
Nucleic Acid Amplification Testing Market Size, Share, & Industry Analysis Report
: By Type (PCR Tests, INAAT Tests, and LCR Tests), By Application, By End Use, and By Region – Market Forecast, 2025–2034
- Published Date:Jun-2025
- Pages: 125
- Format: PDF
- Report ID: PM5711
- Base Year: 2024
- Historical Data: 2020-2023
Market Overview
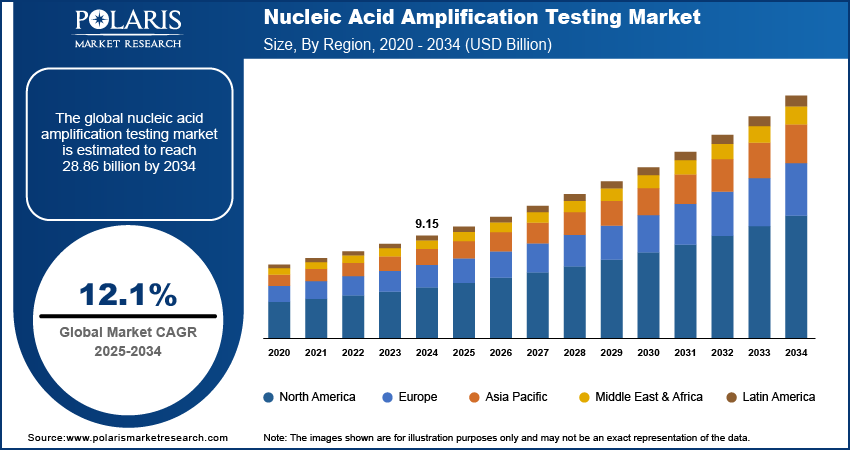
The nucleic acid amplification testing market size was valued at USD 9.15 billion in 2024. It is projected to grow from USD 10.24 billion in 2025 to USD 28.86 billion by 2034, exhibiting a CAGR of 12.1% during 2025–2034.
Nucleic acid amplification testing (NAAT) represents a sophisticated category of molecular diagnostic techniques employed to identify specific genetic material, such as DNA or RNA, within a biological sample. These tests work by amplifying minute quantities of target nucleic acids, making it possible to detect even very low levels of pathogens or genetic markers that might be undetectable by other methods. This amplification process is crucial for early and accurate diagnosis of various diseases, including infectious diseases, genetic disorders, and cancers. The ability of NAAT to provide highly sensitive and specific results has positioned it as a vital tool in clinical diagnostics, playing a significant role in informing treatment decisions and improving patient care management.
To Understand More About this Research: Request a Free Sample Report
The rising global prevalence of infectious diseases, including both emerging and re-emerging pathogens, necessitates the use of highly sensitive diagnostic tools such as NAAT for timely detection and management. Furthermore, the growing incidence of genetic disorders and the increasing application of molecular diagnostics in oncology are driving the adoption of NAAT for early detection, risk assessment, and personalized medicine approaches. Continuous advancements in molecular diagnostic technologies, including the development of more rapid and user-friendly NAAT platforms, are also fueling growth by expanding the accessibility and applicability of these tests in various healthcare settings, including point-of-care diagnostics.
Market Dynamics
Rising Global Prevalence of Infectious Diseases
The escalating global burden of infectious diseases is a significant driver for nucleic acid amplification testing. According to a study published in The Lancet in 2024, analyzing data from 204 countries, infectious diseases accounted for a staggering 704 million disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) in 2019, representing 28% of all DALYs. Pathogens causing tuberculosis (TB), malaria, and HIV had the largest impact. A study published in the CIDRAP (Center for Infectious Disease Research and Policy) at the University of Minnesota analyzed data from 204 countries and estimated that 85 pathogens accounted for 704 million disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) in 2019, highlighting the substantial global burden of infectious diseases. The emergence of new infectious agents, such as novel coronaviruses, and the resurgence of existing ones further underscore the critical need for rapid and accurate diagnostic tools. Nucleic acid amplification testing offers high sensitivity and specificity in detecting these pathogens, even at low concentrations, which is crucial for early diagnosis, effective treatment, and controlling outbreaks. This increasing demand for precise and timely diagnosis of a wide range of infectious diseases directly fuels the growth.
Increasing Incidence of Genetic Disorders
The rising awareness and diagnosis of genetic disorders are also contributing significantly to the development of nucleic acid amplification testing. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that approximately 240,000 newborns die each year due to congenital disorders, and these disorders contribute to 170,000 deaths in children between 1 month and 5 years of age. While individual genetic disorders may be rare, collectively, they affect a substantial portion of the population. As mentioned in a publication on GeneHome, single-gene disorders alone are estimated to affect 10 out of every 1,000 people globally. Nucleic acid amplification testing plays a vital role in the diagnosis of these conditions, including inherited diseases, chromosomal abnormalities, and genetic predispositions to certain diseases. The ability of NAAT to detect specific genetic mutations with high accuracy is increasingly important for genetic screening, carrier testing, prenatal diagnostics, and personalized medicine, thereby driving the demand trends for nucleic acid amplification testing.
