
Antibody Discovery Market Size, Share, Trends, Industry Analysis Report
By Method (Phage Display, Hybridoma, Other), By Antibody Type, By End User, By Region – Market Forecast, 2025–2034
- Published Date:Jul-2025
- Pages: 129
- Format: PDF
- Report ID: PM5947
- Base Year: 2024
- Historical Data: 2020-2023
Overview
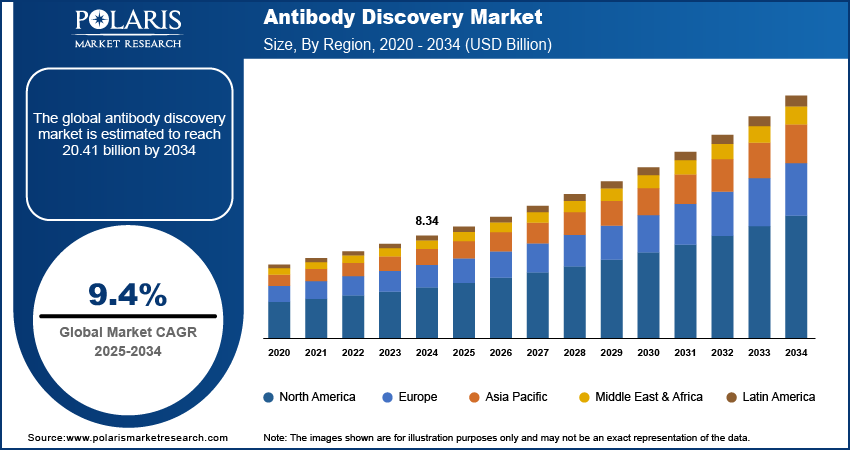
The global antibody discovery market size was valued at USD 8.34 billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 9.4% from 2025 to 2034. The growth is driven by the growing prevalence of chronic and infectious diseases and increasing investments in biopharmaceutical research and development (R&D).
Key Insights
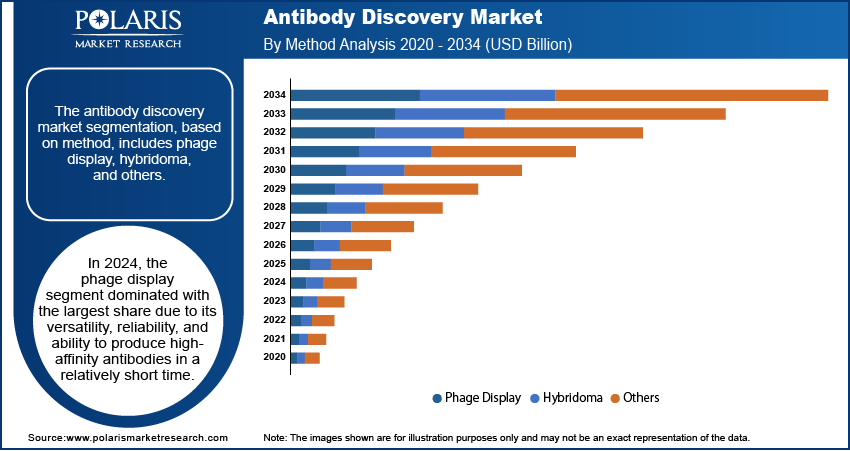
- In 2024, the phage display segment dominated with the largest share.
- The murine antibody centers segment is expected to experience significant growth during the forecast period.
