
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Market Size, Share, Trends, & Industry Analysis Report
By Type, By Treatment (Chemotherapy, Targeted Therapy, Immunotherapy, and Others), By Distribution Channel, and By Region – Market Forecast, 2025–2034
- Published Date:Jul-2025
- Pages: 129
- Format: PDF
- Report ID: PM6101
- Base Year: 2024
- Historical Data: 2020-2023
Overview
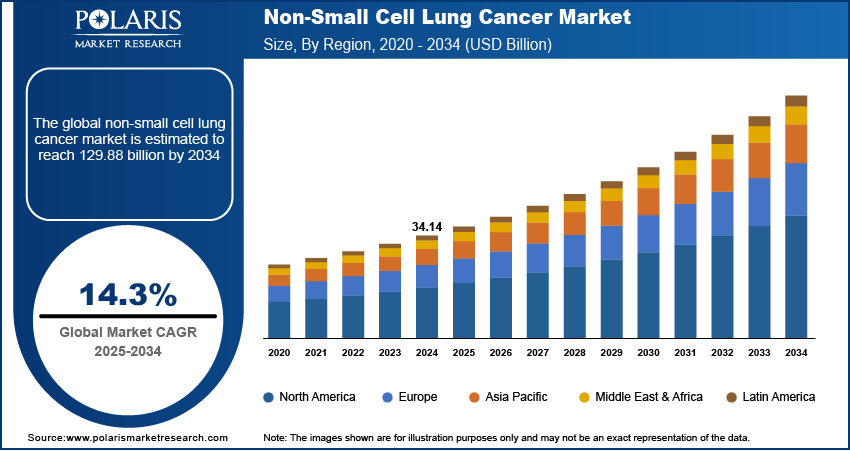
The global non-small cell lung cancer market size was valued at USD 34.14 billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 14.3% from 2025–2034. Rising global incidence of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), coupled with growing adoption of liquid biopsies and multiplexed platforms is enabling non-invasive monitoring in NSCLC.
Key Insights
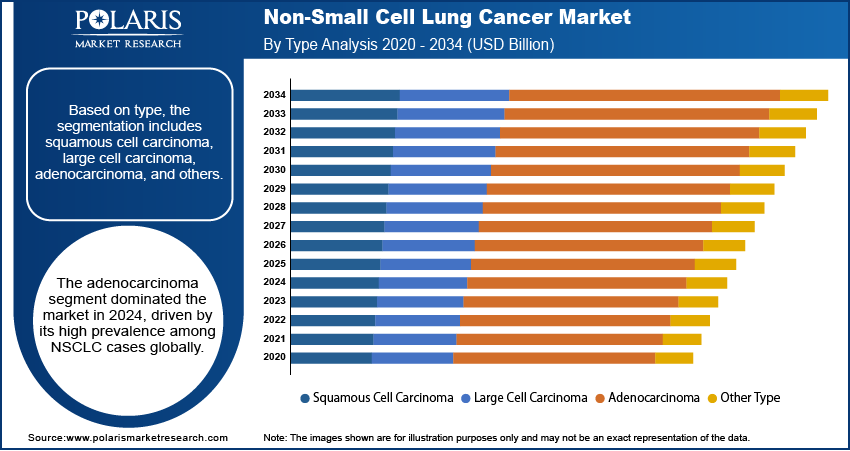
- The adenocarcinoma segment dominated the market share in 2024.
- The large cell carcinoma segment is projected to grow at the fastest CAGR, driven by late-stage diagnosis, reliance on combination therapies and rising use of NGS-guided treatments.