Advancements in Molecular Diagnostic Technologies
Continuous advancements in molecular diagnostic technologies are a crucial growth factor for nucleic acid amplification testing. Techniques such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR), including real-time PCR and digital PCR, have become indispensable tools for rapid and sensitive detection of nucleic acids. Next-generation sequencing (NGS) allows for comprehensive genomic analysis, aiding in the identification of new pathogens and resistance mechanisms. Furthermore, innovative approaches such as loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) and CRISPR-based diagnostics are enhancing the speed, sensitivity, and specificity of nucleic acid detection, making testing more accessible, including in point-of-care settings. These technological developments are improving the performance and expanding the applications of nucleic acid amplification testing, which, in turn, significantly contributes to the development and penetration of these advanced diagnostic methods.
Segmental Insights
Market Assessment By Type
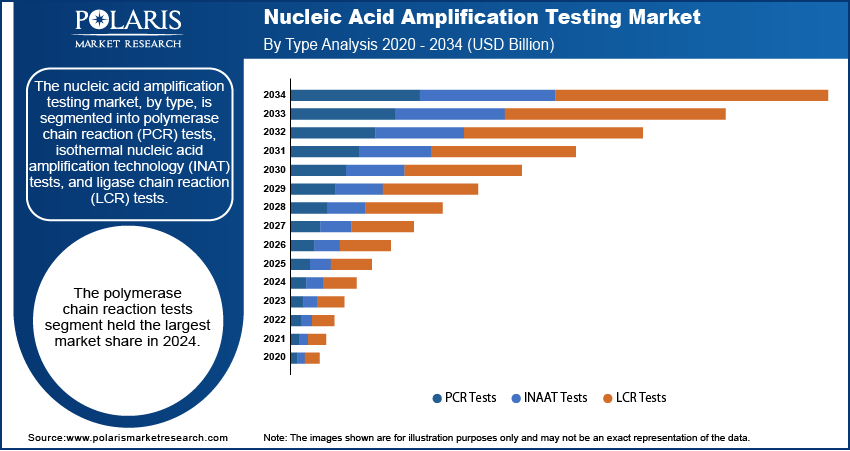
The nucleic acid amplification testing market, by type, is segmented into polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests, isothermal nucleic acid amplification technology (INAT) tests, and ligase chain reaction (LCR) tests. The polymerase chain reaction tests segment holds the largest share. This dominance is attributed to the high specificity and sensitivity of PCR tests, along with their ability to detect a wide array of pathogens. The established efficacy and broad applicability of PCR technology across various diagnostic applications, including infectious disease testing, oncology, and genetic testing, have solidified its position as the leading segment.
The isothermal nucleic acid amplification technology tests segment is expected to exhibit the highest growth rate during the forecast period. Advancements in techniques such as loop-mediated isothermal amplification are simplifying the amplification process, leading to faster and more cost-effective diagnostic solutions. This rapid growth is driven by the increasing demand for point-of-care testing and the need for efficient and accessible diagnostic methods, particularly in resource-limited settings.
Market Evaluation By Application
The segmentation, by application, includes infectious disease testing, oncology testing, genetic & mitochondrial disease testing, and others. The infectious disease testing segment represented the largest share, driven by the widespread use of NAAT for the diagnosis and monitoring of a broad spectrum of infectious agents, including viruses, bacteria, fungi, and parasites. The critical role of these tests in early detection, disease management, and public health initiatives to control outbreaks has established infectious disease diagnostics as the dominant application area.
Oncology testing is anticipated to be the fastest-growing application segment during the forecast period. The increasing adoption of molecular diagnostics in cancer management, including early detection, personalized treatment strategies, and monitoring of therapeutic response, is fueling this rapid growth. Nucleic acid amplification testing plays an increasingly vital role in identifying cancer-specific mutations and rare diseases genetic testing and biomarkers, driving its demand in oncology applications and contributing significantly to the overall development.
Market Evaluation By End Use
The segmentation, by end use, includes hospitals, central and reference laboratories, and others. The central and reference laboratories segment accounted for the largest share, primarily due to the high volume of diagnostic tests processed in these facilities, which serve as key hubs for complex and specialized testing. The established infrastructure, sophisticated equipment, and skilled personnel in central and reference laboratories make them central to the widespread adoption and utilization of nucleic acid amplification testing for various clinical applications, thus contributing significantly to the overall size.
