
Antifungal Drugs Market Size, Share, Trend, Industry Analysis Report
By Drug Class (Azoles, Echinocandins, Polyenes, Allylamines, Others), By Indication, By Dosage Form, By Distribution Channel, By Region – Market Forecast, 2025–2034
- Published Date:Jul-2025
- Pages: 129
- Format: PDF
- Report ID: PM6045
- Base Year: 2024
- Historical Data: 2020-2023
Overview
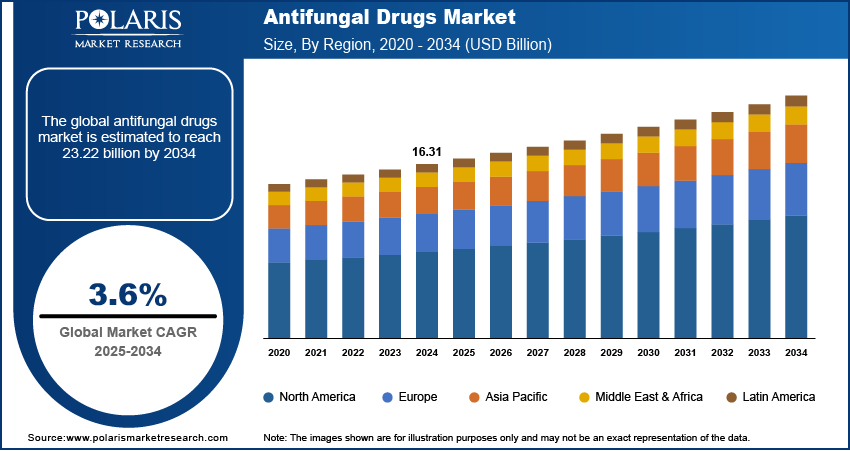
The global antifungal drugs market size was valued at USD 16.31 billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 3.6% from 2025 to 2034. Immunocompromised populations, including cancer patients, organ transplant recipients, and individuals affected by HIV, are increasingly susceptible to fungal infections. The growing patient base prone to fungal infections is driving demand for antifungal therapies.
Key Insights
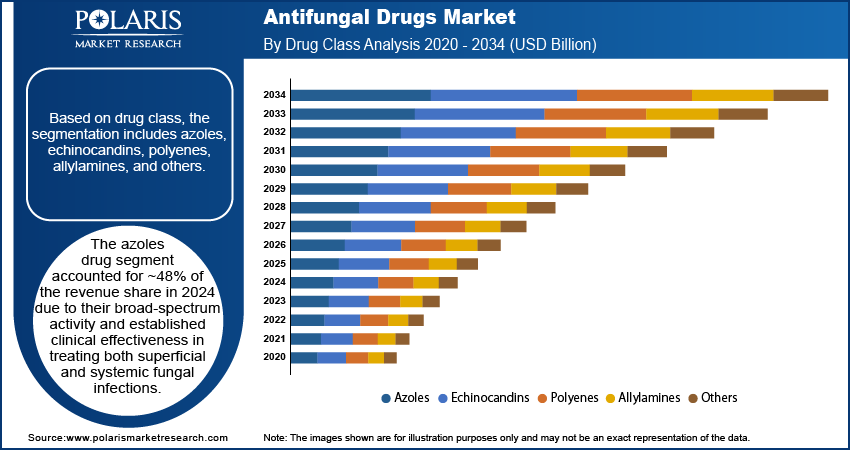
- Azoles drug segment accounted for ~48% of the revenue share in 2024 due to their broad-spectrum activity
- Candidiasis segment held the largest revenue share in 2024 due to its high prevalence among immunocompromised and hospitalized patients.
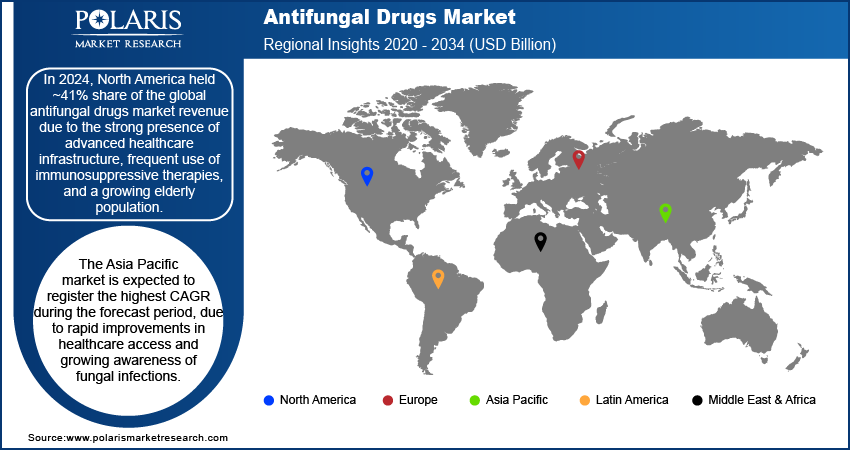
- In 2024, North America antifungal drugs market accounted for ~41% of the revenue share due to strong presence of advanced healthcare infrastructure
- In 2024, the U.S. is accounted for the significant revenue share due to its high incidence of hospital-acquired fungal infections and a large immunocompromised patient base
- Asia Pacific is expected to grow at a fastest CAGR over the forecast period due to rapid improvements in healthcare access and growing awareness of fungal infections
- China is witnessing strong growth due to rising rates of fungal infections linked to an aging population and expanding chronic disease burden.
Industry Dynamics
- The aging population is contributing significantly to the rising demand for antifungal drugs.
