
U.S. Gout Therapeutics Market Size, Share, Trend, Industry Analysis Report
By Disease Condition (Acute Gout, Chronic Gout), By Drug Class, By Distribution Channel – Market Forecast, 2025–2034
- Published Date:Aug-2025
- Pages: 128
- Format: PDF
- Report ID: PM6279
- Base Year: 2024
- Historical Data: 2020-2023
Overview
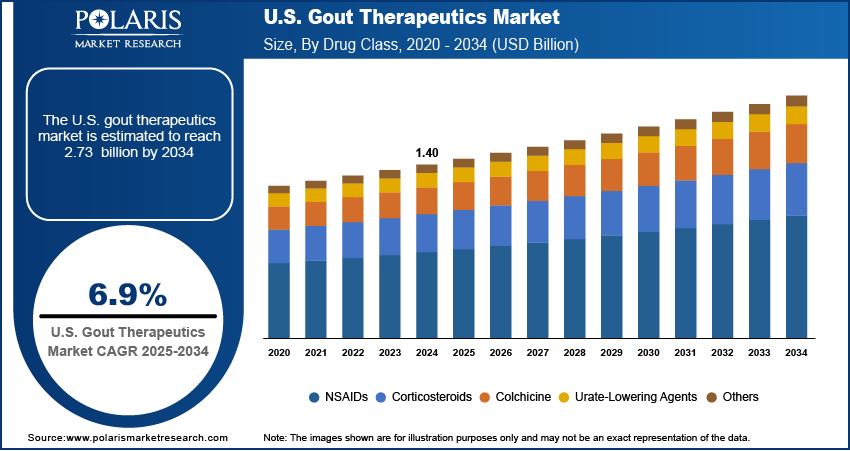
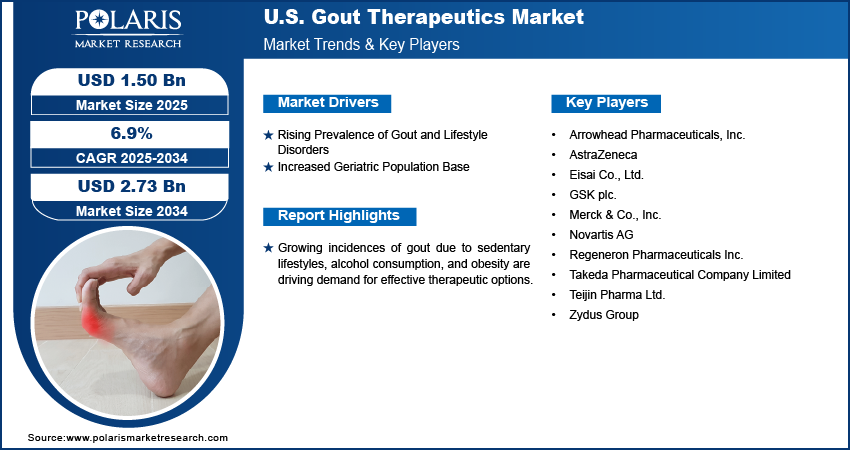
The U.S. gout therapeutics market size was valued at USD 1.40 billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 6.9% from 2025 to 2034. Growing obesity rates and increasing metabolic disorders such as type 2 diabetes and hypertension are directly contributing to higher gout incidence in the U.S. It is creating a sustained demand for long-term urate-lowering and flare-management therapeutics.
Key Insights
- The NSAIDs segment captured ~43% of the market in 2024, driven by fast-acting relief from pain and inflammation during acute gout flares.
- The chronic gout segment led in 2024 due to rising demand for long-term uric acid-lowering and flare-prevention therapies.
- The retail pharmacy segment held the largest share in 2024, supported by widespread accessibility and the high volume of gout medication dispensing.
Industry Dynamics
- Increasing prevalence of gout and hyperuricemia due to rising obesity and metabolic syndrome is driving demand for effective therapeutics in the U.S.
- Strong pipeline of novel uric acid-lowering drugs and biologics is accelerating innovation and expanding treatment options for refractory gout patients.
- Growth of specialty pharmacies enables better patient access to high-cost, branded gout therapies with integrated adherence and monitoring support.
- High drug pricing and payer restrictions limit patient access and slow adoption of newer, more effective gout treatments across insurance plans.
Market Statistics
- 2024 Market Size: USD 1.40 billion
- 2034 Projected Market Size: USD 2.73 billion
- CAGR (2025–2034): 6.9%
Gout is a form of inflammatory arthritis caused by uric acid crystal deposition. The U.S. gout therapeutics market comprises pharmaceutical products and treatment approaches aimed at managing and alleviating symptoms of gout. The market includes urate-lowering therapies, anti-inflammatories, and novel biologics designed to prevent flare-ups, reduce uric acid levels, and address chronic complications. It serves a growing patient population driven by aging demographics, lifestyle factors, and increasing prevalence of metabolic disorders. Strong healthcare infrastructure and frequent screening in the U.S. enable early detection and diagnosis of gout, which supports timely therapeutic intervention and promotes long-term treatment adherence across a broad patient population.
