
Antibiotics Market Size, Share, Trends, Industry Analysis Report
By Drug Class (Cephalosporin, Penicillin, Fluoroquinolone, Macrolides, Carbapenems, Aminoglycosides, Sulfonamides, 7-ACA, Others), By Type, By Action Mechanism, By Region – Market Forecast, 2025–2034
- Published Date:Aug-2025
- Pages: 129
- Format: PDF
- Report ID: PM2083
- Base Year: 2024
- Historical Data: 2020 - 2023
Overview
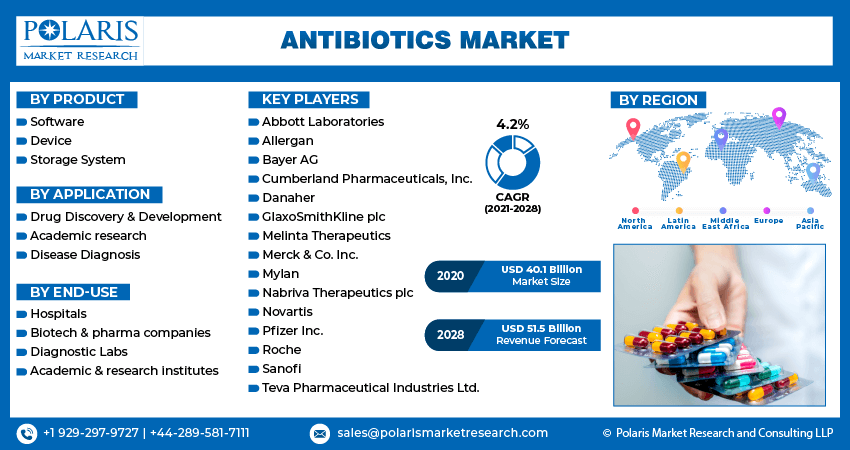
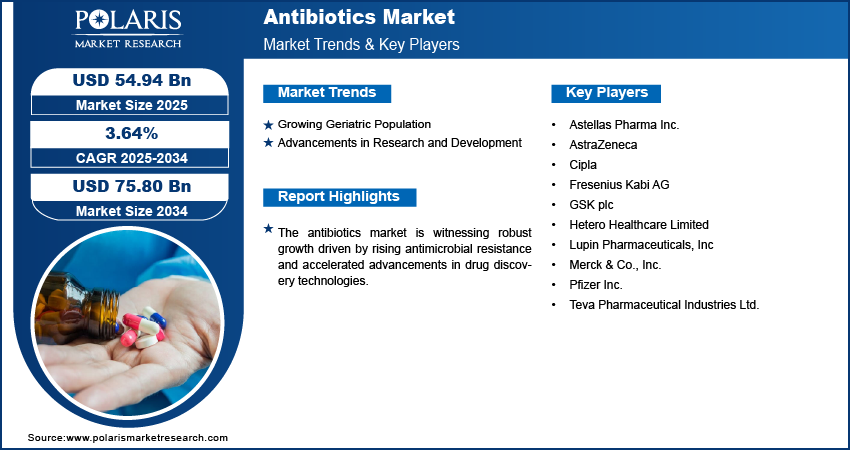
The global antibiotics market size was valued at USD 53.05 billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 3.64% from 2025 to 2034. Key factors driving demand for antibiotics include the growing incidence of bacterial infections worldwide, rising geriatric population, advancements in research and development (R&D).
Key Insights
- The penicillin segment accounted for the largest revenue share of 23.74% in 2024, owing to its broad-spectrum efficacy, widespread clinical use, and established safety profile.
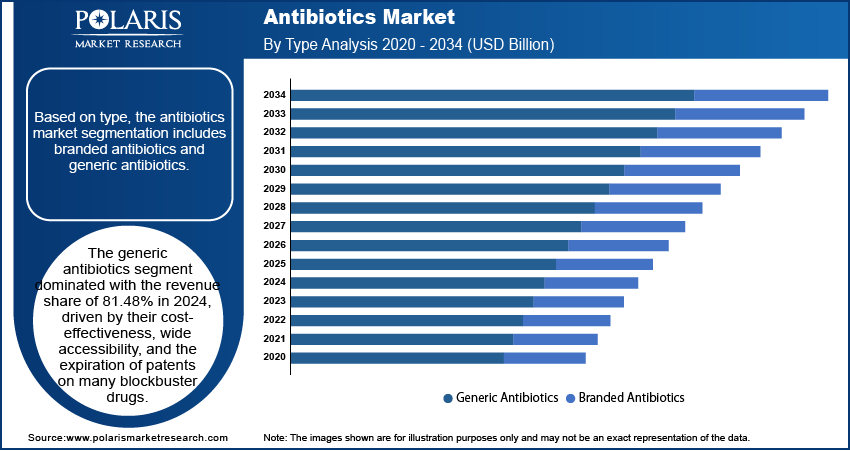
- The generic antibiotics segment dominated the revenue share of 81.48% in 2024, driven by increasing cost-containment efforts in the U.S. healthcare system and growing demand for affordable treatment options.
