
Japan Fuel Cell Market Size, Share, Trends, Industry Analysis Report
By Type (Solid Oxide Fuel Cells, Phosphoric Acid Fuel Cells, Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells), By Application – Market Forecast, 2025–2034
- Published Date:Sep-2025
- Pages: 120
- Format: PDF
- Report ID: PM6265
- Base Year: 2024
- Historical Data: 2020-2023
Market Overview
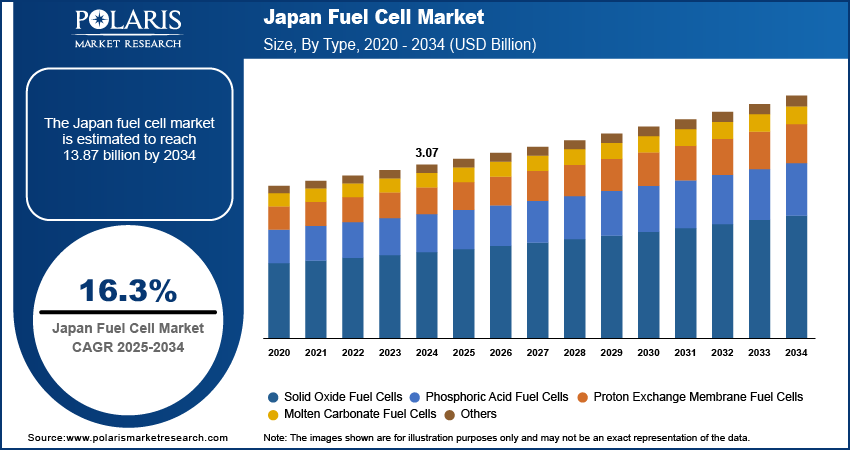
The Japan fuel cell market size was valued at USD 3.07 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to register a CAGR of 16.3% from 2025 to 2034. The landscape is driven by the country's need for energy independence and security. With most of its energy being imported, the shift to a hydrogen society is a key goal. Government policies and financial support also play a major role, promoting the use of fuel cells for residential power and in the transportation sector.
Key Insights
- In 2024, the proton exchange membrane fuel cells, or PEMFCs, dominated the Japan market in 2024. Their high efficiency and ability to be used in the transportation industry, especially for fuel cell electric vehicles (EVs), were the main reasons for their market position.
- The stationary segment held the largest share among all applications in 2024. This was a result of the successful use of fuel cells for combined heat and power systems in both residential and commercial buildings, which received strong support from government programs.
Industry Dynamics
- There is a strong push from the government to create a hydrogen society to improve energy security and reduce dependence on imported fossil fuels. This is supported by initiatives and funding for the development of hydrogen infrastructure and the adoption of fuel cell technology in different sectors.
- The country has also implemented various programs to encourage the use of fuel cells for residential combined heat and power systems. These programs, such as the Ene-Farm project, have led to the wide use of micro-CHP fuel cell systems in homes.
- Stricter regulations on carbon emissions and growing environmental concerns are another key driver. The focus on clean energy and decarbonization has accelerated the move toward zero-emission vehicles and other fuel cell applications.
Market Statistics
- 2024 Market Size: USD 3.07 billion
- 2034 Projected Market Size: USD 13.87 Billion
- CAGR (2025–2034): 16.3%
AI Impact on Japan Fuel Cell Market
- Japan invests heavily in fuel cell-based CHP systems for homes and businesses. AI enhances these systems by optimizing energy distribution and learning usage patterns.
- AI enables fuel cells to respond dynamically to grid demands, which assists in balancing supply and reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
- Japan expands its AI infrastructure, where fuel cells are being explored as backup power sources for data centers, offering clean and scalable energy.
- Rising focus on carbon neutrality across Japan drives AI-enabled fuel cell deployment to meet increasing electricity demands from AI systems.
A fuel cell devices convert chemical energy from a fuel, such as hydrogen, into electricity through an electrochemical process. Unlike a battery, a fuel cell device needs a constant supply of fuel to generate power. They produce very few emissions, with water and heat being the main byproducts, making them a clean and efficient energy source.
The development of a robust hydrogen supply chain drives the Japan fuel cell market growth. This includes the production, transportation, and storage of hydrogen. For the market to expand beyond early adopters, a reliable and accessible hydrogen infrastructure is essential. This allows for wider use in transportation and other applications, making fuel cell technology a more practical and convenient option for many consumers and businesses.
Another contributing factor is the increasing technological advancements that are improving the efficiency and durability of fuel cells. Research and development efforts are focused on making the systems more compact, lightweight, and cost-effective. These innovations are helping to solve some of the past challenges with fuel cells and are making them more competitive with other energy technologies.