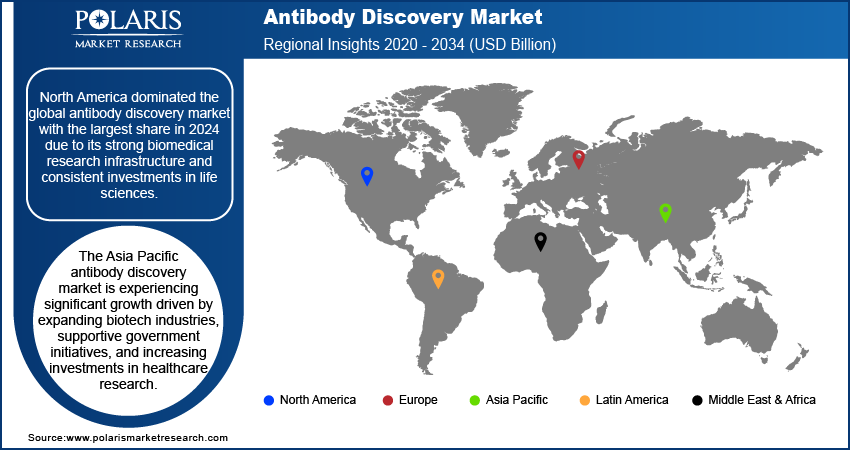
- North America dominated with the largest share in 2024, due to its strong biomedical research infrastructure
- The antibody discovery industry in the U.S. is expected to witness significant growth during the forecast period due to its advanced research capabilities and strong presence of biotech firms
- The market in Asia Pacific is projected to witness substantial growth driven by expanding biotech industries and supportive government initiatives.
- Countries such as China, India, South Korea, and Japan are investing in biotechnology infrastructure to improve domestic research capabilities
Antibody discovery is the process of identifying and developing antibodies that specifically bind to target molecules, such as proteins on the surface of pathogens or diseased cells. It is a critical step in creating therapeutic antibodies for treating various diseases such as cancer, autoimmune disorders, and infectious diseases. The process involves immunizing animals or using synthetic libraries, isolating B cells, and screening for antibodies with high affinity and specificity. Modern techniques, such as single B-cell screening, phage display, and bioinformatics services, have accelerated discovery timelines, enabling the development of fully human or humanized antibodies with reduced immunogenicity and improved therapeutic potential.
To Understand More About this Research: Request a Free Sample Report
Regulatory agencies such as the FDA and EMA (European Medicines Agency) are actively supporting the development of biologics, including antibodies, by creating fast-track approval pathways and providing clearer guidelines. This support encourages pharmaceutical companies to invest in antibody discovery. In particular, orphan drug status and priority review programs benefit antibody therapies designed for rare or life-threatening diseases. This regulatory clarity reduces uncertainty and delays in development timelines. Additionally, harmonization of international regulations makes it easier for companies to work across borders and develop therapies for global industries. These changes lower the risk and cost associated with drug development, making antibody discovery more accessible to companies of different sizes, thereby driving the growth.
The rising adoption of technological advancements to discover antibodies is driving the growth. Traditional methods such as hybridoma technology are being replaced or supported by more efficient tools such as single B-cell screening, phage display, and microfluidic systems. These newer approaches enable researchers to identify antibodies more quickly, with greater accuracy and less trial and error. Technologies that enable high-throughput screening, artificial intelligence-based selection, and sequencing of individual cells have reduced the time and cost involved in early-stage drug discovery. These improvements further help find antibodies that work well in humans and have fewer side effects. Consequently, more companies and research labs are adopting these advanced tools, which is increasing the pace of innovation in the field.
Industry Dynamics
- The growing prevalence of chronic and infectious diseases drives the demand for antibodies for effective therapeutics.
- Increase in Investments in biopharmaceutical R&D is driving the growth.
- Technological advancements in the antibody discovery platform make the platform more appealing and user-friendly.
- The high cost and time involved in research and development are restraining market growth, as developing and validating effective antibodies require complex technologies, skilled personnel, and lengthy clinical trials, which limit accessibility for smaller biotech firms.
Growing Prevalence of Chronic and Infectious Diseases: The number of chronic and infectious disease cases is rising worldwide, which is driving the demand for effective therapeutics and medications. According to the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services, in the U.S. alone, 1.2 million people are affected by HIV as of 2025. Conditions such as cancer, autoimmune disorders, and viral infections (such as COVID-19 and HIV) require more advanced and targeted treatment options. Antibodies offer a way to target specific cells or pathogens without affecting healthy tissues, making them a preferred approach in modern medicine. The need for new antibody-based therapies increases as these diseases continue to spread globally due to aging populations, lifestyle changes, and urbanization. This demand pushes research organizations, pharmaceutical companies, and biotech firms to invest in faster and more efficient antibody discovery methods. Additionally, emerging diseases require the rapid development of new therapies, which drives the use of modern antibody screening and development platforms to identify effective candidates quickly and safely, thereby fueling the demand for antibody discovery.
