
Satellite Launch Vehicle Market Share, Size, Trends, Industry Analysis Report
By Orbit (GEO, MEO, LEO, SSO); By Payload (0-150 kg, 150-1000 kg, Above 1000 kg); By End-Use; By Region; Segment Forecast, 2023 - 2032
- Published Date:Jul-2023
- Pages: 115
- Format: PDF
- Report ID: PM3257
- Base Year: 2022
- Historical Data: 2019-2021
Report Outlook
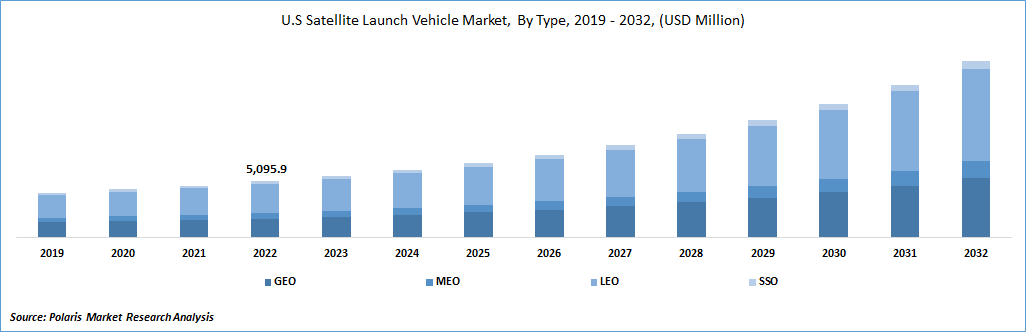
The global satellite launch vehicle market was valued at USD 15,210.00 million in 2022 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 12.2% during the forecast period. Satellite launch vehicles are the vehicles used to place satellites in their targeted orbits. A rocket-powered launch transports a spacecraft beyond Earth's atmosphere into orbit around Earth or to some other destination in outer space. The Launch vehicles have sent uncrewed space probes, crewed spacecraft, and satellites into space. Large launch vehicles are currently utilized to deploy satellites into orbit. These vehicles can carry payloads weighing thousands of kilograms, requiring a significant velocity change (?V) to travel from Earth's surface to orbit.
To Understand More About this Research: Request a Free Sample Report
The Satellite Launch Vehicle (SLV) Market has become an increasingly important component of the larger space economy, driven by the growing demand for satellite launches for various purposes, including Earth observation, navigation, communication, and scientific research. Further, the increasing demand from military, government, commercial, academic, and end users for small satellite constellations has influenced SLV manufacturers to develop more advanced technologies.
Most launch vehicles have been developed via government funding. However, some launch vehicles have been shifted to the private sector to provide commercial space transport services. Mainly in the United States, there have also been several entrepreneurial tries to develop a privately funded launch vehicle.
- For instance, Rocket Lab USA, Inc. launched services and space systems in February 2023. It introduced two brand-new, high-performance space systems products to expand the global market for small satellite components.
However, expendable launch vehicles are being used worldwide. Countries like the United States and Russia, which are highly active, have developed numerous launch vehicles that are best suited for specific purposes. Meanwhile, the ESA, China, India, and Japan have fewer launch vehicles available. Israel and Iran only have one type of launch vehicle.
Growth Drivers
Increasing demand for satellite-based services
The market for satellite launch vehicles is growing rapidly due to the increasing demand for the emergence of private and public space missions and satellite-based services. This has created new opportunities for satellite launch vehicle (SLV) launches and is shaping the industry's landscape.
One of the main drivers behind the growth is expanding demand for broadcasting, weather monitoring, satellite-based services, including communication, Earth observation, navigation, and scientific research. As the reliance on satellite connectivity for communication, data transmission, and global coverage grows, more satellites are needed, which drives the demand for SLV launches.
The satellite launch vehicle market has also been impacted by the emergence of private space companies, such as SpaceX, Blue Origin, and Rocket Lab, which are revolutionizing the industry with innovative launch vehicles and cost-effective solutions. These companies are working on reusable rocket technologies to reduce launch costs and increase launch frequency, making space more accessible.