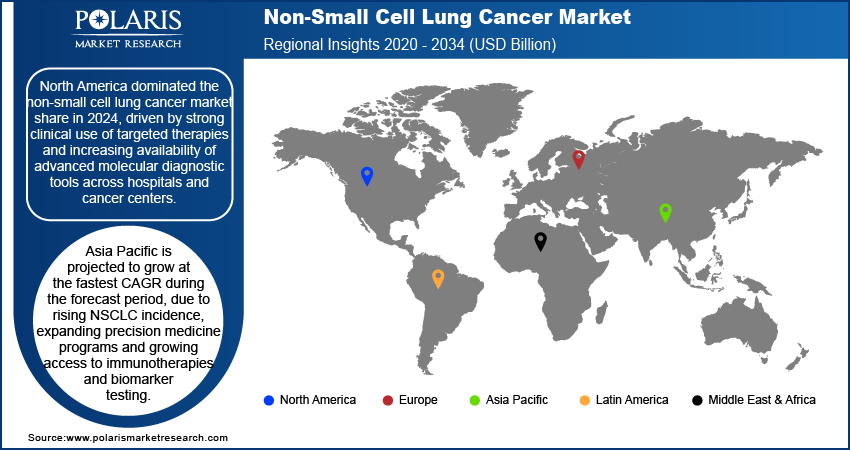
- The North America non-small cell lung cancer market dominated the global market share in 2024.
- The U.S. non-small cell lung cancer market held the largest regional share of the North America market in 2024, fueled by early adoption of targeted therapies and strong access to companion diagnostic services.
- The market in Asia Pacific is projected to grow at the fastest CAGR during the forecast period, owing to rising NSCLC incidence and growing access to immunotherapy and precision treatment platforms.
- The China non-small cell lung cancer market is expanding steadily, driven by increasing public investment in oncology drug development, domestic production of targeted therapies and expansion of genomic testing infrastructure.
Market Dynamics
- Rising global incidence of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is accelerating the demand for molecular diagnostics, targeted therapies, and mutation-specific assays to enable early detection and personalized treatment planning.
- Growing clinical adoption of liquid biopsies and multiplexed testing platforms is supporting non-invasive monitoring of treatment response and detection of actionable genetic alterations in NSCLC patients.
- Increasing investments in biomarker discovery and oncology research are creating opportunities for the development of next-generation companion diagnostics with improved accuracy and faster turnaround times.
- High costs associated with advanced diagnostic tools and limited access to genomic testing infrastructure in low- and middle-income countries remain key challenges for widespread adoption of precision oncology in NSCLC care.
Market Statistics
- 2024 Market Size: USD 34.14 billion
- 2034 Projected Market Size: USD 129.88 billion
- CAGR (2025-2034): 14.3%
- North America: Largest market in 2024
To Understand More About this Research: Request a Free Sample Report
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is the most prevalent form of lung cancer, accounting for approximately 80% to 85% of all diagnosed cases as reported by the American Cancer Society. Advances in diagnostic imaging, biomarker testing and histological subtyping significantly improved the early detection and classification of NSCLC. These tools enable the identification of genetic mutations such as EGFR, ALK, ROS1, and KRAS, which are critical in determining targeted therapy options. For instance, in May 2024, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved a new companion diagnostic test for KRAS G12C mutations, expanding access to precision therapies for NSCLC patients. Such developments are enhancing the clinical adoption of molecular diagnostics across oncology care settings. The growing focus on early-stage detection and biomarker-driven treatment strategies is accelerating the use of advanced diagnostics in NSCLC management.
The NSCLC treatment landscape is undergoing a rapid transformation driven by the increasing use of targeted therapies and immunotherapies. The introduction of checkpoint inhibitors, tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) and antibody-drug conjugates improved survival outcomes in patients with advanced and metastatic NSCLC. Pharmaceutical companies are investing in clinical trials and biomarker validation studies to expand the applicability of existing therapies across broader patient groups. Additionally, the growing advancements in combination regimens and personalized treatment plans are creating opportunities for drug developers to launch novel therapeutics with improved efficacy and safety profiles. This shift shows the global healthcare industry’s focus on precision oncology, driven by favorable regulatory pathways, rising cancer burden and increasing patient access to molecular testing services.
The growing complexity of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) treatment protocols is driving the development of advanced companion diagnostics and mutation-specific assays. Clinical laboratories are rapidly prioritizing speed, sensitivity and standardization to support timely therapeutic decision-making. This trend is fueling the adoption of multiplexed testing platforms and liquid biopsy-based assays that enable non-invasive detection of circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) and multiple genetic alterations from a single sample. The shift toward data-driven personalized oncology is pushing developers to introduce diagnostics integrated with AI-based interpretation tools to improve result accuracy and clinical relevance. As an example, in April 2025, Roche announced that its AI-enabled digital pathology algorithm received U.S. FDA Breakthrough Device Designation to support clinical decision-making in non-small cell lung cancer. This solution leverages artificial intelligence (AI) to analyze tissue samples and identify key biomarkers, aiming to enhance diagnostic accuracy and enable personalized treatment strategies for NSCLC patients. These advancements are streamlining diagnostic workflows and accelerating the transition toward decentralized and point-of-care testing models in NSCLC care.