Increasing Investments in Biopharmaceutical R&D: Pharmaceutical and biotech companies invest more in research and development, particularly in the area of biologics, which includes antibodies. In April 2025, Merck opened the Biologics Center of Excellence in Wilmington, Delaware worth of USD 1 billion. This increase in R&D budgets is a significant driver of the demand for antibody discovery. Companies recognize that biologics are becoming more important in treating complex diseases, and antibodies are a large part of this category. Governments and private investors are further funding antibody research to support innovation and respond to global health challenges. These investments support the development of specialized discovery platforms, expansion of lab infrastructure, and hiring of skilled researchers. The increased funding further allows companies to take on more experimental projects, increasing the chances of discovering breakthrough therapies. Confidence in these investments continues to grow as the success rate and approval of antibody-based drugs rise, further fueling discovery efforts, thereby driving the growth.

Segmental Insights
Method Analysis
The segmentation, based on method, includes phage display, hybridoma, and others. In 2024, the phage display segment dominated with the largest share due to its versatility, reliability, and ability to produce high-affinity antibodies in a relatively short time. This method involves using bacteriophages to display antibody fragments on their surfaces, which are then screened against a target antigen. Phage display is particularly useful for identifying antibodies with desired binding properties, eliminating the need for animal immunization. It allows researchers to explore large libraries of antibody variants efficiently, making it suitable for both early-stage discovery and later optimization. The technique is widely adopted because of its compatibility with automation and scalability. Pharmaceutical companies prefer it for its cost-effectiveness and proven track record in developing several FDA-approved therapeutics. Its use is widespread across drug development pipelines for cancer, autoimmune, and infectious diseases, which is further driving the segment growth.
The hybridoma segment is expected to experience significant growth during the forecast period due to ongoing improvements in its efficiency and applications. This method involves fusing B-cells from immunized animals with myeloma cells to create hybrid cells that produce large quantities of a single type of antibody. While it was once considered slower and less scalable than newer technologies, recent advancements have made hybridoma processes faster and more reliable. Improved screening tools and better animal models help researchers get more relevant and functional antibodies through this method. Hybridoma-derived antibodies are widely used in research and diagnostics, and they remain valuable for generating murine antibodies, which are then humanized for therapeutic use, thereby driving the segment growth.
Antibody Type Analysis
The segmentation, based on antibody type, includes humanized antibody, human antibody, chimeric antibody, and murine antibody. The murine antibody segment is expected to experience significant growth during the forecast period, as these antibodies are the starting point for therapeutic antibody development. Murine antibodies are widely used in research, diagnostics, and as templates for further engineering into humanized or fully human antibodies. Murine antibodies can now be efficiently converted into safer and more effective therapies with advancements in humanization techniques and genetic modification of mice. Their use further continues to grow in laboratory settings where cost and speed are important, such as in early-stage screening. The demand for murine-derived platforms has remained strong, particularly as new transgenic mouse models such as HUGO-Ab enable the production of human-like antibodies, thereby driving the segment growth.
End User Analysis
The segmentation, based on end user, includes pharmaceutical and biotechnology industry, research laboratory, and academic laboratory. The pharmaceutical and biotechnology industry segment is expected to experience significant growth during the forecast period as these companies are increasingly focused on developing biologic drugs, including monoclonal antibodies, to treat a wide range of conditions such as cancer, autoimmune diseases, and infectious diseases. Antibody-based drugs have shown strong clinical success, prompting further investments in discovery platforms. Biotech startups and large pharmaceutical firms alike are expanding their internal capabilities or partnering with specialized service providers to access high-throughput screening tools, AI-powered analysis, and single B-cell discovery methods. These industries are further driving demand for personalized and targeted therapies, which rely heavily on precise antibody identification, thereby driving the segment growth.