Drivers and Trends
Strong Government Support and Policies: The Japanese government has demonstrated a strong commitment to promoting fuel cell technology and building a hydrogen-based society. This is a crucial growth factor, with a focus on both R&D and commercial adoption. The government has established strategic roadmaps and provided significant funding to support the development of hydrogen infrastructure and various fuel cell applications, including those for transportation and residential use. This sustained public-sector support creates a stable environment for private investment and innovation, which drives the market forward.
The Japanese government has implemented policies, subsidies, and incentives to promote hydrogen and fuel cell technologies as part of its clean energy transition. According to the Green Hydrogen Organization, the Japanese government passed the ‘Hydrogen Society Promotion Act’ in May 2024, under which subsidies of USD 20.85 billion are provided for the adoption of low-carbon hydrogen and the government’s 2023 Basic Hydrogen Strategy. Japan is investing in hydrogen infrastructure, fuel cell vehicles, and residential fuel cell systems with growing concerns over energy imports and the need to reduce carbon emissions. These initiatives are aligned with its long-term vision for a hydrogen-based society, fueling the adoption and commercialization of fuel cells across sectors.
Energy Security and Decarbonization: Japan's limited domestic energy resources have made it highly dependent on imported fossil fuels. This dependency poses risks to the nation's energy security and is a major driver behind the push for alternative energy sources such as hydrogen. Fuel cells, which use hydrogen to generate electricity with minimal emissions, are seen as a way to diversify the energy mix and reduce carbon footprints. This strategic shift aligns with global trends toward decarbonization and positions the country as a leader in clean energy technology.
The Japanese government has set a goal to achieve carbon neutrality by 2050 and a 46% reduction in greenhouse gas emissions by fiscal year 2030 (compared to 2013 levels). Fuel cell technology is seen as a crucial tool to help reach these ambitious targets. These targets demonstrate a clear long-term strategy to replace fossil fuels with hydrogen, which is a major factor fueling the Japan fuel cell market growth.
Segmental Insights
Type Analysis
Based on type, the segmentation includes solid oxide fuel cells, phosphoric acid fuel cells, proton exchange membrane fuel cells, molten carbonate fuel cells, and others. The proton exchange membrane fuel cells segment held the largest share in 2024. especially in the transportation sector. These fuel cells have a compact and lightweight design, high efficiency, and low operating temperature. These advantages make them ideal for use in fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs), as well as in small-scale stationary power generation. Japan has been a global leader in the development and deployment of FCEVs. The government's support for a hydrogen-based economy has further boosted the adoption of this technology. The growing demand for zero-emission vehicles and the need for portable power solutions have solidified the dominance of PEMFCs in the overall landscape.
The solid oxide fuel cells, or SOFC, segment is anticipated to register the highest growth rate during the forecast period. This is largely driven by their high efficiency and ability to use a variety of fuels, including synthetic natural gas and hydrogen. These characteristics make SOFCs well-suited for stationary power generation and combined heat and power, or CHP, systems for residential and commercial use. As the country continues to push for decentralizing its energy supply and improving energy efficiency, the demand for SOFCs in these applications is increasing. The ongoing research and development into new materials and designs are improving the durability and cost-effectiveness of these systems. This is helping them to gain traction and expand their presence in the market.
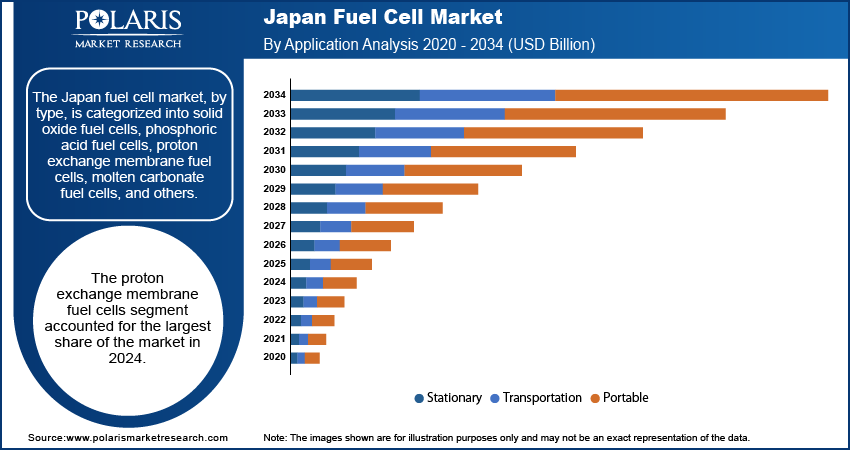
Application Analysis
Based on application, the segmentation includes stationary, transportation, and portable. The stationary segment held the largest share in 2024. This is mainly due to the long-standing and successful deployment of fuel cells in residential and commercial settings, particularly through government-backed programs. These initiatives have supported the widespread use of fuel cells for combined heat and power systems, or CHP, which provide both electricity and heating for buildings. The focus on energy efficiency and decentralizing power generation has made stationary fuel cells a favored solution. Their ability to offer a reliable, on-site power source with low emissions has made them a popular choice for homes and businesses across the country.
