
Tumor-Induced Osteomalacia Market Size, Share, Trends, Industry Analysis Report
: By Treatment Type (Drugs & Supplements and Surgery), End Users, and Region (North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America and the Middle East & Africa) – Market Forecast, 2025–2034
- Published Date:Nov-2024
- Pages: 118
- Format: PDF
- Report ID: PM5232
- Base Year: 2024
- Historical Data: 2020-2023
Tumor-Induced Osteomalacia Market Overview
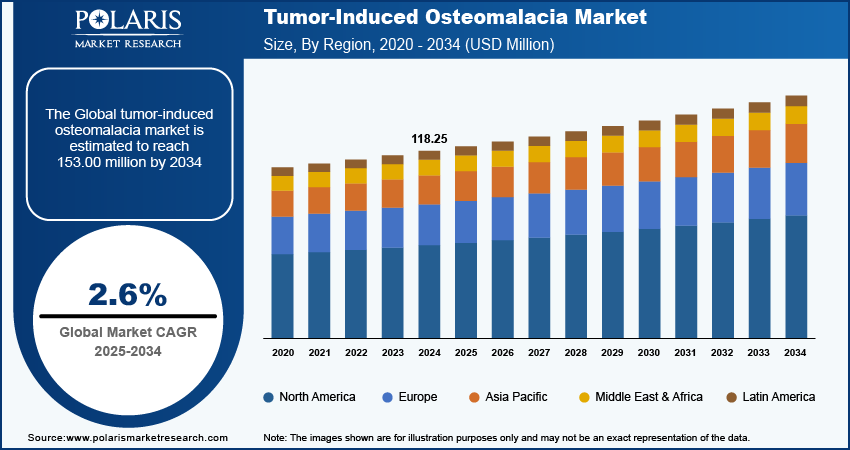
The tumor-induced osteomalacia market size was valued at USD 118.25 million in 2024. The market is projected to grow from USD 121.12 million in 2025 to USD 153.00 million by 2034, exhibiting a CAGR of 2.6% from 2025 to 2034.
The tumor-induced osteomalacia (TIO) market focuses on the diagnosis and treatment of a rare disorder caused by benign tumors that lead to weakened bones due to phosphate loss. Key drivers in this market include advancements in diagnostic technologies, increasing awareness about rare bone diseases, and the growing focus on targeted therapies. The development of novel therapies, such as fibroblast growth factor-23 (FGF23) inhibitors, and increased research and development activities for better treatment options are expected to be the major trends in the market. The market is also seeing collaborations between pharmaceutical companies and research institutes aimed at addressing unmet clinical needs.
To Understand More About this Research: Request a Free Sample Report
Tumor-Induced Osteomalacia Market Trends and Drivers
Increasing Focus on Targeted Therapies
One of the major trends in the tumor-induced osteomalacia (TIO) market will be the growing focus on targeted therapies. With advancements in molecular biology, researchers have developed therapies that specifically target the underlying causes of TIO, particularly by inhibiting the fibroblast growth factor-23 (FGF23) responsible for phosphate loss. Clinical trials involving FGF23 inhibitors, such as burosumab, have shown promising results in treating patients suffering from TIO, improving phosphate levels and reducing bone pain. A study published in Nature Communications in 2018 demonstrated the efficacy of burosumab, with phosphate levels normalizing in over 90% of patients treated with the drug.
Rising Awareness and Diagnosis of Rare Diseases
Awareness surrounding rare diseases, including tumor-induced osteomalacia, has significantly increased over the last decade. This rise in awareness has led to more timely and accurate diagnoses of the condition, which is essential for early treatment and prevention of severe complications. Global initiatives such as Rare Disease Day and the establishment of patient advocacy groups have played a crucial role in educating both healthcare professionals and the public about the signs and symptoms of TIO. According to the National Organization for Rare Disorders, there has been a marked increase in the number of TIO cases diagnosed early, reflecting the success of these awareness campaigns.
Advancements in Diagnostic Technologies
Advancements in diagnostic technologies are also driving the tumor-induced osteomalacia (TIO) market forward. With the increasing use of next-generation sequencing (NGS) and positron emission tomography (PET) scans, physicians can more accurately locate the tumors causing osteomalacia. Traditional imaging methods often fail to detect the small, elusive tumors responsible for TIO, leading to delayed diagnoses. However, with the advent of newer diagnostic tools, the identification of these tumors has become more precise. A study published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism in 2020 highlighted that PET scans combined with computed tomography (CT) identified tumors in 87% of TIO cases, significantly improving treatment outcomes.