- The RNA synthesis inhibitors segment is expected to witness the fastest growth during the forecast period driven by the increasing focus on combating resistant bacterial strains and the need for novel antimicrobial targets.
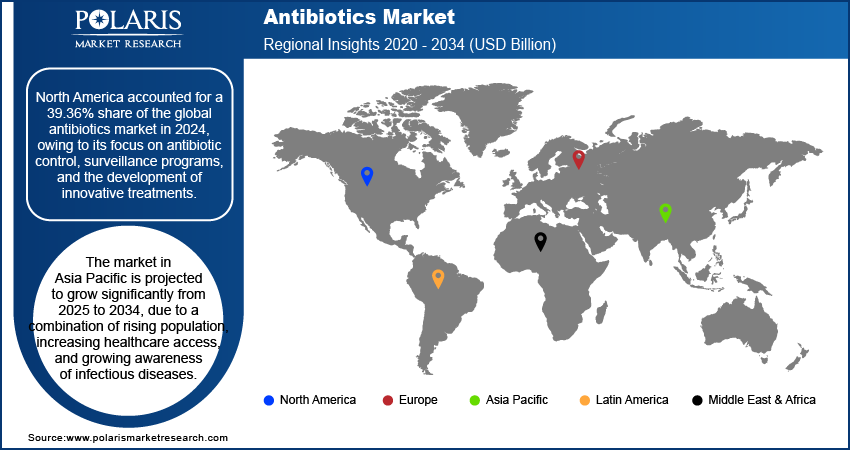
- North America accounted for 39.36% of the global antibiotics market share in 2024 owing to its focus on antibiotic control, surveillance programs, and the development of innovative treatments.
- The U.S. held the largest share in North America antibiotics landscape in 2024 due to its advanced healthcare infrastructure, high per capita antibiotic consumption, and strong presence of pharmaceutical innovators.
- The market in Asia Pacific is projected to grow significantly from 2025-2034, due to a combination of rising population, increasing healthcare access, and growing awareness of infectious diseases.
- The market in India is expanding, driven by a large and densely populated patient base, as well as an increasing incidence of bacterial infections.
Industry Dynamics
- The aging population's increasing vulnerability to infections is boosting antibiotic demand, as elderly individuals face greater risks of bacterial complications.
- Innovations in antibiotic R&D, including novel drug discovery and AMR-focused therapies, are enhancing treatment efficacy and expanding therapeutic options.
- Rising antimicrobial resistance (AMR) reduces treatment efficacy, increasing healthcare costs and mortality rates globally.
- Expanding geriatric populations and emerging markets propel the demand for next-generation antibiotics and innovative therapies.
Market Statistics
- 2024 Market Size: USD 53.05 billion
- 2034 Projected Market Size: USD 75.80 billion
- CAGR (2025–2034): 3.64%
- North America: Largest market in 2024
To Understand More About this Research: Request a Free Sample Report
Antibiotics are antimicrobial substances used to prevent and treat bacterial infections by inhibiting the growth or destroying bacteria in the body. The growing incidence of bacterial infections worldwide boosts the demand for antibiotics, as these medications remain essential in treating a range of life-threatening and common bacterial diseases. According to a February 2025 report by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the U.S. records over 2.8 million cases of antimicrobial-resistant infections annually. Factors such as increasing antimicrobial resistance, urban crowding, and weakened immunity in aging populations contribute to the elevated prevalence of infections, thereby reinforcing the essential role of antibiotics in modern medicine. The need for effective antibiotic therapies is becoming increasingly urgent and persistent as the global health landscape grapples with the emergence of evolving bacterial strains.
