
Ultra-Thin Solar Cells Market Size, Share, Trend, Industry Analysis Report
By Material (Cadmium Telluride, Copper Indium Gallium Selenide, Perovskite Solar Cell), By End Use, By Region – Market Forecast, 2025–2034
- Published Date:Jun-2025
- Pages: 129
- Format: PDF
- Report ID: PM5828
- Base Year: 2024
- Historical Data: 2020-2023
Market Overview
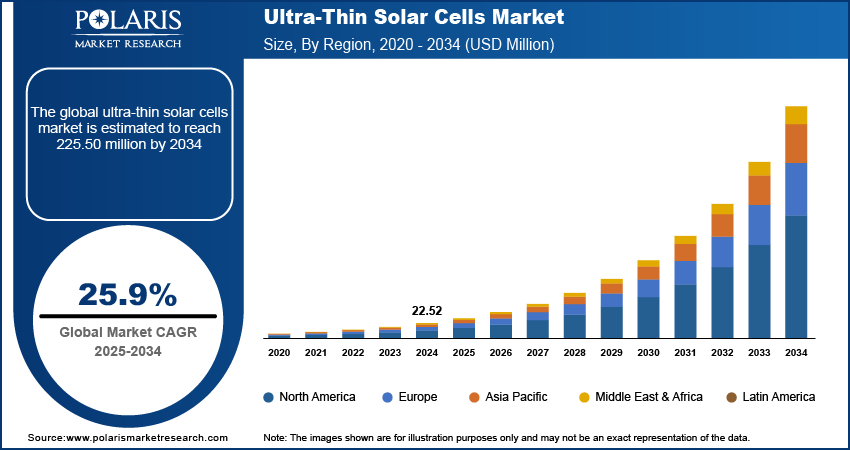
The global ultra-thin solar cells market size was valued at USD 22.52 million in 2024 and is projected to register a CAGR of 25.9% from 2025 to 2034. Ultra-thin solar cells offer portability and flexibility, making them ideal for use in consumer electronics, wearables, and off-grid applications, driving overall market growth.
The market refers to the segment of the solar energy industry focused on developing and commercializing ultra-thin solar cells that are significantly thinner than conventional photovoltaic (PV) cells, often just a few micrometers or even nanometers thick. These cells are typically made from advanced materials such as amorphous silicon (a-Si), CIGS (Copper Indium Gallium Selenide), perovskite, or organic PV materials. Due to their lightweight, flexible, and semi-transparent properties, ultra-thin solar cells are ideal for building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV), wearable electronics, portable chargers, IoT devices, and automotive applications, where traditional rigid panels are unsuitable. Innovations in material science are improving efficiency and lowering production costs, accelerating the commercialization and scalability of ultra-thin solar technologies.
To Understand More About this Research: Request a Free Sample Report
Ultra-thin solar cells provide sustainable power sources for sensors, wearables, and IoT devices, supporting the expansion of connected ecosystems, which is fueling overall expansion. Additionally, global push toward clean energy and sustainability is encouraging investments in next-gen solar technologies, including ultra-thin variants. According to The International Trade Administration, global energy investments reached over USD 3 trillion for the first time in 2024, with around USD 2 trillion allocated to clean energy technologies and infrastructure.
Market Dynamics
Rising Demand for Lightweight & Flexible Solar Solutions
Rising interest in lightweight and flexible energy solutions is fueling demand for ultra-thin solar cells across a wide range of consumer and portable electronics. These cells can be integrated into surfaces where traditional rigid panels are unsuitable, such as on backpacks, windows, curved devices, and clothing. Their thin, bendable nature makes them ideal for wearables and compact off-grid systems where portability and weight are key concerns. Companies developing power solutions for remote sensors, travel gear, and outdoor electronics are increasingly turning to ultra-thin solar technology to meet compact energy needs. The demand is further supported by growing awareness of sustainable alternatives to battery power in mobile devices. As production methods improve and material costs fall, manufacturers are able to offer more durable and efficient versions of ultra-thin solar cells, making them an increasingly attractive option for small-scale, flexible energy generation in consumer markets.