The hospitals segment is expected to register the highest growth rate over the forecast period. The increasing adoption of molecular diagnostics within hospital settings, driven by the rising need for rapid turnaround times and enhanced patient care. The availability of advanced NAAT platforms within hospitals allows for quicker diagnostic results, facilitating timely clinical decision-making and contributing to improved patient outcomes, thereby increasing the penetration of nucleic acid amplification testing in this end-use segment.
Regional Analysis
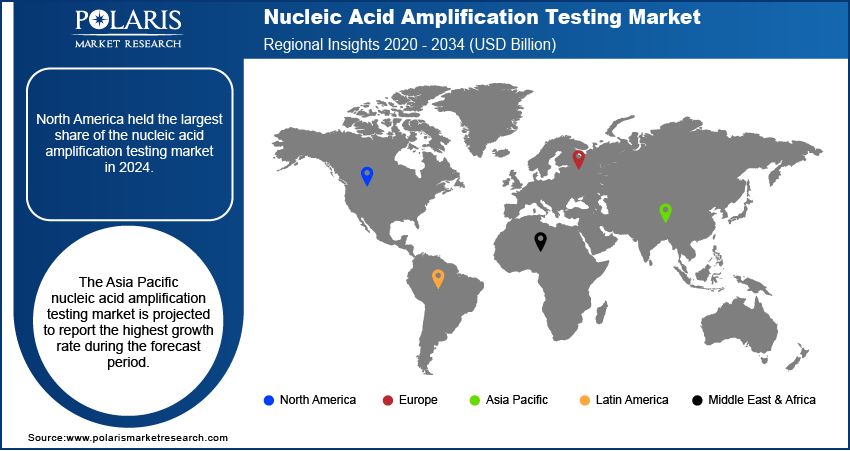
The industry demonstrates a global presence, with significant industry activity observed across North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East & Africa. Each of these regions exhibits unique dynamics influenced by factors such as healthcare infrastructure, prevalence of infectious diseases, research and development activities, and regulatory landscapes. While North America and Europe have historically been key contributors, Asia Pacific is emerging as a region with substantial growth potential, driven by its large population base and increasing healthcare investments. Latin America and the Middle East & Africa also present growing opportunities for penetration, albeit from a smaller base.
North America held the largest share, owing to the well-established healthcare infrastructure in the region, high adoption rates of advanced diagnostic technologies, and significant presence of leading players. Furthermore, the strong emphasis on early disease detection and the availability of sophisticated research and development facilities contribute to the North America nucleic acid amplification testing market expansion.
The Asia Pacific nucleic acid amplification testing market is projected to report the highest growth rate during the forecast period. This rapid expansion is fueled by several factors, including the increasing prevalence of infectious diseases in densely populated countries, rising healthcare expenditure, growing awareness of advanced diagnostic techniques, and a burgeoning medical tourism industry. Moreover, the increasing focus on improving healthcare access and the growing investments in research and development activities in countries such as China and India are expected to significantly boost the demand trends for nucleic acid amplification testing in Asia Pacific.
Key Players and Competitive Insights
A few of the major players actively operating in the market include F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG; Abbott Laboratories; Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.; QIAGEN N.V.; bioMérieux S.A.; Becton, Dickinson and Company (BD); Siemens Healthineers AG; Danaher Corporation (Cepheid); Hologic, Inc.; Agilent Technologies, Inc.; and Illumina, Inc.
The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of well-established multinational corporations and emerging players. Competition is intense, driven by factors such as technological innovation, product differentiation, pricing strategies, and geographical expansion. Key competitive insights include a focus on developing more rapid, accurate, and cost-effective testing solutions, expanding test menus to cover a wider range of applications, and increasing the accessibility of NAAT technologies through point-of-care devices. Strategic collaborations, partnerships, and acquisitions are also common strategies employed by players to enhance their penetration and expand their product portfolios.
F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG: Headquartered in Basel, Switzerland, Roche offers a comprehensive portfolio of molecular diagnostic solutions relevant. Their offerings include a wide range of PCR-based assays and platforms for infectious diseases, oncology, and genetic testing. Roche's integrated systems and extensive test menu make it a significant participant in providing diagnostic solutions for various healthcare needs.
Abbott Laboratories: Based in Abbott Park, Illinois, USA, Abbott has a strong presence with its diverse range of molecular diagnostic products. Their offerings include real-time PCR systems and assays for infectious disease testing, molecular oncology diagnostics, and genetic analysis. The company’s focus on innovation and expanding its diagnostic capabilities positions it as a key contributor to the nucleic acid amplification testing market.
List of Key Companies in Nucleic Acid Amplification Testing Market
- Abbott Laboratories
- Agilent Technologies, Inc.
- Becton, Dickinson and Company (BD)
- bioMérieux S.A.