The transportation application is anticipated to register the highest growth rate during the forecast period. This is driven by the country's push toward a hydrogen society and its commitment to reducing carbon emissions from the transportation sector. As major automotive fuel cell companies continue to invest heavily in the development of fuel cell electric vehicles, or FCEVs, and as the hydrogen refueling infrastructure expands, the adoption of this technology is set to increase significantly. The government's strategic roadmaps and targets for FCEV deployment, along with a growing global trend toward clean mobility, are providing a strong boost to this segment. The high-performance and zero-emission benefits of fuel cell vehicles are making them a viable alternative to traditional gasoline and diesel cars and an important part of the future of transportation.
Key Players and Competitive Insights
The market comprises several key players, such as Toyota Motor Corporation, Honda Motor Co., Ltd., Panasonic Corporation, and Mitsubishi Heavy Industries. The competitive landscape is marked by a mix of established automotive and electronics companies, along with specialized fuel cell manufacturers. These players are focused on developing and commercializing fuel cell technology across various applications, from vehicles to residential power systems. Competition is driven by ongoing technological innovations, with companies striving to improve the efficiency, durability, and cost of their fuel cell products.
A few prominent companies in the industry include Panasonic Corporation; Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.; Toyota Motor Corporation; Honda Motor Co., Ltd.; Toshiba Corporation; Aisin Corporation; Fuji Electric Co., Ltd.; Kyocera Corporation; Doosan Fuel Cell Co., Ltd.; and Ballard Power Systems Inc.
Key Players
- Aisin Corporation
- Ballard Power Systems Inc.
- Doosan Fuel Cell Co., Ltd.
- Fuji Electric Co., Ltd.
- Honda Motor Co., Ltd.
- Kyocera Corporation
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.
- Panasonic Corporation
- Toshiba Corporation
- Toyota Motor Corporation
Japan Fuel Cell Industry Developments
February 2025: Toyota launched a new, third-generation fuel cell system. This new system is designed to be more durable and fuel-efficient. The company announced its plan to expand its use from passenger cars to heavy-duty commercial vehicles.
Japan Fuel Cell Market Segmentation
By Type Outlook (Revenue – USD Billion; Volume, Units; 2020–2034)
- Solid Oxide Fuel Cells
- Phosphoric Acid Fuel Cells
- Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells
- Molten Carbonate Fuel Cells
- Others
By Application Outlook (Revenue – USD Billion; Volume, Units; 2020–2034)
- Stationary
- Transportation
- Portable
Japan Fuel Cell Market Report Scope
|
Report Attributes |
Details |
|
Market Size in 2024 |
USD 3.07 billion |
|
Market Size in 2025 |
USD 3.56 billion |
|
Revenue Forecast by 2034 |
USD 13.87 billion
|
|
CAGR |
16.3% from 2025 to 2034 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Historical Data |
2020–2023 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025–2034 |
|
Quantitative Units |
Revenue in USD billion, Volume in Units, and CAGR from 2025 to 2034 |
|
Report Coverage |
Revenue Forecast, Competitive Landscape, Growth Factors, and Industry Insights |
|
Segments Covered |
|
|
Competitive Landscape |
|
|
Report Format |
|
|
Customization |
Report customization as per your requirements with respect to countries, regions, and segmentation. |
FAQ's
The market size was valued at USD 3.07 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow to USD 13.87 billion by 2034.
The market is projected to register a CAGR of 16.3% during the forecast period.
A few key players in the market include Panasonic Corporation; Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd.; Toyota Motor Corporation; Honda Motor Co., Ltd.; Toshiba Corporation; Aisin Corporation; Fuji Electric Co., Ltd.; Kyocera Corporation; Doosan Fuel Cell Co., Ltd.; and Ballard Power Systems Inc.
The proton exchange membrane fuel cells segment accounted for the largest share of the market in 2024.
The transportation segment is expected to witness the fastest growth during the forecast period.
