
South Korea Geothermal Energy Market Size, Share, Trends, Industry Analysis Report
By Technology (Flash Steam, Dry Steam, Binary Cycle Power Plants), By Power Output, By Application, By Region – Market Forecast, 2025–2034
- Published Date:Aug-2025
- Pages: 129
- Format: PDF
- Report ID: PM6190
- Base Year: 2024
- Historical Data: 2020-2023
Overview
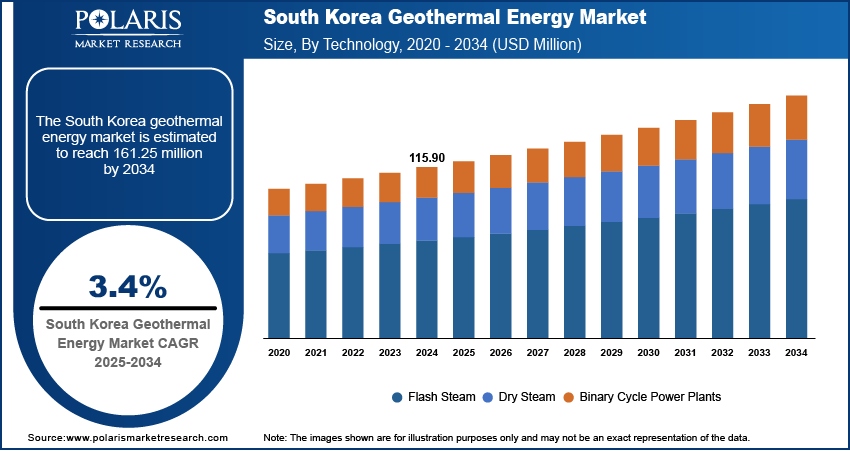
The South Korea geothermal energy market size was valued at USD 115.90 million in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 3.4% from 2025 to 2034. The market growth is driven by urban development and smart city projects and rising adoption in the industrial and commercial sector.
Key Insights
- In 2024, the binary cycle power plants segment dominated with the largest share. The technology is ideal for the country’s geothermal conditions, where moderate to low-temperature geothermal resources are more common.
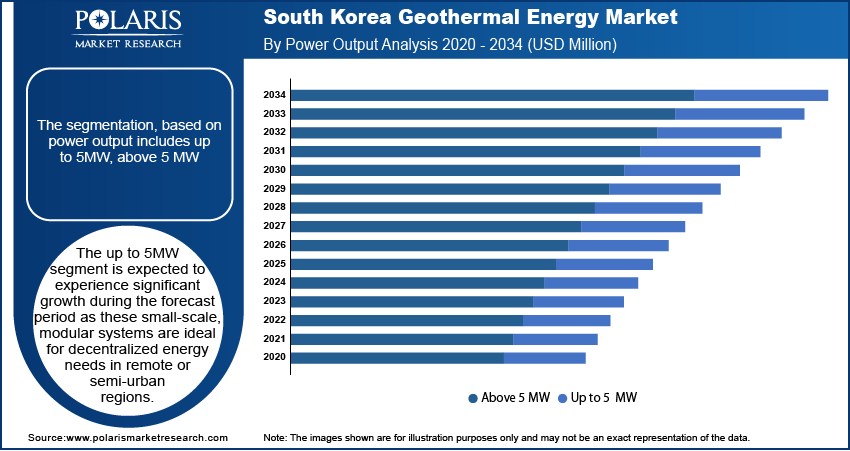
- The up to 5MW segment is expected to experience significant growth during the forecast period as these small-scale, modular systems are ideal for decentralized energy needs in remote or semi-urban regions.
Industry Dynamics
- Urban development and smart city projects drive the adoption of geothermal energy.
- Increasing adoption in the industrial and commercial sector is fueling the industry growth.
- Advance technology is making geothermal energy more practical and affordable.
- High upfront capital costs for exploration, drilling, and plant setup restrain the industry growth.
Market Statistics
- 2024 Market Size: USD 115.90 million
- 2034 Projected Market Size: USD 161.25 million
- CAGR (2025–2034): 3.4%
Geothermal energy is heat derived from the Earth’s interior, generated by the natural decay of radioactive elements in the Earth’s core, mantle, and crust. It can be harnessed to produce electricity, provide direct heating, or support industrial processes. As a renewable and reliable energy source, geothermal offers constant, low-emission power with minimal environmental impact.
South Korea is aiming stable energy supply while reducing greenhouse gas emissions as energy consumption continues to rise due to industrial growth and urbanization. Geothermal energy is a clean, reliable, and continuous energy source that can operate 24/7 regardless of weather. This makes it especially valuable for meeting base-load power needs. Geothermal energy is gaining attention as a sustainable solution that can help meet South Korea’s growing energy demand in an environmentally friendly way with rising public awareness about climate change and the need for cleaner air, thereby driving the growth.
South Korea is investing in advanced geothermal technologies, including Enhanced Geothermal Systems (EGS), which allow energy generation even in areas with less naturally occurring hot water. Geothermal systems are becoming more efficient and economically viable with continuous progress in drilling, heat extraction, and monitoring technologies. Local research institutions and partnerships with global technology providers are helping develop tailored solutions suitable for Korea’s unique geology. These advancements are making it possible to expand geothermal power generation beyond traditional locations, increasing the potential and encouraging wider adoption across the country.