Tumor-Induced Osteomalacia Market Segment Insights
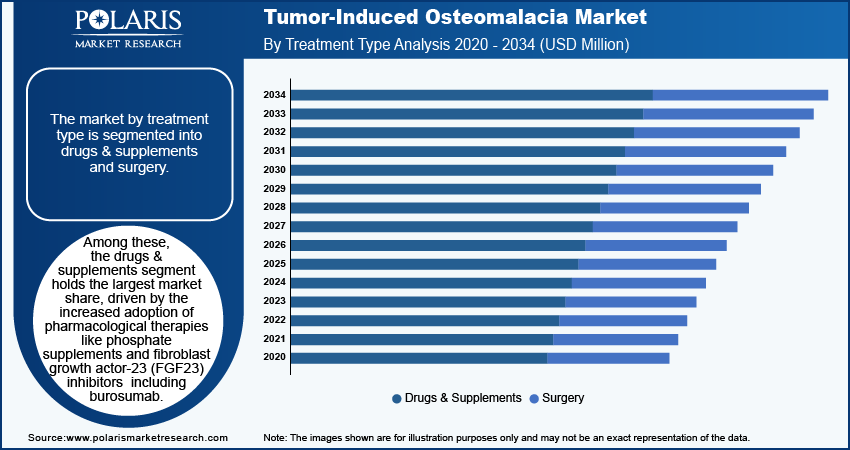
Tumor-Induced Osteomalacia Market Breakdown by Treatment Type Insights
The market by treatment type is segmented into drugs & supplements and surgery. Among these, the drugs & supplements segment holds the largest market share, driven by the increased adoption of pharmacological therapies like phosphate supplements and fibroblast growth factor-23 (FGF23) inhibitors, including burosumab. These medications have gained prominence due to their ability to correct phosphate levels and alleviate symptoms without invasive procedures, making them a preferred choice for both patients and healthcare providers. The rising demand for long-term management of TIO using non-surgical treatments further fuels the growth of this segment.
On the other hand, the surgery segment is also experiencing steady growth, primarily in cases where drug treatments fail to locate or effectively manage the tumor causing osteomalacia. Surgical removal of the tumor is considered a definitive treatment, leading to complete resolution in many patients. However, due to the complex nature of diagnosing TIO, the surgical approach is often reserved for more severe cases. This segment, while not the largest in terms of market share, is expected to see growth due to advancements in minimally invasive surgical techniques and better diagnostic tools enabling more precise tumor localization.
Tumor-Induced Osteomalacia Market Breakdown by End Users Insights
The market by end users is segmented into hospitals, ambulatory surgery centers, speciality clinics, and others. The hospitals segment holds the largest market share, driven by the availability of advanced diagnostic and treatment facilities, including imaging technologies and surgical interventions. Hospitals are often the primary choice for patients requiring comprehensive care, from diagnosis to post-treatment follow-up, making them a dominant segment. The presence of multidisciplinary teams, including endocrinologists, radiologists, and surgeons, further strengthens their role in the management of TIO cases.
Specialty clinics are registering the highest growth in this market, largely due to their focus on rare diseases and specialized treatments for conditions like TIO. These clinics often offer targeted therapies, advanced diagnostic options, and long-term management plans, making them increasingly attractive to patients seeking specialized care. The personalized care provided by these clinics, combined with advancements in treatment options, positions them as a key growth area in the market. Additionally, the rise in collaborations between pharmaceutical companies and specialty clinics to conduct clinical trials for novel TIO treatments contributes to the segment’s rapid growth.
Tumor-Induced Osteomalacia Market Breakdown by Regional Insights
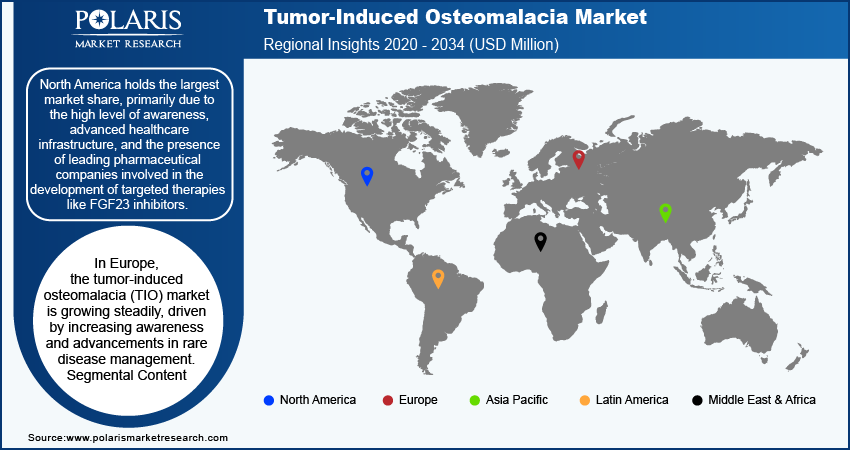
By region, the study provides market insights into North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Latin America, and the Middle East & Africa. In the regional analysis of the tumor-induced osteomalacia (TIO) market, North America holds the largest market share, primarily due to the high level of awareness, advanced healthcare infrastructure, and the presence of leading pharmaceutical companies involved in the development of targeted therapies like FGF23 inhibitors. The availability of advanced diagnostic technologies, coupled with strong investment in research and development, drives the dominance of North America in this market. Europe follows closely, with significant advancements in rare disease treatments, while Asia Pacific is experiencing rapid growth due to increasing healthcare expenditure and rising awareness of rare bone disorders. Other regions, such as Latin America and the Middle East & Africa, are emerging markets with gradual improvements in diagnostic capabilities and access to specialized treatments.