Regional Analysis
North America Antibody Discovery Market Trend
North America dominated with the largest share in 2024, due to its strong biomedical research infrastructure and consistent investment in life sciences. The presence of major pharmaceutical companies and biotech firms across the region drives innovation and early adoption of advanced technologies. Governments and private sectors in countries such as the U.S. and Canada actively support R&D initiatives through funding and collaboration with academic institutions. Moreover, there is a growing demand for targeted therapies and biologics, which rely heavily on the discovery of specific, high-affinity antibodies. The region further benefits from well-established regulatory frameworks that support clinical trials and product development. The increasing prevalence of chronic diseases such as cancer and autoimmune disorders is further pushing the demand for novel antibody-based therapies, thereby driving the growth.
U.S. Antibody Discovery Market Insights
The market in the U.S. is expected to witness significant growth during the forecast period, due to its advanced research capabilities and strong presence of biotech firms. Federal agencies such as the NIH offer extensive funding, while partnerships between universities and industry players accelerate innovation. High healthcare spending and a well-structured regulatory framework support the development and commercialization of antibody-based drugs. Moreover, a large number of clinical trials are conducted in the U.S., facilitating faster validation of new therapies. Demand for monoclonal antibodies in oncology, immunology, and infectious diseases continues to grow, reinforcing the need for efficient discovery platforms. Technological advancements, such as AI-driven screening and single-cell analysis, are being rapidly adopted. The U.S. is further influenced by a skilled workforce and access to advance lab infrastructure, making it a vital hub for global antibody discovery efforts, thereby driving the growth.
Asia Pacific Antibody Discovery Market Analysis
The market in Asia Pacific is projected to witness substantial growth driven by expanding biotech industries, supportive government initiatives, and increasing investment in healthcare research. Countries such as China, India, South Korea, and Japan are investing in biotechnology infrastructure to improve domestic research capabilities. The region is witnessing growing demand for biologics, including antibody-based treatments, due to rising incidences of chronic diseases and an aging population. Additionally, local pharmaceutical companies are forming global partnerships to access advanced discovery technologies. Regulatory systems are gradually becoming more streamlined, making it easier for companies to conduct preclinical and clinical research. Asia Pacific’s cost-effective R&D capabilities and growing talent pool make it an attractive region for antibody discovery, thereby driving the growth.
China Antibody Discovery Market Overview
The market in China is expected to experience significant growth, driven by strong government support and increasing investments in biotech innovation. National initiatives such as "Made in China 2025" and significant funding from local and central governments have encouraged the development of advanced biologics, including monoclonal antibodies. Chinese pharmaceutical companies are expanding their capabilities in antibody discovery through partnerships, acquisitions, and collaborations with academic institutions. The country has also made progress in building a more structured regulatory environment, which supports clinical development and market entry for biologics. There is a strong demand for innovative therapies with a large patient population and a high burden of diseases such as cancer and autoimmune disorders. Additionally, China's growing expertise in areas such as AI and big data is being integrated into drug discovery processes, improving speed and accuracy, thereby driving the growth.
Europe Antibody Discovery Market Outlook
The market in Europe is expected to experience significant growth driven by a robust network of academic institutions, pharmaceutical companies, and research organizations. The region benefits from strong public and private investments in life sciences, particularly in countries such as the UK, Germany, France, and Switzerland. The European Union has consistently funded biotech research through initiatives such as Horizon Europe, which supports innovation across therapeutic areas. Europe's focus on precision medicine and targeted therapies continues to drive demand for novel antibody-based treatments. In addition, the region has a clear regulatory pathway through the European Medicines Agency (EMA), which encourages the development and approval of biologics. Collaborative research projects across borders are common, and the presence of skilled researchers and advanced facilities further accelerates discovery efforts. The increasing focus on chronic diseases, rare conditions, and immune therapies is further driving the growth.
Germany Antibody Discovery Market Assessment
The market growth in Germany is driven by its strong biotechnology sector, world-class research institutions, and a supportive regulatory environment. The country comprises numerous biotech startups and large pharmaceutical firms actively involved in antibody research and development. Government programs and funding initiatives, such as those from the Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF), support innovation and partnerships between academia and industry. Germany’s emphasis on high-quality research infrastructure, including state-of-the-art laboratories and clinical trial facilities, provides a solid foundation for early-stage discovery. Additionally, Germany has a growing interest in therapeutic antibodies for cancer, autoimmune diseases, and infectious conditions, reflecting global trends in healthcare. The integration of emerging technologies, such as AI and high-throughput screening, is improving the efficiency of antibody identification and development.