Increased availability and use of biologics targeting IL-1β and other inflammatory pathways are transforming treatment paradigms for refractory gout patients, improving outcomes and expanding therapeutic options in complex or advanced-stage cases. Moreover, robust partnerships between academic institutions, biopharma companies, and CROs in the U.S. are accelerating clinical trials and data generation for new gout treatments, ensuring steady pipeline progression and market evolution.
Drivers & Opportunities
Rising Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome Prevalence: The steady increase in obesity and related metabolic conditions such as type 2 diabetes and hypertension has significantly raised the risk of gout in the U.S. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), in the U.S., approximately 58% of adults with obesity are diagnosed with hypertension. Excess body weight leads to higher uric acid levels, which contribute to urate crystal buildup in joints, triggering gout flares. These underlying conditions complicate disease management and require more tailored and prolonged therapeutic strategies. The growing pool of patients with overlapping metabolic issues continues to drive demand for urate-lowering treatments, anti-inflammatory medications, and preventive regimens, pushing the market toward sustained innovation and expanding treatment protocols.
Strong Commercial and Insurance Coverage: The presence of a well-established insurance framework in the U.S., including Medicare, Medicaid, and private health plans, has improved access to advanced gout treatments. Many high-cost therapies, including biologics and novel urate-lowering drugs, are reimbursed, making them affordable for a larger segment of the population. This coverage also supports early-stage treatment and long-term disease control, encouraging patients to adhere to prescribed therapies. The financial accessibility of new and effective medications has strengthened market penetration and is expected to support wider adoption of personalized treatment approaches in the coming years.
Segmental Insights
Disease Condition Analysis
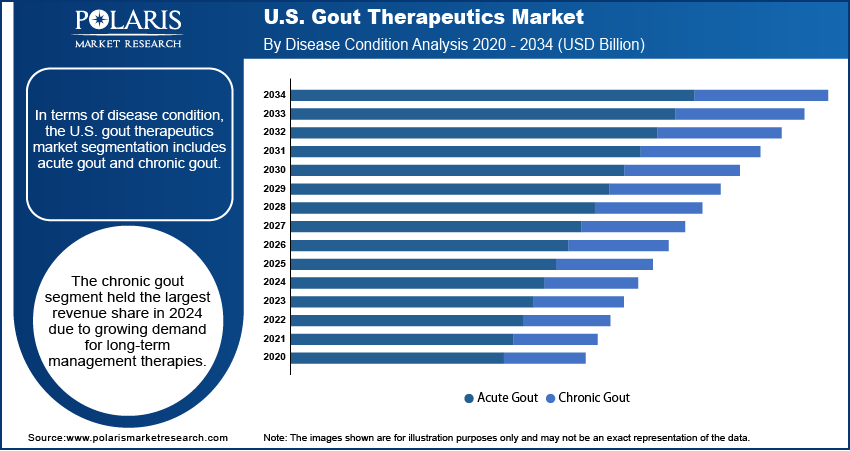
In terms of disease condition, the U.S. gout therapeutics market segmentation includes acute gout and chronic gout. The chronic gout segment held the largest revenue share in 2024 due to the increasing number of patients progressing from acute flare episodes to persistent, poorly controlled hyperuricemia. These patients often require continuous pharmacologic management to prevent joint damage and reduce flare frequency. Longer treatment durations and the need for specialized drugs, such as urate-lowering therapies and biologics, contribute to higher per-patient expenditures. Enhanced diagnostic awareness and early intervention programs have led to greater identification of chronic cases, encouraging structured, long-term care approaches that generate significant revenue in the therapeutic market.
The acute gout segment is witnessing increasing traction due to rising emergency visits for sudden joint pain and inflammation. Increased sedentary lifestyles, poor dietary habits, and metabolic imbalances are causing more individuals to experience their first gout flare at a younger age. The demand for rapid symptom relief has fueled the use of NSAIDs, corticosteroids, and colchicine. Additionally, real-time telehealth consultations and urgent care clinics are improving access to immediate intervention. These dynamics are expanding the patient pool and increasing drug sales specific to acute episodes, making the segment more commercially relevant than before.
Drug Class Analysis
Based on drug class, the U.S. gout therapeutics market segmentation includes NSAIDs, corticosteroids, colchicine, urate-lowering agents, and others. The NSAIDs segment dominated the market in 2024 with ~45% of the revenue share due to their widespread use as the first-line treatment for managing acute flare-ups. Their fast onset of action and ability to reduce inflammation and pain make them a preferred option among physicians and patients alike. High prescription volumes in emergency and outpatient settings reflect their accessibility and clinical familiarity. Additionally, the availability of both branded and generic formulations ensures affordability and broad adoption, sustaining the segment's market dominance across diverse patient demographics and healthcare settings.