In Europe, the tumor-induced osteomalacia (TIO) market is growing steadily, driven by increasing awareness and advancements in rare disease management. The region benefits from a robust healthcare system and strong support for orphan drug development, which plays a crucial role in treating rare conditions like TIO. Countries such as Germany, France, and the United Kingdom lead in terms of research initiatives and clinical trials for novel therapies. The European Medicines Agency's (EMA) regulatory framework for orphan drugs further supports the growth of targeted treatments, improving patient outcomes across the region.
Asia Pacific is experiencing rapid growth in the TIO market, largely attributed to increasing healthcare expenditure, rising awareness of rare diseases, and improvements in diagnostic infrastructure. Countries like China, Japan, and India are seeing a surge in healthcare investments, leading to better access to advanced diagnostic tools and therapies for conditions like TIO. Additionally, government initiatives aimed at improving rare disease management and the growing collaboration between local and global pharmaceutical companies are boosting the development of innovative treatments in this region.
Tumor-Induced Osteomalacia Market – Key Players and Competitive Insights
Key players actively involved in the tumor-induced osteomalacia (TIO) market include Ultragenyx Pharmaceutical Inc., Kyowa Kirin Co., Ltd., Eli Lilly and Company, Amgen Inc., Novartis AG, Sanofi S.A., Pfizer Inc., AbbVie Inc., and Horizon Therapeutics. These companies are engaged in developing therapies aimed at addressing the underlying causes of TIO, such as inhibiting fibroblast growth factor-23 (FGF23) activity or managing phosphate levels in patients.
Competitive analysis reveals that companies like Ultragenyx and Kyowa Kirin are at the forefront of innovation in TIO treatment, particularly with the development of burosumab, an FGF23 inhibitor, which has gained significant traction due to its efficacy in correcting phosphate levels. These companies are focused on further clinical research to expand the indications for this treatment while also collaborating with research institutions to enhance treatment protocols. Meanwhile, major pharmaceutical companies such as Novartis, Pfizer, and Bayer are investing heavily in R&D, focusing on both drug therapies and diagnostic advancements to address the complex nature of diagnosing and treating TIO.
The competitive landscape is also shaped by strategic partnerships and collaborations among key players, aimed at expanding their product portfolios and improving patient access to advanced therapies. Companies like Sanofi and Takeda Pharmaceutical are leveraging their global reach to introduce innovative treatments in emerging markets. Roche and GlaxoSmithKline are focusing on integrating diagnostic advancements with their treatment options. As the market evolves, competition is expected to intensify, with companies exploring both novel treatments and improved diagnostic solutions to cater to the growing demand for effective TIO management.
Ultragenyx Pharmaceutical is a global player in the tumor-induced osteomalacia (TIO) market, particularly known for its development of burosumab, a therapy that targets fibroblast growth factor-23 (FGF23) to treat TIO. The company focuses on developing treatments for rare and ultra-rare diseases, with burosumab being a significant milestone in its portfolio.
Kyowa Kirin Co. is another major player actively involved in the TIO market, particularly through its collaboration with Ultragenyx for the development and commercialization of burosumab. The company has a strong presence in the field of rare diseases, with a focus on innovative biotechnological solutions for challenging medical conditions.
List of Key Companies in Tumor-Induced Osteomalacia Market
- Ultragenyx Pharmaceutical Inc.
- Kyowa Kirin Co., Ltd.
- Eli Lilly and Company
- Amgen Inc.
- Novartis AG
- Sanofi S.A.
- Pfizer Inc.