- Danaher Corporation (Cepheid)
- F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG
- Hologic, Inc.
- Illumina, Inc.
- QIAGEN N.V.
- Siemens Healthineers AG
- Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
Nucleic Acid Amplification Testing Industry Developments
- November 2024: Thermo Fisher Scientific introduced a new polymerase chain reaction (PCR) kit aimed at accelerating research in genetic analysis. This kit features enhanced enzyme technology for improved sensitivity and faster results in gene expression studies and genotyping applications.
- March 2023: Becton, Dickinson and Company (BD) announced that it had received 510(k) clearance from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for its BD Vaginal Panel on the BD COR System. This is a high-throughput molecular diagnostic test designed for large laboratories to detect common causes of vaginitis.
Nucleic Acid Amplification Testing Market Segmentation
By Type Outlook (Revenue – USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- PCR Tests
- INAAT Tests
- LCR Tests
By Application Outlook (Revenue – USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- Infectious Disease Testing
- Oncology Testing
- Genetic & Mitochondrial Disease Testing
- Others
By End Use Outlook (Revenue – USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- Hospitals
- Central
- Reference Laboratories
- Others
By Regional Outlook (Revenue – USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- UK
- Italy
- Spain
- Netherlands
- Russia
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- Malaysia
- Suth Korea
- Indnesia
- Australia
- Vietnam
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Middle East & Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Israel
- Suth Africa
- Rest of Middle East & Africa
- Latin America
- Mexic
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
Nucleic Acid Amplification Testing Market Report Scope:
|
Report Attributes |
Details |
|
Market Size Value in 2024 |
USD 9.15 billion |
|
Market Size Value in 2025 |
USD 10.24 billion |
|
Revenue Forecast by 2034 |
USD 28.86 billion |
|
CAGR |
12.1% from 2025 to 2034 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Historical Data |
2020–2023 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025–2034 |
|
Quantitative Units |
Revenue in USD billion and CAGR from 2025 to 2034 |
|
Report Coverage |
Revenue Forecast, Market Competitive Landscape, Growth Factors, and Industry Insights |
|
Segments Covered |
|
|
Regional Scope |
|
|
Competitive Landscape |
|
|
Report Format |
|
|
Customization |
Report customization as per your requirements with respect to countries, regions, and segmentation. |
How is the report valuable for an organization?
Workflow/Innovation Strategy: The nucleic acid amplification testing market has been segmented into detailed segments of type, application, and end use. Moreover, the study provides the reader with a detailed understanding of the different segments at both the global and regional levels.
Market Entry Strategies: Growth strategies in the field of nucleic acid amplification testing are centered around continuous technological innovation, focusing on developing faster, more sensitive, and user-friendly assays and platforms. Expanding the application of NAAT beyond infectious diseases into areas such as oncology and genetic disorders is another key growth avenue. Market players are also focusing on geographical expansion, particularly in emerging economies with increasing healthcare investments. Strategic collaborations, partnerships, and acquisitions play a crucial role in enhancing market reach and expanding product portfolios. Furthermore, a strong emphasis on point-of-care testing solutions is anticipated to drive market penetration by making diagnostics more accessible.
FAQ's
The global market size was valued at USD 9.15 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow to USD 28.86 billion by 2034.
The market is projected to register a CAGR of 12.1% during the forecast period.
North America had the largest share of the market in 2024.
A few of the major players include F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG; Abbott Laboratories; Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.; QIAGEN N.V.; bioMérieux S.A.; Becton, Dickinson and Company (BD); Siemens Healthineers AG; Danaher Corporation (Cepheid); Hologic, Inc.; Agilent Technologies, Inc.; and Illumina, Inc.
The polymerase chain reaction tests segment accounted for the largest share of the market in 2024.
Following are a few of the trends ? Increasing Demand for Rapid and Accurate Diagnostics: The rising global prevalence of infectious diseases and genetic disorders is driving the need for quick and precise diagnostic solutions, where NAAT plays a crucial role due to its sensitivity and specificity. ? Expansion of Point-of-Care Testing (POCT): There is a growing trend toward decentralized diagnostics and point-of-care testing, making NAAT technologies more accessible in various healthcare settings beyond traditional laboratories. ? Technological Advancements in Amplification Techniques: Innovations in isothermal amplification methods such as LAMP and RPA, as well as digital PCR, are enhancing the speed, ease of use, and accuracy of nucleic acid testing
Nucleic Acid Amplification Testing (NAAT) is a sophisticated molecular diagnostic technique used to detect specific genetic material, such as DNA or RNA, of a target organism or sequence within a biological sample. These tests work by amplifying minute amounts of the target nucleic acids. This amplification process makes it possible to detect even very low levels of the target, which might be undetectable by other methods.
