their ability to improve grid stability and reduce energy costs supports their rising adoption in the U.S., further fueling the segment growth.
Key Players and Competitive Analysis
The U.S. microgrid market is highly competitive, driven by the growing demand for resilient, decentralized energy systems. Key players such as ABB, General Electric, and Siemens AG leverage their global presence and advanced grid technologies to lead in system integration and automation. Eaton Corp. and Honeywell International focus on intelligent energy management and cybersecurity solutions, critical for commercial and industrial microgrids. Exelon and NRG International bring utility-scale expertise, supporting large-scale deployments and utility-owned microgrid models. Northern Power and Spirae specialize in software-driven control systems and modular solutions, catering to community and remote applications. Pareto Energy is notable for its work in urban microgrids and interconnection innovations. The landscape is shaped by strategic partnerships, R&D investments, and pilot projects aimed at demonstrating cost-effectiveness and grid reliability. Competition is intensifying around scalable, secure, and economically viable microgrid solutions across the U.S. market as regulatory support and clean energy targets increase.
Key Players
- ABB
- Eaton Corp.
- Exelon
- General Electric
- Honeywell International
- Northern Power
- NRG International
- Pareto Energy
- Siemens AG
- Spirae
U.S. Microgrid Industry Developments
In June 2025, Groton Electric Light Department and Lightshift Energy launched their second 3-MW energy storage microgrid, Groton II, which enhances resilience, lowers energy costs, and provides backup power to Florence Roche Elementary School in Groton, Massachusetts.
In February 2025, Schneider Electric inaugurated new microgrid testing laboratories at its Global R&D Center in Andover, Massachusetts, enhancing its ability to simulate, validate, and accelerate the deployment of efficient and resilient energy solutions.
U.S. Microgrid Market Segmentation
By Power Source Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- Natural Gas
- CHP
- Solar PV
- Diesel
- Fuel Cell
- Others
By Product Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- Remote
- Grid Connected
- Hybrid
By Application Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- Government
- Education
- Commercial
- Utility
- Defense
- Others
U.S. Microgrid Market Report Scope
|
Report Attributes |
Details |
|
Market Size in 2024 |
USD 24.71 Billion |
|
Market Size in 2025 |
USD 28.52 Billion |
|
Revenue Forecast by 2034 |
USD 106.96 Billion |
|
CAGR |
15.8% from 2025 to 2034 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Historical Data |
2020–2023 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025–2034 |
|
Quantitative Units |
Revenue in USD Billion and CAGR from 2025 to 2034 |
|
Report Coverage |
Revenue Forecast, Competitive Landscape, Growth Factors, and Industry Trends |
|
Segments Covered |
|
|
Competitive Landscape |
|
|
Report Format |
|
|
Customization |
Report customization as per your requirements with respect to countries, regions, and segmentation. |
FAQ's
The market size was valued at USD 24.71 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow to USD 106.96 billion by 2034.
The market is projected to register a CAGR of 15.8% during the forecast period.
A few of the key players in the market are ABB, Eaton Corp., Exelon, General Electric, Honeywell International, Northern Power, NRG International, Pareto Energy, Siemens AG, and Spirae.
The CHP segment dominated the market share in 2024.
The connected grid segment is expected to witness the fastest growth during the forecast period.