Drivers & Opportunities
Rapidly Rising Cases of NSCLC Globally: The global burden of non-small cell lung cancer is increasing due to factors such as aging populations, high tobacco consumption and environmental exposures. The American Cancer Society estimates that around 226,650 new lung cancer cases will be reported in the U.S. by the end of 2025. A large share of these cases will be non-small cell lung cancer, which is also expected to account for most of the 124,730 projected deaths. NSCLC accounts for the majority of lung cancer cases, thus raising the demand for early detection and treatment solutions. With incidence rates rising across developed and emerging economies, healthcare systems are expanding oncology services to manage growing patient volumes. This shift is driving investments in molecular diagnostics, advanced imaging technologies and targeted therapies while driving the market growth. In addition, growing national cancer screening programs and supportive policy initiatives are promoting earlier diagnosis, further accelerating the market expansion for NSCLC-related treatments.
Rapidly Expanding Biopharmaceutical R&D and Drug Discovery: The growing clinical reliance on liquid biopsies and multiplexed testing platforms is transforming NSCLC diagnosis and treatment planning. These tools allow non-invasive and real-time detection of circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) and multiple genetic mutations from a single blood sample, reducing the need for invasive tissue biopsies. This approach enhances patient compliance and supports rapid, personalized treatment decisions. Healthcare providers are adopting these platforms to monitor disease progression and therapeutic resistance more efficiently. The ability to conduct comprehensive genomic profiling through high-throughput and automated systems is improving workflow efficiency and expanding access to precision diagnostics in hospital and reference laboratory settings.
Segmental Insights
Type Analysis
Based on type, the segmentation includes squamous cell carcinoma, large cell carcinoma, adenocarcinoma, and other types. The adenocarcinoma segment dominated the market in 2024, driven by its high prevalence among NSCLC cases globally. Adenocarcinoma is the most common histological subtype, particularly among non-smokers and in younger populations, which expands its patient base. This form of NSCLC is generally diagnosed at an advanced stage, fueling higher demand for advanced diagnostics and targeted therapies. Increasing availability of biomarker-driven treatments such as EGFR and ALK inhibitors is further driving the growth of this segment. The rising early-stage detection through screening programs is contributing to the dominance of the adenocarcinoma segment.
The large cell carcinoma segment is projected to grow at the fastest CAGR during the forecast period, due to its aggressive nature and the need for rapid clinical intervention. This type of lung cancer is less common than adenocarcinoma, however, large cell carcinoma is generally diagnosed late, which increases the reliance on combination therapies and innovative treatment modalities. The segment is witnessing growing interest in molecular profiling to identify actionable mutations. Rising research on immune checkpoint inhibitors and next-generation sequencing (NGS)-guided treatment strategies is expected to further accelerate market growth for large cell carcinoma-related therapeutics.
Treatment Analysis
By treatment, the targeted therapy segment dominated the market in 2024, due to the known driver mutations such as EGFR, ALK, and ROS1. Increasing adoption of companion diagnostics is enabling physicians to personalize treatments and improve response rates. The availability of novel tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) and resistance-specific therapies is enhancing progression-free survival in advanced-stage patients. Rising strategic collaborations between diagnostics and pharmaceutical companies are improving drug accessibility. Thus, this approach is widely adopted in oncology guidelines, making it a suitable effective treatment option in clinical practice.
The immunotherapy segment is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR during the forecast period, due to its ability to significantly extend survival in advanced-stage NSCLC patients. For instance, in April 2025, Akeso announced that its PD-1/CTLA-4 bispecific antibody, cadonilimab received marketing approval in China for the treatment of recurrent or metastatic cervical cancer patients who have failed prior platinum-based chemotherapy. This marks the world’s first approved dual immune checkpoint inhibitor bispecific antibody, reflecting a major advancement in cancer immunotherapy. In addition, the rising approval and expansion of immune checkpoint inhibitors targeting PD-1/PD-L1 transformed the treatment landscape. Moreover, the increasing biomarker testing to determine immunotherapy eligibility is further accelerating its adoption, as it enables precise patient stratification and enhances treatment efficacy. Additionally, favorable clinical outcomes and ongoing trials evaluating combination therapies are expanding its use across multiple treatment lines.