Growing Adoption in Automotive and Aerospace Industries
Ultra-thin solar cells are gaining attention in the automotive and aerospace industries due to their lightweight structure and ability to conform to non-flat surfaces. The rise in electric vehicle adoption is driving demand for ultra-thin solar cells, as manufacturers seek lightweight, efficient power solutions to enhance vehicle range and sustainability. For instance, according to the International Trade Administration, in 2024, global electric vehicle (EV) sales surpassed 17 million units, achieving a market penetration of over 20%. This represents an increase of 3.5 million electric vehicles sold compared to 2023. In electric vehicles, these solar cells are used for auxiliary power functions such as battery support and powering interior systems, helping reduce overall grid dependency. Aerospace companies are adopting ultra-thin solar panels for drones, high-altitude aircraft, and satellites where every gram of weight impacts performance and cost. Their low-profile design allows easy integration without disrupting aerodynamics. These solar cells also support long-duration missions by generating power in remote and space environments. Continued advancements in efficiency and durability are expanding their applications, making ultra-thin solar technology an essential component in the push for energy independence and weight optimization across mobility sectors.

Segment Insights
Material Analysis
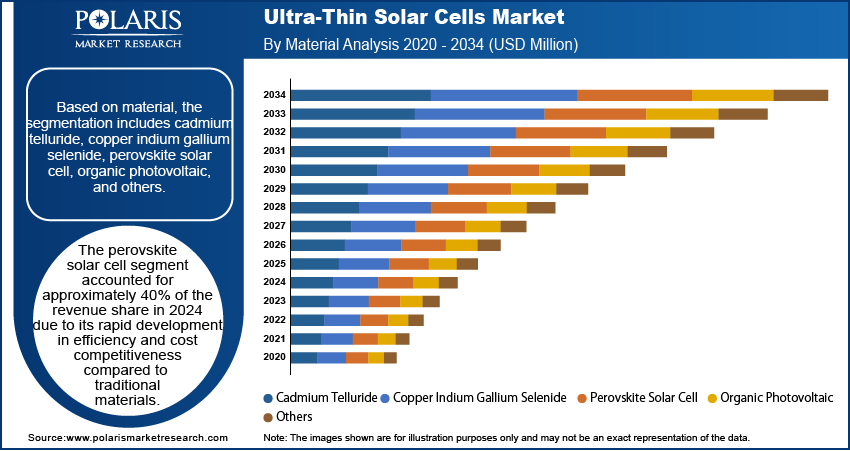
Based on material, the segmentation includes cadmium telluride, copper indium gallium selenide, perovskite solar cell, organic photovoltaic, and others. The perovskite segment accounted for approximately 40% of the revenue share in 2024 due to its rapid development in efficiency and cost competitiveness compared to traditional materials. This segment has gained attention for its lightweight properties and ease of production, which allow integration into flexible surfaces and portable power systems. Research breakthroughs have led to higher conversion efficiencies, making perovskite cells more suitable for large-scale and consumer-oriented applications. Oxford researchers developed a new ultra-thin perovskite solar cell with a record 27% conversion efficiency, marking a major step forward in high-performance, lightweight solar technology. This breakthrough could lead to more efficient and flexible solar solutions for various applications. The material’s compatibility with roll-to-roll manufacturing is driving scalable production, supporting growth in industrial use. In addition, the potential for tandem cell structures is attracting further investment, enhancing performance without significantly increasing cost or weight.
The copper indium gallium selenide segment is projected to grow significantly during the forecast period, supported by its excellent performance under low-light and high-temperature conditions. This characteristic makes CIGS solar cells ideal for off-grid, mobile, and vehicle-mounted applications. CIGS offers better aesthetic flexibility and can be deposited on lightweight substrates, expanding its usability across building-integrated photovoltaics and portable electronics. Increased demand from industries that prioritize form factor, such as aerospace and transportation, is creating new opportunities for this material. Improvements in thin-film deposition techniques are also making production more cost-efficient, further accelerating acceptance across multiple high-growth sectors.
End Use Analysis
Based on end use, the segmentation includes residential and commercial. In 2024, the commercial segment accounted for approximately 65% of the revenue share, driven by rising demand for lightweight, space-efficient solar installations across warehouses, office buildings, and industrial complexes. Businesses are prioritizing sustainability goals, and ultra-thin solar solutions offer an easier retrofit onto existing infrastructure without structural concerns. These systems are preferred for their quick installation, minimal maintenance, and design adaptability, especially for curved surfaces and lightweight roofs. The declining cost per watt and regulatory incentives encouraging solar adoption in commercial settings are further supporting widespread deployment. Flexible power systems also meet backup energy needs in off-grid operations, expanding their appeal in remote commercial zones.
The residential segment is expected to register a higher CAGR over the forecast period, driven by growing consumer demand for sleek, lightweight solar solutions that blend with building aesthetics. Homeowners are increasingly opting for ultra-thin solar cells to power small-scale systems, especially where traditional panels are not feasible. Rooftops with limited load-bearing capacity and off-grid rural setups benefit from the flexibility and low installation burden of these cells. Technological improvements in cell efficiency and material durability are making these systems more viable for daily home energy needs. Rising electricity prices and an increased focus on energy independence are motivating more individuals to explore thin-film solar as an alternative to conventional installations.