The urate-lowering agents segment is expected to register a significant CAGR from 2025 to 2034, driven by increasing focus on long-term disease management and reduction of serum uric acid levels. The shift toward preventive treatment strategies expanded the use of these drugs in patients with recurrent flares and tophi formation. Recent clinical approvals and pipeline development for next-generation urate-lowering therapies, including xanthine oxidase inhibitors and uricosurics, are enhancing treatment outcomes and addressing unmet needs. Physician preference for durable control over disease progression further supports the demand for these agents, especially among chronic gout patients requiring lifelong management.
Distribution Channel Analysis
In terms of distribution channel, the U.S. gout therapeutics market segmentation includes hospital pharmacy, retail pharmacy, and online pharmacy. The retail pharmacy segment held the largest revenue share in 2024 due to it central role in dispensing maintenance and acute gout medications. Strong foot traffic, widespread availability of both prescription and over-the-counter treatments, and pharmacist-led patient education support adherence and refills. Many patients prefer the convenience of nearby community pharmacies for ongoing access to NSAIDs, colchicine, and urate-lowering drugs. Integrated insurance billing systems and partnerships with healthcare providers further streamline the purchasing process. These factors collectively enhance sales volume and position retail pharmacies as a key distribution channel for gout therapeutics across urban and suburban populations.
Online pharmacy is gaining momentum due to the increasing shift toward digital health and home-based care models. Chronic gout patients prefer the convenience of doorstep delivery for maintenance medications, avoiding frequent trips to physical stores. Subscription-based models and auto-refill services help ensure consistent treatment adherence. In addition, competitive pricing, access to a wider range of brands, and privacy benefits are driving consumer interest. E-prescriptions integrated into telemedicine platforms are streamlining the digital purchase process, enabling seamless ordering of flare and maintenance drugs from licensed online providers.
Key Players & Competitive Analysis
The competitive landscape of the U.S. gout therapeutics market is shaped by continuous innovation, strategic expansion, and aggressive portfolio diversification. Industry analysis highlights a strong focus on advanced urate-lowering agents and biologics targeting treatment-resistant cases. Market expansion strategies include the development of novel formulations with improved safety profiles and reduced dosing frequency to enhance patient adherence. Companies are pursuing joint ventures and strategic alliances to accelerate clinical trials and broaden drug access. Mergers and acquisitions are used to strengthen research pipelines and improve distribution capabilities, particularly for specialty therapeutics. Post-merger integration efforts are streamlining operations and optimizing market penetration. Technology advancements in drug delivery and precision medicine are being leveraged to improve therapeutic efficacy and safety. The emphasis remains on differentiated value propositions, including rapid symptom resolution and long-term flare prevention. Competitive intensity is also increasing around securing favorable reimbursement terms and maintaining strong relationships with healthcare providers and pharmacy networks across the country.
Key Players
- Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
- AstraZeneca
- Eisai Co., Ltd.
- GSK plc.
- Merck & Co., Inc.
- Novartis AG
- Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc.
- Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited
- Teijin Pharma Ltd.
- Zydus Group
U.S. Gout Therapeutics Industry Developments
July 2024: Novartis announced that it is approving Phase III results for LNP023. It is a novel chronic gout treatment, showing significant uric acid reduction and effective flare control by targeting a key inflammatory pathway.
U.S. Gout Therapeutics Market Segmentation
By Disease Condition Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- Acute Gout
- Chronic Gout
By Drug Class Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- NSAIDs
- Corticosteroids
- Colchicine
- Urate-Lowering Agents
- Others
By Distribution Channel Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- Hospital Pharmacy
- Retail Pharmacy
- Online Pharmacy
U.S. Gout Therapeutics Market Report Scope
|
Report Attributes |
Details |
|
Market Size in 2024 |
USD 1.40 billion |
|
Market Size in 2025 |
USD 1.50 billion |
|
Revenue Forecast by 2034 |
USD 2.73 billion |
|
CAGR |
6.9% from 2025 to 2034 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Historical Data |
2020–2023 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025–2034 |
|
Quantitative Units |
Revenue in USD billion and CAGR from 2025 to 2034 |
|
Report Coverage |
Revenue Forecast, Competitive Landscape, Growth Factors, and Industry Trends |
|
Segments Covered |
|
|
Competitive Landscape |
|
|
Report Format |
|
|
Customization |
Report customization as per your requirements with respect to countries, regions, and segmentation. |
FAQ's
The market size was valued at USD 1.40 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow to USD 2.73 billion by 2034.
The market is projected to register a CAGR of 6.9% during the forecast period.
A few of the key players in the market are Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; AstraZeneca; GSK plc.; Eisai Co., Ltd.; Merck & Co., Inc.; Novartis AG; Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc.; Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited; Teijin Pharma Ltd.; and Zydus Group.
The NSAIDs segment dominated the market with ~43% of the revenue share in 2024 due to their rapid action in reducing inflammation and pain associated with acute gout flares.
The chronic gout segment held the largest revenue share in 2024 due to growing demand for long-term management therapies.