The commercialization of space activities has further driven the market for satellite launch vehicles. Small satellite launch vehicles and rideshare options have gained popularity, making space more affordable for small satellites and fostering innovation in various sectors. This has led to a dynamic and rapidly evolving industry of launch services.
Report Segmentation
The market is primarily segmented based on orbit, payload, application, and region.
|
By Orbit |
By Payload |
By Application |
By Region |
|
|
|
|
To Understand the Scope of this Report: Speak to Analyst
By Orbit
LEO segment holds the largest revenue shares of the market in 2022
LEO segment holds the largest revenue shares of the market in 2022 and will continue its dominance over the forecast period. Low Earth Orbit (LEO) is a relatively close orbit to the Earth's surface, typically ranging from a few hundred kilometers to around 2,000 kilometers. Satellites in LEO complete an orbit around the Earth in a relatively short period, typically within a few hours. LEO is commonly used for satellite applications, including Earth observation, communication, scientific research, and satellite constellations. In the Satellite Launch Vehicle (SLV) market, launching satellites into LEO is a common requirement due to the versatility and advantages offered by this orbit.
Satellites operating in LEO offer faster communications and low-latency networking and are easy to set up, thus ideal for deployment. Moreover, government and private organizations are investing in deploying satellites in LEO. In April 2023, according to the Indian Space Research Organization's Department of Space (ISRO), the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) earned the title 'the Workhorse of ISRO' due to its continuous record in deploying numerous satellites to Low Earth Orbits (LEO). The PSLV can carry payloads weighing up to 1,750 kg to Sun-Synchronous Polar Orbits (SSPO) at an altitude of 600 km. Its consistent performance has solidified its reputation as a dependable launch vehicle for ISRO's satellite missions.
By Payload
150-1000 kg segment accounted for the largest market share in 2022
150-1000 kg payload segment accounted for the largest market share in 2022. Payload capacity is a crucial specification for launch vehicles as it determines the size and weight limitations of the satellites or other payloads that can be launched using that particular vehicle. Launch vehicles are typically designed to cater to a specific payload range, and the 150-1000 kg range indicates that the vehicle can launch satellites or payloads weighing between 150 kilograms and 1000 kilograms.
The 150-1000 kg range is particularly relevant for smaller- medium-sized satellites. It encompasses various applications and missions, including Earth observation, communication, scientific research, and technology demonstration. Satellites within this payload range are often called smallsats or medium-sized satellites.
By launching vehicles specifically designed to cater to the 150-1000 kg payload range, satellite operators can choose the most suitable launch vehicle for their specific mission requirements and payload size.
By Application
Communication segment is expected to grow fastest over the forecast period
Communication segment is anticipated to hold the fastest growth over the forecast period with the highest CAGR. Satellite launch vehicles play a crucial role in deploying communication satellites into space. These vehicles are designed to deliver satellites into their intended orbits, allowing them to provide various communication services such as television broadcasting, internet connectivity, and telecommunication. Several types of SLVs used for communication satellites include geostationary transfer orbit (GTO) launch vehicles, medium earth orbit (MEO) launch vehicles, low earth orbit (LEO) launch vehicles, and small satellite launch vehicles. Major applications of communication satellites include television, radio networking, telecommunications, telemedicine, and tele-education.
The ISRO Telemedicine pilot project commenced in 2001 as a proof-of-concept demonstration program. It established a connection between Apollo Hospital in Chennai and Apollo Rural Hospital in Aragonda village, located in the Chittoor district of Andhra Pradesh. This initiative aimed to showcase the feasibility and potential of telemedicine by leveraging technology to bridge the healthcare gap between urban and rural areas.
Regional Insights
North America region dominated the global market in 2022
North America dominated the market with the largest revenue shares of the market. North America's satellite launch vehicle market has been experiencing significant growth due to the region has dominance of prominent player in the industry with the involvement of government agencies like NASA and commercial space companies such as SpaceX, United Launch Alliance (ULA), and Blue Origin.