Regional Analysis
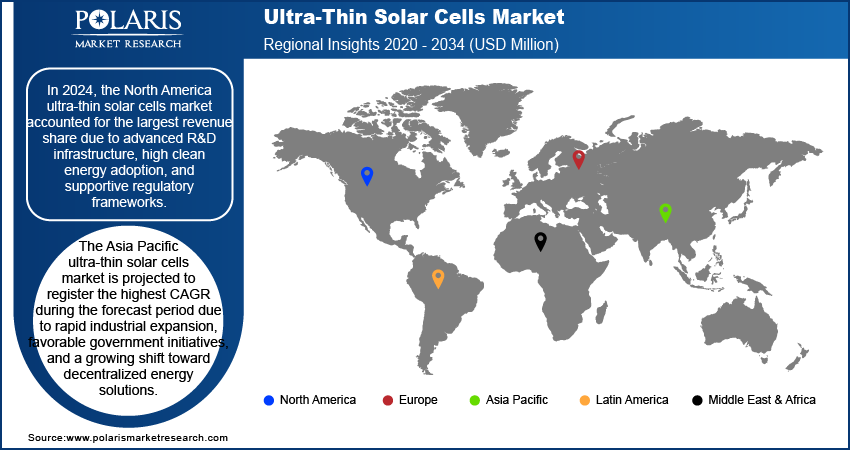
In 2024, the North America ultra-thin solar cells market accounted for the largest revenue share due to advanced R&D infrastructure, high clean energy adoption, and supportive regulatory frameworks. Strong investments in flexible photovoltaic materials from the government and private sectors are accelerating product innovation and deployment. The region’s focus on decentralized energy systems, especially in commercial and remote applications, aligns well with the benefits offered by lightweight, portable solar technologies. Market leaders are expanding production capacity and establishing partnerships with electronics, automotive, and construction companies to integrate ultra-thin solar components into a wide range of products and infrastructure. Consumer awareness around sustainable energy use also continues to rise.
US Ultra-Thin Solar Cells Market Trends
The US market led the regional landscape in 2024, supported by aggressive clean energy targets and demand for next-generation solar technologies in both urban and off-grid environments. Companies in the US are deploying thin-film systems across unconventional settings such as RVs, boats, and mobile workstations. The rise in smart building projects and energy-efficient construction is driving the adoption of lightweight, aesthetic solar solutions that minimize structural changes. Government-backed grants and tax credits are encouraging both startups and established firms to scale up production. The presence of key material suppliers, advanced research labs, and a growing ecosystem of solar technology integrators positions the US as a dominant player in the ultra-thin solar cells sector.
Asia Pacific Ultra-Thin Solar Cells Market Overview
The Asia Pacific market is projected to register the highest CAGR during the forecast period, due to rapid industrial expansion, favorable government initiatives, and a growing shift toward decentralized energy solutions. Countries in the region are investing in next-generation solar technologies to support rural electrification and reduce reliance on imported energy. Flexible and lightweight solar cells are ideal for compact urban settings and mobile infrastructure, which are increasingly common in fast-growing cities. Local manufacturing capabilities are improving, reducing costs and expanding accessibility for regional users. Demand from sectors such as transportation, consumer electronics, and temporary power solutions is rising steadily. Strong government backing, especially through subsidies and solar mandates, is creating a favorable environment for thin-film solar innovation and commercialization. For instance, the Indian government approved the PM Surya Ghar: Muft Bijli Yojana in February 2024 to boost solar rooftop capacity and enable households to produce their own electricity. The scheme, with a budget of approximately USD billion , is set to be implemented until 2027..
China Ultra-Thin Solar Cells Market Assessment
The China market accounted for the largest revenue share in Asia Pacific in 2024, fueled by strong domestic production, rising deployment across new infrastructure projects, and national goals tied to renewable energy expansion. The country has become a leader in solar material processing and thin-film technology development, enabling large-scale manufacturing of ultra-thin cells at competitive prices. Integration of solar technologies into commercial buildings, smart city projects, and transport networks is growing rapidly. Companies are increasingly adopting perovskite and CIGS-based solutions for their efficiency and adaptability in curved or lightweight applications. The strategic focus on clean energy exports and domestic grid modernization is further accelerating the adoption of flexible solar platforms that support varied use cases, both in rural and urban settings.