Drivers & Opportunities
Urban Development and Smart City Projects: Geothermal energy is being integrated into building designs and community energy systems as South Korea develops smart cities and eco-friendly urban zones. Cities such as Sejong and Busan are incorporating geothermal heating and cooling into new developments to reduce emissions and energy costs. These urban projects include decentralized energy systems, and geothermal plays a key role due to its reliability and minimal environmental footprint. The demand for geothermal technology grows as more smart and green infrastructure projects are launched across the country.
Industrial and Commercial Sector Adoption: The industrial and commercial sectors in South Korea are increasingly adopting geothermal systems for heating and cooling due to their energy efficiency and cost savings over time. Facilities such as factories, schools, hospitals, and office buildings are turning to geothermal heat pumps to reduce operational costs and meet environmental regulations. Geothermal systems offer long-term economic and environmental benefits with rising electricity prices and carbon reduction targets. This growing demand in non-power sectors is opening up new opportunities, supporting the overall development of geothermal infrastructure and services across South Korea.
Segmental Insights
Technology Analysis
The South Korea geothermal energy market segmentation, based on technology, includes flash steam, dry steam, and binary cycle power plants. In 2024, the binary cycle power plants segment dominated with the largest share. The technology is ideal for the country’s geothermal conditions, where moderate to low-temperature geothermal resources are more common. Binary cycle plants efficiently generate electricity even from lower-temperature reservoirs, making them a practical fit for South Korea’s geology. These systems are further compact and environmentally friendly, aligning well with the country’s sustainability goals. Additionally, South Korea continues to explore more geothermal fields and prioritizing clean energy further driving the segment growth.
Power Output Analysis
The South Korea geothermal energy market segmentation, based on power output, includes up to 5MW and above 5 MW. The up to 5MW segment is expected to experience significant growth during the forecast period as these small-scale, modular systems are ideal for decentralized energy needs in remote or semi-urban regions. They can be installed near consumption points, such as industrial parks, schools, or residential zones, helping reduce transmission losses and energy costs. These compact geothermal units are becoming more attractive with the government promoting distributed energy systems and smart city projects. Their flexibility, lower installation footprint, and ability to supply stable energy make them well-suited to South Korea’s evolving energy landscape, thereby driving the segment growth.
Key Players and Competitive Analysis
The competitive landscape of the South Korea geothermal energy market is shaped by a mix of global technology providers and engineering firms offering advanced solutions tailored to the country's unique geothermal conditions. Key players include Ansaldo Energia, General Electric, and Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, all of which bring extensive expertise in turbine and power plant technologies. Ormat Technologies and Turboden S.p.A. are prominent for their binary cycle systems, which are well-suited to South Korea's moderate-temperature geothermal resources. Toshiba Corporation and TAS Energy contribute with scalable and modular energy solutions, while Atlas Copco Group supports drilling and surface operations with precision equipment. These companies compete through innovation, partnerships with Korean energy firms, and localization of technologies to align with national renewable energy goals. The focus is increasingly on efficient, small- to mid-scale systems, and environmentally friendly technologies that meet government sustainability targets and support the growing demand for distributed energy systems.
Key Players
- Ansaldo Energia
- Atlas Copco Group
- General Electric
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
- Ormat Technologies
- TAS Energy
- Toshiba Corporation
- Turboden S.p.A.
Geothermal Energy Industry Developments
In November 2023, Seoul officially launched its ambitious geothermal plan, aiming to expand heating and cooling capacity from 278 MW to 1 GW by 2030, targeting major facilities and public buildings while offering incentives and R&D support to boost private sector participation.
South Korea Geothermal Energy Market Segmentation
By Technology Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2020–2034)
- Flash Steam
- Dry Steam
- Binary Cycle Power Plants
By Power Output Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2020–2034)
- Up to 5MW
- Above 5 MW
By Application Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2020–2034)
- Residential
- Commercial
- Industrial
South Korea Geothermal Energy Market Report Scope
|
Report Attributes |
Details |
|
Market Size in 2024 |
USD 115.90 Million |
|
Market Size in 2025 |
USD 119.71 Million |
|
Revenue Forecast by 2034 |
USD 161.25 Million |
|
CAGR |
3.4% from 2025 to 2034 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Historical Data |
2020–2023 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025–2034 |
|
Quantitative Units |
Revenue in USD Million and CAGR from 2025 to 2034 |
|
Report Coverage |
Revenue Forecast, Competitive Landscape, Growth Factors, and Industry Trends |
|
Segments Covered |
|
|
Competitive Landscape |
|
|
Report Format |
|
|
Customization |
Report customization as per your requirements with respect to countries, regions, and segmentation. |
FAQ's
The market size was valued at USD 115.90 million in 2024 and is projected to grow to USD 161.25 million by 2034.
The market is projected to register a CAGR of 3.4% during the forecast period.
A few of the key players in the market are Ansaldo Energia, Atlas Copco Group, General Electric, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ormat Technologies, TAS Energy, Toshiba Corporation, and Turboden S.p.A.
The binary cycle power plant segment dominated the market share in 2024.
The up to 5 MW segment is expected to witness the significant growth during the forecast period.