Increased healthcare expenditure across both developed and emerging economies is boosting access to advanced antibiotics and improved treatment options. According to a 2024 WHO report, global health expenditure reached USD 9.8 trillion in 2022, accounting for 9.9% of worldwide GDP. Rising public and private investments in healthcare infrastructure, insurance coverage, and pharmaceutical research and development (R&D) led to greater affordability and availability of antibiotics. This upward shift in spending also enables governments and institutions to allocate more resources toward the development of novel antibiotic formulations and the establishment of effective distribution networks. Therefore, as healthcare systems expand and modernize, particularly in middle-income regions, the growing expenditure catalyzes increased antibiotic usage and deeper market penetration.
Drivers & Opportunities
Growing Geriatric Population: The growing geriatric population is driving the use of antibiotics, primarily due to the increased susceptibility of older adults to bacterial infections. In 2024, the World Health Organization reported that the global population aged 60 and above is projected to rise from 1.1 billion in 2023 to 1.4 billion by 2030, indicating a substantial demographic shift toward aging. Elderly individuals become more prone to conditions such as pneumonia, urinary tract infections (UTI), and skin infections, which often require antibiotic treatment as the immune system weakens with age. Additionally, the prevalence of chronic illnesses in aging populations further elevates the risk of secondary infections, thereby increasing the need for consistent and effective antibiotic therapies.
Advancements in Research and Development: Advancements in research and development are driving the market expansion by addressing the rising challenge of antimicrobial resistance and introducing more effective treatment options. Innovations in drug discovery technologies, including genomics, synthetic biology, and AI-assisted screening, have enabled the development of novel antibiotics with improved efficacy and safety profiles. In March 2024, Stanford researchers developed SyntheMol, a generative AI model that designs novel antibiotic compounds and synthesis recipes. It produced six potential drugs targeting drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii, a critical WHO-priority pathogen. These R&D efforts are expanding the range of available antibiotic classes and also enhancing the precision with which bacterial pathogens are targeted. As a result, continued investments in research are propelling growth by providing advanced antibiotic solutions that meet evolving clinical needs.
Pipeline Analysis
The antibiotics market is witnessing active innovation, with several promising prospects in development aimed at combating multidrug-resistant pathogens. Continued efforts in antibiotic R&D are focused on introducing novel mechanisms of action to overcome resistance and broaden therapeutic efficacy. For instance, in June 2025, Roche, in collaboration with Harvard University, advanced its antibiotic candidate zosurabalpin into Phase 3 trials, targeting carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii (CRAB), a critical Gram-negative pathogen. Additionally, in March 2025, Wockhardt filed ZAYNICH (zidebactam/cefepime) for approval in India after Phase III trials showed a 96.8% clinical cure rate for cUTI. Superior to meropenem (89% vs. 68.4%), US filing planned by August 2025.
Antibiotics Market Patent Summary
|
Antibiotic |
Brand Name |
Patent Expiry |
Notes |
|
Amikacin Sulfate |
ARIKAYCE |
2035 |
Aminoglycoside is an antibiotic for severe Gram-negative infections, including resistant Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC). |
|
Clindamycin Phosphate |
XACIATO |
2036 |
Lincosamide antibiotic is used for bacterial vaginosis, effective against anaerobes and Gram-positive bacteria. |
|
Vancomycin Hydrochloride |
VANCOCIN |
2035 |
Glycopeptide antibiotic is used for MRSA, C. difficile (oral), and severe Gram-positive infections. |
Segmental Insights
Drug Class Analysis
Based on drug class, the segmentation includes cephalosporin, penicillin, fluoroquinolone, macrolides, carbapenems, aminoglycosides, sulfonamides, 7-ACA, and others. The penicillin segment accounted for the largest revenue share of 23.74% in 2024, due to its broad-spectrum activity, affordability, and extensive clinical usage across various infections. Penicillins remain a cornerstone in the treatment of respiratory tract infections, skin infections, and other common bacterial conditions as one of the earliest discovered and most widely prescribed classes of antibiotics. Their well-established safety profile and consistent efficacy continue to make them a preferred choice among healthcare providers. Additionally, the widespread availability of both branded and generic formulations contributes to high consumption volumes, supporting the segment's dominant position.