Distribution Channel Analysis
Based on distribution channel, the segmentation includes a hospital pharmacy, a drug store and retail pharmacy, and online pharmacy. The hospital pharmacy segment accounted for the highest market share in 2024. This is due to their role in administering complex treatments such as immunotherapy and combination regimens. Most targeted and biologic therapies require physician oversight and infusion facilities, which are readily available in hospitals. Additionally, hospitals are better equipped for pharmacovigilance and adverse event monitoring for newly approved oncology drugs. In addition, the integration of molecular diagnostic services with oncology care in hospital networks fuels timely treatment decisions, while driving hospital pharmacies as the dominant distribution point for NSCLC drugs.
The online pharmacy segment is projected to grow at the fastest pace during the forecast period, due to improving digital health access and rising patient preference for home delivery of medications. The expansion of e-pharmacy platforms is improving patient access to oral targeted therapies and supportive medications. Rising adoption of telemedicine and e-prescriptions is streamlining the purchase of oncology drugs for patients in remote or underserved regions. Online pharmacies are offering competitive pricing, convenience and adherence-support programs, making them a viable channel for chronic NSCLC treatment management.
Regional Analysis
North America non-small cell lung cancer market dominated the global market in 2024. This is driven by the high prevalence of EGFR, ALK, and KRAS mutations among lung cancer patients, which supports the clinical demand for companion diagnostics and mutation-specific therapies. Additionally, strong reimbursement frameworks and early FDA approvals for next-generation immunotherapies are accelerating the adoption of advanced treatment options across oncology centers in the U.S. and Canada.
The US Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Market Insight
The US held a dominating market share in the North America non-small cell lung cancer landscape in 2024, driven by the widespread availability of molecular testing services and early adoption of FDA-approved targeted therapies. As an example, in May 2025, AbbVie announced that the U.S. FDA approved EMRELIS (telisotuzumab vedotin-tkll) for adults with previously treated advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) exhibiting high c-Met protein overexpression. This approval is based on data demonstrating meaningful clinical benefit in patients with limited treatment options. Moreover, the rising investments in cancer genomics and a strong pipeline of immuno-oncology agents are further enhancing treatment access across academic hospitals and cancer research centers.
Asia Pacific Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Market
The market in Asia Pacific is projected to grow at the fastest CAGR during the forecast period. This growth is witnessed due to the rising incidence of NSCLC across China, Japan, and South Korea, driven by government-backed lung cancer screening programs. Moreover, the growing availability of domestic biosimilars and the rapid expansion of oncology-focused clinical trials are improving patient access to targeted therapies and immunotherapies across the region.
China Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Market Overview
The market in China is expanding due to the government’s “Healthy China 2030” initiative, which prioritizes early cancer detection and access to precision therapies. In addition, the increasing inclusion of innovative c drugs in the National Reimbursement Drug List (NRDL) is expanding the reach of targeted and immune-based treatments across public and private healthcare institutions. Furthermore, the growing expansion of NSCLC product portfolios in China by leading companies to address HER2-mutant metastatic cases through HER2-directed therapies is driving market growth. In October 2024, AstraZeneca and Daiichi Sankyo’s Enhertu received approval in China as the first HER2-directed therapy for patients with HER2-mutant metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). This approval aims to boost significant advancement, providing a targeted treatment option for a subset of NSCLC patients with limited prior therapies.
Europe Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Market
The non-small cell lung cancer landscape in Europe is projected to hold a substantial share in 2034. This is owing to the increasing adoption of immuno-oncology drugs under public health insurance schemes in countries such as Germany, the UK, France, Spain, and Switzerland. For instance, in April 2025, Novocure’s Optune Lua received CE Mark approval for the treatment of metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) in combination with immune checkpoint inhibitors. This approval enables the company to commercialize the therapy across the European Economic Area for eligible patients. Additionally, the integration of molecular profiling into national cancer treatment protocols is expanding the use of targeted therapies and biomarker-driven treatment plans across major European healthcare systems.