Europe Ultra-Thin Solar Cells Market Outlook
The market in Europe is experiencing steady growth, driven by rising demand for sustainable building materials and a strong regulatory push toward carbon neutrality. Thin-film solar technologies are gaining traction in applications where architectural integration, aesthetic design, and weight limitations matter. Building-integrated photovoltaics and transport-related solar applications are emerging as key areas of adoption. European innovation in organic and perovskite solar cell research is also supporting the commercialization of advanced ultra-thin technologies. Public and private funding for clean energy innovation is helping companies bring prototypes to market. Strict energy efficiency standards and a maturing solar market are encouraging the adoption of these newer, flexible formats to meet evolving energy performance goals across residential and commercial sectors.
Key Players and Competitive Analysis
The competitive landscape of the ultra-thin solar cells market is shaped by rapid technology advancements, evolving manufacturing methods, and increasing emphasis on lightweight and flexible energy solutions. Industry analysis shows the growing focus on expansion strategies such as joint ventures, licensing agreements, and collaborative R&D to accelerate product development and scale-up. Leading players are leveraging mergers and acquisitions to consolidate intellectual property and access innovative thin-film technologies, including perovskite and CIGS platforms. Strategic alliances between solar module producers and end-user industries such as automotive, aerospace, and consumer electronics are driving customized applications. Post-merger integration efforts often focus on streamlining material sourcing and enhancing production efficiency. Key dynamics are being influenced by innovations in printable photovoltaics, tandem cell structures, and roll-to-roll fabrication techniques. Companies are investing heavily in pilot-scale projects and commercial trials to validate performance in real-world conditions. The push toward energy-efficient, lightweight solar modules continues to define competitive strategies and product positioning across regions.
List of Key Companies
- Exeger Operations AB
- Fujikura Europe Ltd.
- G24 Power Ltd.
- Greatcell Solar Limited
- Konica Minolta Sensing Europe B.V.
- Merck KGaA
- Oxford PV
- Peccell Technologies, Inc.
- Sharp Corporation
- Solaronix SA
Ultra-Thin Solar Cells Industry Developments
In April 2025, Oxford PV and Trinasolar signed a patent licensing deal for the production and sale of perovskite-based PV products in China, including the right to sublicense. The agreement supports the growth of high-efficiency solar technology in one of the world’s largest renewable energy markets.
Ultra-Thin Solar Cells Market Segmentation
By Material Outlook (Revenue USD Million, 2020–2034)
- Cadmium Telluride
- Copper Indium Gallium Selenide
- Perovskite Solar Cell
- Organic Photovoltaic
- Others
By End Use Outlook (Revenue USD Million, 2020–2034)
- Residential
- Commercial
By Regional Outlook (Revenue USD Million, 2020–2034)
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- UK
- Italy
- Spain
- Netherlands
- Russia
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- Malaysia
- South Korea
- Indonesia
- Australia
- Vietnam
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Middle East & Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Israel
- South Africa
- Rest of Middle East & Africa
- Latin America
- Mexico
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
Ultra-Thin Solar Cells Market Report Scope
|
Report Attributes |
Details |
|
Market Size in 2024 |
USD 22.52 million |
|
Market Size in 2025 |
USD 28.33 million |
|
Revenue Forecast by 2034 |
USD 225.50 million |
|
CAGR |
25.9% from 2025 to 2034 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Historical Data |
2020–2023 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025–2034 |
|
Quantitative Units |
Revenue in USD million and CAGR from 2025 to 2034 |
|
Report Coverage |
Revenue Forecast, Competitive Landscape, Growth Factors, and Industry Trends |
|
Segments Covered |
|
|
Regional Scope |
|
|
Competitive Landscape |
|
|
Report Format |
|
|
Customization |
Report customization as per your requirements with respect to countries, regions, and segmentation. |
FAQ's
The global market size was valued at USD 22.52 million in 2024 and is projected to grow to USD 225.50 million by 2034.
The global market is projected to register a CAGR of 25.9% during the forecast period.
In 2024, North America accounted for the largest revenue share due to advanced R&D infrastructure, high clean energy adoption, and supportive regulatory frameworks.
A few of the key players are Exeger Operations AB; Fujikura Europe Ltd.; G24 Power Ltd.; Greatcell Solar Limited; Konica Minolta Sensing Europe B.V.; Merck KGaA; Oxford PV; Peccell Technologies, Inc.; Sharp Corporation; and Solaronix SA.
The perovskite solar cell segment accounted for approximately 40% of the revenue share in 2024, due to its rapid development in efficiency and cost competitiveness compared to traditional materials.
In 2024, the commercial segment accounted for approximately 65% of the revenue share, driven by rising demand for lightweight, space-efficient solar installations across warehouses, office buildings, and industrial complexes.