- AbbVie Inc.
- Horizon Therapeutics
Tumor-Induced Osteomalacia Industry Developments
- In July 2023, Ultragenyx announced positive long-term data from a study on burosumab, showing sustained improvements in phosphate levels and quality of life in patients with TIO, further supporting its use as a key treatment option for this rare condition.
- In May 2023, Kyowa Kirin expanded access to burosumab in several European countries following regulatory approvals, reinforcing its commitment to addressing unmet needs in TIO treatment across different regions.
Tumor-Induced Osteomalacia Market Segmentation
By Treatment Type Outlook
- Drugs & Supplements
- Surgery
By End Users Outlook
- Hospitals
- Ambulatory Surgery Centers
- Speciality Clinics
- Others
By Regional Outlook
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- UK
- Italy
- Spain
- Netherlands
- Russia
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- Malaysia
- South Korea
- Indonesia
- Australia
- Vietnam
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Middle East & Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Israel
- South Africa
- Rest of the Middle East & Africa
- Latin America
- Mexico
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
Tumor-Induced Osteomalacia Market Report Scope
|
Report Attributes |
Details |
|
Market Size Value in 2024 |
USD 118.25 million |
|
Market Size Value in 2025 |
USD 121.12 million |
|
Revenue Forecast in 2034 |
USD 153.00 million |
|
CAGR |
2.6% from 2025 to 2034 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Historical Data |
2020–2023 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025–2034 |
|
Quantitative Units |
Revenue in USD million and CAGR from 2025 to 2034 |
|
Report Coverage |
Revenue Forecast, Market Competitive Landscape, Growth Factors, and Trends |
|
Segments Covered |
|
|
Regional Scope |
|
|
Competitive landscape |
|
|
Report Format |
|
|
Customization |
Report customization as per your requirements with respect to countries, regions, and segmentation. |
FAQ's
The tumor-induced osteomalacia market size was valued at USD 118.25 million in 2024 and is projected to grow to USD 153.00 million by 2034.
The market is projected to register a CAGR of 2.6% from 2025 to 2034.
North America holds the largest share of the market.
Key players actively involved in the tumor-induced osteomalacia (TIO) market include Ultragenyx Pharmaceutical, Kyowa Kirin Co., Novartis AG, Pfizer Inc., Bayer AG, Sanofi, Takeda Pharmaceutical, F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Teijin Pharma Limited, GlaxoSmithKline plc, Amgen Inc., Johnson & Johnson, AstraZeneca, AbbVie, and Eli Lilly and Company.
The drugs & supplement segment accounts for the largest share of the market.
The hospital segment accounts for the largest share of the tumor-induced osteomalacia market.
Tumor-Induced Osteomalacia (TIO) is a rare paraneoplastic syndrome characterized by the development of bone pain, fractures, and muscle weakness due to abnormal bone mineralization. This condition is caused by tumors, typically mesenchymal tumors, that secrete fibroblast growth factor-23 (FGF23). Elevated levels of FGF23 lead to phosphate wasting in the kidneys, resulting in hypophosphatemia (low phosphate levels in the blood). The lack of phosphate impairs bone mineralization, leading to soft, weak bones and the clinical symptoms associated with osteomalacia.
A few key trends in the tumor-induced osteomalacia market are described below: Growing Awareness and Improved Diagnosis- Increased recognition of TIO as a distinct medical condition is leading to more accurate and earlier diagnoses. Advancements in imaging techniques (e.g., MRI, PET scans) and biomarkers (such as FGF23 testing) are helping clinicians identify TIO more effectively. The rise in genetic testing and awareness of rare diseases has contributed to better detection of mesenchymal tumors associated with TIO. Advances in Targeted Therapies- Targeted therapies aimed at blocking the action of FGF23 (which causes phosphate wasting) are gaining traction. Drugs like burosumab, an FGF23 inhibitor, are showing promise in correcting the phosphate imbalance and improving bone mineralization in TIO patients. The biologic drug market for TIO is expanding, with new treatments being explored in clinical trials. Increase in Rare Disease Research and Investment- There is growing investment in rare disease research due to the potential to treat small but underserved patient populations. Pharmaceutical companies and biotech firms are increasingly focusing on orphan drug development, which may bring more treatment options for TIO patients. Collaborations between pharmaceutical companies and academic research institutions are fostering new treatments and diagnostic tools
A new company could focus on innovative diagnostic tools, targeted therapies (like FGF23 inhibitors), personalized medicine, and patient access programs. Emphasizing early diagnosis, precision treatment, and cost-effective solutions will help differentiate and stay ahead in the TIO market