Key Players & Competitive Analysis Report
The non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is moderately competitive, with major players focusing on expanding their oncology portfolios through targeted therapies, immunotherapies and companion diagnostics. Key companies are prioritizing clinical collaborations, regulatory approvals and biomarker-driven innovations to strengthen market presence. The growing business strategies include accelerating drug development through precision oncology trials, enhancing access via strategic licensing and expanding into emerging markets with high NSCLC burden. Additionally, rising partnerships with diagnostic firms and investments in liquid biopsy platforms are supporting integrated treatment solutions, which in turn drive long-term competitiveness in the global NSCLC landscape.
Major companies operating in the non-small cell lung cancer industry include Roche Holding AG, AstraZeneca PLC, Merck & Co., Inc., Bristol-Myers Squibb Company, Pfizer Inc., Eli Lilly and Company, Novartis AG, Johnson & Johnson, Amgen Inc., Beigene Ltd., Exelixis Inc., and Mirati Therapeutics Inc.
Key Players
- Amgen Inc.
- AstraZeneca PLC
- Beigene Ltd.
- Bristol-Myers Squibb Company
- Eli Lilly and Company
- Exelixis Inc.
- Johnson & Johnson
- Merck & Co., Inc.
- Mirati Therapeutics Inc.
- Novartis AG
- Pfizer Inc.
- Roche Holding AG
Industry Developments
- June 2025: AstraZeneca’s DatroWay received FDA approval in the U.S. for the treatment of adult patients with EGFR exon 20 insertion-mutated non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) whose disease progressed on or after platinum-based chemotherapy. This approval aims at a significant advancement in targeted therapies for a subset of NSCLC patients with limited treatment options.
- May 2025: NeoGenomics launched a new c-MET CDx assay designed to support treatment decisions in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). This companion diagnostic aims to identify MET gene alterations, helping clinicians determine eligibility for targeted therapies.
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Market Segmentation
By Type Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- Large Cell Carcinoma
- Adenocarcinoma
- Other Type
By Treatment Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- Chemotherapy
- Targeted Therapy
- Immunotherapy
- Others
By Distribution Channel Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- Hospital Pharmacy
- Drug Store and Retail Pharmacy
- Online Pharmacy
By Regional Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- UK
- Italy
- Spain
- Netherlands
- Russia
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- Malaysia
- South Korea
- Indonesia
- Australia
- Vietnam
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Middle East & Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Israel
- South Africa
- Rest of Middle East & Africa
- Latin America
- Mexico
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Market Report Scope
|
Report Attributes |
Details |
|
Market Size in 2024 |
USD 34.14 Billion |
|
Market Size in 2025 |
USD 38.88 Billion |
|
Revenue Forecast by 2034 |
USD 129.88 Billion |
|
CAGR |
14.3% from 2025 to 2034 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Historical Data |
2020–2023 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025–2034 |
|
Quantitative Units |
Revenue in USD Billion and CAGR from 2025 to 2034 |
|
Report Coverage |
Revenue Forecast, Competitive Landscape, Growth Factors, and Industry Trends |
|
Segments Covered |
|
|
Regional Scope |
|
|
Competitive Landscape |
|
|
Report Format |
|
|
Customization |
Report customization as per your requirements with respect to countries, regions, and segmentation. |
FAQ's
The global market size was valued at USD 34.14 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow to USD 129.88 billion by 2034.
The global market is projected to register a CAGR of 14.3% during the forecast period.
North America dominated the market in 2024, due to high adoption of targeted therapies and early integration of companion diagnostics across oncology care facilities.
A few of the key players in the market are Roche Holding AG, AstraZeneca PLC, Merck & Co., Inc., Bristol-Myers Squibb Company, Pfizer Inc., Eli Lilly and Company, Novartis AG, Johnson & Johnson, Amgen Inc., BeiGene Ltd., Exelixis Inc., and Mirati Therapeutics Inc.
The adenocarcinoma segment dominated the market in 2024, driven by its high prevalence and increasing availability of mutation-specific therapies across clinical settings.
The online pharmacy segment is projected to grow at the fastest CAGR, driven by rising telemedicine adoption and growing demand for home-delivered NSCLC medications.