Type Analysis
In terms of type, the segmentation includes branded antibiotics and generic antibiotics. The generic antibiotics dominated the revenue share of 81.48% in 2024, driven by their cost-effectiveness, wide accessibility, and the expiration of patents on many blockbuster drugs. Healthcare systems globally, especially in emerging and price-sensitive markets, are increasingly relying on generics to manage treatment costs while maintaining therapeutic efficacy. Regulatory support for generic drug approvals, combined with the active participation of numerous pharmaceutical manufacturers, further strengthens the supply chain and fosters competitive pricing. This environment has led to increased uptake across hospitals, clinics, and pharmacies, consolidating the dominance of the generic antibiotics landscape.
Action Mechanism Analysis
The segmentation, based on action mechanism, includes cell wall synthesis inhibitors, protein synthesis inhibitors, DNA synthesis inhibitors, RNA synthesis inhibitors, mycolic acid inhibitors, and others. The RNA synthesis inhibitors segment is expected to witness the fastest growth during the forecast period due to its emerging role in targeting specific bacterial mechanisms with higher precision. These antibiotics work by inhibiting bacterial RNA polymerase activity, thereby preventing the transcription process that is essential for bacterial survival. RNA synthesis inhibitors are gaining attention for their novel mechanism of action and potential to address drug-resistant pathogens as resistance to traditional antibiotic classes rises. Additionally, ongoing research efforts and the introduction of newer agents in this category are further driving its anticipated expansion in the coming years.
Regional Analysis
The North America antibiotics market accounted for 39.36% of global revenue share in 2024, primarily due to its advanced healthcare infrastructure, high prescription rates, and strong presence of leading pharmaceutical companies. The region benefits from investments in research, well-established regulatory frameworks, and robust antibiotic usage monitoring systems. Furthermore, high public awareness of infectious diseases and access to insurance coverage enhance antibiotic uptake. Collectively, these factors contribute to North America's dominant position in the global antibiotics industry.
U.S. Antibiotics Market Insights
The U.S. held the largest share in North America antibiotics landscape in 2024 due to its advanced healthcare infrastructure, high per capita antibiotic consumption, and strong presence of pharmaceutical innovators. The country's proactive surveillance programs and streamlined drug approval processes also support timely access to a broad range of antibiotics. Additionally, high awareness levels and widespread insurance coverage contribute to consistent and large-scale antibiotic utilization across both outpatient and inpatient environments.
Asia Pacific Antibiotics Market Trends
The market in Asia Pacific is projected to grow significantly from 2025 to 2034, due to a combination of rising population, increasing healthcare access, and growing awareness of infectious diseases. In August 2024, India's Health Ministry reported 245 AES cases (82 deaths, a CFR of 33%), including 64 confirmed Chandipura virus (CHPV) infections, marking the largest outbreak in 20 years. CHPV, transmitted by sandflies/mosquitoes, causes seasonal AES in western/central India. Antibiotic accessibility is improving across both urban and rural areas as regional governments continue to expand healthcare infrastructure and pharmaceutical manufacturing capabilities. Additionally, the rising incidence of communicable diseases in densely populated regions is fueling consistent demand. Favorable regulatory reforms and the expansion of generic drug production in key markets across the region further support this sustained growth momentum.
India Antibiotics Market Overview
The market in India is expanding, driven by a large and densely populated patient base, as well as an increasing incidence of bacterial infections. Rapid urbanization and improvements in public healthcare delivery are enhancing access to essential medications. Furthermore, India's robust generic manufacturing sector enables high-volume production and competitive pricing, positioning the country as a major supplier and consumer in the global antibiotics market.
Europe Antibiotics Market Outlook
The antibiotics industry in Europe is projected to hold a substantial share in 2034 owing to its focus on antibiotic control, surveillance programs, and the development of innovative treatments. According to an April 2024 EU report, the EMA approved Emblaveo, a new antibiotic for treating drug-resistant Gram-negative bacterial infections, addressing critical treatment gaps for complex cases of abdominal, urinary, and pneumonia infections. It aims to reduce AMR-linked deaths, which are 35,000 annually in the EU. European healthcare systems highlight rational use of antibiotics, which helps manage resistance while maintaining effective treatment protocols. Moreover, the region is home to several research-intensive companies and public health institutions actively contributing to antibiotic innovation and policy development. These factors collectively support the long-term stability and strength of the Europe antibiotics market.
Germany Antibiotics Market Assessment
The market growth in Germany is driven by strong regulatory oversight, emphasis on rational antibiotic use, and investments in research for innovative antimicrobial therapies. The country maintains high standards for infection control and pharmacovigilance, which support consistent demand for effective antibiotics. Additionally, collaboration between public health institutions and pharmaceutical companies promotes the development and availability of next-generation antibiotic solutions.