The increasing demand for satellite-based services, including telecommunications, Earth observation, weather monitoring, and navigation systems, has been a major driver for this growth. Moreover, technological advancements, well established infrastructure and high government spendings in space sector collectively accelerate the market in this region
The market has also expanded due to the rise of small satellites or CubeSats, requiring frequent launches and leading to a higher demand for launch services.
For instance, SpaceX builds with their Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy rockets, featuring reusable technology that significantly reduces launch costs. United Launch Alliance (ULA), a joint venture between Boeing and Lockheed Martin, offers launch options such as the Atlas V and Delta IV, with a track record of launching government and commercial payloads.
However, Asia Pacific region is anticipated to hold the highest CAGR rate during the forecast period. The satellite industry in the Asia Pacific region is experiencing tremendous growth due to the high demand for satellites across various sectors, including telecommunications, broadcasting, earth observation, navigation, and scientific research. This demand has led to a significant market for satellite launches and has been driven by the rapid economic growth experienced in most Asian countries.
To Understand More About this Research: Request a Free Sample Report
Governments and private companies in countries like China, India, Japan, and South Korea have invested heavily in their space programs, developing and launching satellite launch vehicles. Additionally, the region has made significant progress in developing advanced space technologies and capabilities, making it possible to offer competitive launch services at relatively lower costs than some international counterparts.
Furthermore, the Asia Pacific region has engaged in regional collaborations and partnerships in space exploration, which have fostered knowledge sharing, technology transfer, and joint ventures, contributing to the overall growth of the satellite launch vehicle industry.
Key Market Players & Competitive Insights
The satellite launch vehicle market for the years 2023 to 2032 is covered in the study along with various industry trends and fresh technological developments.
Some of the major players operating in the global market include:
- ABL Space Systems
- Arianespace
- Astra Space, Inc.
- Blue Origin
- China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC)
- Firefly Aerospace Inc.
- Interorbital Systems
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries
- Northrop Grumman Corporation
- Rocket Lab USA, Inc.
- SpaceX
- United Launch Alliance, LLC.
Recent Developments
- In May 2023, India launched its second-generation navigation satellite, NVS-01, and injected it into the geosynchronous transfer orbit. The NVS-01 satellite is a part of the Indian navigation system, NavIC, and was carried by Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV).
- In November 2022, Russia successfully launched the final GLONASS-M navigation satellite into orbit. GLONASS-M is a series of satellites used in the GLONASS (Global Navigation Satellite System) constellation, Russia's equivalent to the Global Positioning System (GPS). The GLONASS-M satellites provide users with global positioning, velocity, and timing information worldwide
Satellite Launch Vehicle Market Report Scope
|
Report Attributes |
Details |
|
Market size value in 2023 |
USD 16,545.71 million |
|
Revenue forecast in 2032 |
USD 46,708.29 million |
|
CAGR |
12.2% from 2023 – 2032 |
|
Base year |
2022 |
|
Historical data |
2019 – 2021 |
|
Forecast period |
2023 – 2032 |
|
Quantitative units |
Revenue in USD million and CAGR from 2023 to 2032 |
|
Segments covered |
By Orbit, By Payload, By End-Use, By Region |
|
Regional scope |
North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America; Middle East & Africa |
|
Customization |
Report customization as per your requirements with respect to countries, region and segmentation. |
FAQ's
key companies in satellite launch vehicle market are ABL Space Systems, Arianespace, Astra Space, Inc., Blue Origin, China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC), Firefly Aerospace Inc.
The satellite launch vehicle market projected CAGR of 12.2% in forecast period.
The satellite launch vehicle market report covering key segments are orbit, payload, application, and region.
key driving factors in satellite launch vehicle market are Increasing number of private and public space missions.
The global satellite launch vehicle market size is expected to reach USD 46,708.29 million by 2032