Key Players and Competitive Analysis
The field of antibody discovery is highly competitive, driven by innovation, speed, and technological integration. Key players such as Biocytogen and Genscript Technology Corporation leverage advanced gene-editing and single B-cell platforms to accelerate fully human antibody discovery. Charles River Laboratories and Eurofins Scientific offer comprehensive CRO services, supporting end-to-end biologic development. Danaher Corporation, through subsidiaries such as Cytiva and Beckman Coulter, provides critical instrumentation and reagents that underpin discovery workflows. Creative Biolabs and Fairjourney Biologics S.A specialize in custom antibody generation, including phage display and hybridoma technologies. Twist Bioscience stands out for its synthetic biology expertise, offering high-throughput DNA synthesis for antibody libraries. Evotec combines AI-driven drug discovery with antibody development capabilities, while Sartorius AG supports process development with scalable bioprocessing tools. As the market shifts toward fully human and bispecific antibodies, competition is intensifying around speed, precision, and platform innovation, with strategic partnerships and acquisitions playing a key role in market consolidation.
Key Players
- Biocytogen
- Charles River Laboratories
- Creative Biolabs
- Danaher Corporation
- Eurofins Scientific
- Evotec
- Fairjourney Biologics S.A
- Genscript Technology Corporation
- Sartorius AG
- Twist Bioscience
Industry Developments
In April 2025, Antibody Solutions launched its new single plasma B-cell discovery service through the Cellestive platform, enabling clients to access deeper antibody screening data and tackle difficult targets with high-throughput, AI-driven analysis and optimized recovery of antibody sequences.
In March 2025, Biointron launched its high-throughput fully human antibody discovery platform, combining AbDrop microfluidic screening technology with Cyagen’s HUGO-Ab mice. This platform enabled rapid, precise development of fully human antibodies in as little as three months, offering enhanced genetic diversity, reduced immunogenicity, and cost-effective therapeutic antibody discovery for a wide range of biomedical applications.
Antibody Discovery Market Segmentation
By Method Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- Phage Display
- Hybridoma
- Others
By Antibody Type Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- Humanized Antibody
- Human Antibody
- Chimeric Antibody
- Murine Antibody
By End User Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- Pharmaceutical and Biotechnology industry
- Research laboratory
- Academic laboratory
By Regional Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- North America
- U.S.
- Canada
- Mexico
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- UK
- Italy
- Spain
- Netherlands
- Russia
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- Malaysia
- South Korea
- Indonesia
- Australia
- Vietnam
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Middle East & Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Israel
- South Africa
- Rest of Middle East & Africa
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
Report Scope
|
Report Attributes |
Details |
|
Market Size in 2024 |
USD 8.34 Billion |
|
Market Size in 2025 |
USD 9.11 Billion |
|
Revenue Forecast by 2034 |
USD 20.41 Billion |
|
CAGR |
9.4% from 2025 to 2034 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Historical Data |
2020–2023 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025–2034 |
|
Quantitative Units |
Revenue in USD Billion and CAGR from 2025 to 2034 |
|
Report Coverage |
Revenue Forecast, Competitive Landscape, Growth Factors, and Industry Trends |
|
Segments Covered |
|
|
Regional Scope |
|
|
Competitive Landscape |
|
|
Report Format |
|
|
Customization |
Report customization as per your requirements with respect to countries, regions, and segmentation. |
FAQ's
The global market size was valued at USD 8.34 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow to USD 20.41 billion by 2034.
The global market is projected to register a CAGR of 9.4% during the forecast period.
North America dominated the market share in 2024.
A few of the key players in the market are Biocytogen, Charles River Laboratories, Creative Biolabs, Danaher Corporation, Eurofins Scientific, Evotec, Fairjourney Biologics S.A, Genscript Technology Corporation, Sartorius AG, and Twist Bioscience.
The phage display segment dominated the market share in 2024.
The pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies segment is expected to witness the significant growth during the forecast period.