Key Players and Competitive Analysis
The antibiotics market is witnessing intensified competition, driven by strategic investments in R&D to combat antimicrobial resistance (AMR) and address latent demand in both developed markets and emerging markets. Major players such as Pfizer, Novartis, and generic manufacturers are leveraging technological advancements, including AI-driven drug discovery and mRNA platforms, to develop novel therapies. Disruptions and trends, including the rise of WHO-priority pathogens and regulatory incentives such as the U.S. Pasteur Act, are reshaping industry trends, with a focus on sustainable value chains and equitable access. Economic and geopolitical shifts, including increased AMR funding and strategic partnerships, drive revenue growth. Vendor strategies emphasize targeting high-burden infections while navigating supply chain disruptions in API production. Future development strategies highlight biologics and phage therapy as high-growth segments, though small and medium-sized businesses face barriers in scaling innovation. Expert insights highlight the need for expansion opportunities in neglected tropical disease markets, where the total addressable market potential remains largely untapped.
A few major companies operating in the antibiotics industry include Astellas Pharma Inc.; AstraZeneca; Cipla; Fresenius Kabi AG; GSK plc; Hetero Healthcare Limited; Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Inc; Merck & Co., Inc.; Pfizer Inc.; and Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.
Key Players
- Astellas Pharma Inc.
- AstraZeneca
- Cipla
- Fresenius Kabi AG
- GSK plc
- Hetero Healthcare Limited
- Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Inc
- Merck & Co., Inc.
- Pfizer Inc.
- Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.
Antibiotics Industry Developments
- November 2024: Zai Lab and Pfizer entered a strategic collaboration to commercialize the antibacterial drug XACDURO (sulbactam-durlobactam) in Mainland China. Pfizer’s affiliates will lead commercialization efforts, leveraging their anti-infective expertise to enhance patient access through 2028.
- September 2024: HCAH, a provider of out-of-hospital healthcare solutions, announced its partnership with Aroa Antibiotics to develop medical and surgical products for soft tissue regeneration and complex wound healing.
- May 2024: Sanofi announced an investment of more than €1 billion to establish new bioproduction capacity at its French sites.
Antibiotics Market Segmentation
By Drug Class Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- Cephalosporin
- Penicillin
- Fluoroquinolone
- Macrolides
- Carbapenems
- Aminoglycosides
- Sulfonamides
- 7-ACA
- Others
By Type Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- Branded Antibiotics
- Generic Antibiotics
By Action Mechanism Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- Cell Wall Synthesis Inhibitors
- Protein Synthesis Inhibitors
- DNA Synthesis Inhibitors
- RNA Synthesis Inhibitors
- Mycolic Acid Inhibitors
- Others
By Regional Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- North America
- U.S.
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- UK
- Italy
- Spain
- Netherlands
- Russia
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- Malaysia
- South Korea
- Indonesia
- Australia
- Vietnam
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Middle East & Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Israel
- South Africa
- Rest of Middle East & Africa
- Latin America
- Mexico
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
Antibiotics Market Report Scope
|
Report Attributes |
Details |
|
Market Size in 2024 |
USD 53.05 Billion |
|
Market Size in 2025 |
USD 54.94 Billion |
|
Revenue Forecast by 2034 |
USD 75.80 Billion |
|
CAGR |
3.64% from 2025 to 2034 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Historical Data |
2020–2023 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025–2034 |
|
Quantitative Units |
Revenue in USD Billion and CAGR from 2025 to 2034 |
|
Report Coverage |
Revenue Forecast, Competitive Landscape, Growth Factors, and Industry Trends |
|
Segments Covered |
|
|
Regional Scope |
|
|
Competitive Landscape |
|
|
Report Format |
|
|
Customization |
Report customization as per your requirements with respect to countries, regions, and segmentation. |
FAQ's
The global market size was valued at USD 53.05 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow to USD 75.80 billion by 2034.
The global market is projected to register a CAGR of 3.64% during the forecast period.
North America dominated the market in 2024.
A few of the key players in the market are Astellas Pharma Inc.; AstraZeneca; Cipla; Fresenius Kabi AG; GSK plc; Hetero Healthcare Limited; Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Inc; Merck & Co., Inc.; Pfizer Inc.; and Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.
The generic antibiotics dominated the revenue share of 81.48% in 2024.
The RNA synthesis inhibitors segment is expected to witness fastest growth during the forecast period.