- The increasing number of individuals having compromised immune systems is driving the prevalence of fungal infections worldwide
- Wider use of immunosuppressive treatments in oncology and autoimmune diseases is raising the incidence of opportunistic fungal infections.
- High cost of the product hinders the market expansion.
Market Statistics
- 2024 Market Size: USD 16.31 billion
- 2034 Projected Market Size: USD 23.22 billion
- CAGR (2025–2034): 3.6%
- North America: Largest market in 2024
The antifungal drugs market involves the development, production, and distribution of medications used to treat fungal infections in humans. These drugs target infections caused by fungi such as Candida, Aspergillus, and Cryptococcus, addressing both superficial and systemic infections. Fungal infections such as candidiasis are becoming more common in clinical settings due to invasive procedures, catheter use, and prolonged ICU stays, pushing hospitals to adopt antifungal drugs as part of infection control protocols.
To Understand More About this Research: Request a Free Sample Report
The wider use of immunosuppressive treatments in oncology and autoimmune diseases is increasing the incidence of opportunistic fungal infections, leading to a growing demand for preventive and therapeutic antifungal drugs. Moreover, improved antifungal formulations, including extended-release tablets, liposomal delivery systems, and topical solutions, are enhancing efficacy and patient compliance, driving market growth.
Drivers and Opportunities
Growing Geriatric Population: The aging population is contributing significantly to the rising demand for antifungal drugs. According to the World Health Organization, the global population of individuals aged 60 years and above will increase to ~2.1 billion by 2050. Older adults often experience a decline in immune function, making them more vulnerable to fungal infections that affect the skin, nails, lungs, and mucous membranes. Conditions such as onychomycosis, oral thrush, and systemic fungal infections are more common in this group due to various factors such as diabetes, use of immunosuppressive medications, and chronic illnesses. Healthcare providers are seeing a growing need for targeted antifungal treatments that are both safe and effective for elderly patients. Thus, this demographic shift is steadily increasing the consumption of antifungal medications.
Rising Prevalence of Fungal Infections: The increasing number of individuals having compromised immune systems is driving the prevalence of fungal infections worldwide. According to the International Society for Infectious Diseases, global estimates indicate an annual incidence of ~6.5 million cases of invasive fungal infections. These infections are associated with roughly 3.8 million fatalities, with around 2.5 million of these deaths (68%, with a range of 35–90%) being directly attributable to the infections themselves. Cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy, HIV-positive individuals, and organ transplant recipients are at a higher risk of contracting serious fungal diseases such as candidiasis and aspergillosis. These infections, often life-threatening if not treated early, require prompt and potent antifungal therapy. Hospitals and clinics are expanding antifungal drug use as part of their treatment protocols to manage complications in vulnerable patients. This growing patient base is directly contributing to the steady rise in antifungal drug prescriptions and new drug development.

Segmental Insights
Drug Class Analysis
Based on drug class, the segmentation includes azoles, echinocandins, polyenes, allylamines, and others. The azoles segment accounted for ~48% of the revenue share in 2024 due to their broad-spectrum activity and established clinical effectiveness in treating both superficial and systemic fungal infections. These drugs are commonly prescribed for various conditions such as candidiasis, dermatophytosis, and aspergillosis, making them a staple in antifungal therapy. Their availability in multiple formulations, including oral and topical, supports widespread clinical use across different care settings. Healthcare providers prefer azoles due to their predictable pharmacokinetics and lower toxicity profile compared to other antifungal classes. Continued use in both hospital and outpatient treatments has helped sustain their market dominance.
The echinocandins drug segment is projected to register the highest CAGR from 2025 to 2034, due to their targeted mechanism of action against Candida and Aspergillus species, including drug-resistant strains. These drugs are often used in hospitalized patients where systemic fungal infections present serious risks. Their low toxicity and high efficacy make them suitable for critically ill individuals. Growing awareness of antifungal resistance is pushing healthcare systems to adopt newer-generation echinocandins. Their intravenous administration supports controlled dosing in inpatient settings, which is particularly valuable in cases of invasive fungal infections. Continued innovation and updated clinical guidelines are boosting their usage in advanced care settings.
Indication Analysis
In terms of indication, the segmentation includes dermatophytosis, aspergillosis, candidiasis, and others. The candidiasis segment held the largest revenue share in 2024 due to its high prevalence among immunocompromised and hospitalized patients. This fungal infection manifests in various forms, ranging from oral and vaginal candidiasis to life-threatening systemic infections. The use of catheters, broad-spectrum antibiotics, and intensive care procedures increases the risk of infection, prompting early and aggressive antifungal treatment. Azoles and echinocandins are widely used to manage different stages of candidiasis, contributing to strong pharmaceutical demand. The condition’s frequency across outpatient and inpatient environments, along with growing diagnostic capabilities, continues to support its leading position within the antifungal treatment landscape.
The aspergillosis segment is expected to register a significant CAGR during the forecast period, due to rising cases among patients undergoing chemotherapy, transplants, and other immunosuppressive therapies. This opportunistic fungal infection poses serious risks in hospital settings, particularly among individuals with weakened immune systems. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are critical, often requiring intravenous antifungal drugs such as echinocandins or voriconazole. Increasing awareness of invasive aspergillosis and improvements in fungal diagnostic technologies are leading to earlier intervention. Expanding use of antifungal prophylaxis in high-risk populations is also contributing to rising demand for effective medications targeting this specific indication.
Dosage Form Analysis
In terms of dosage form, the segmentation includes oral drugs, ointments, powders, and others. The oral drugs segment accounted for the largest revenue share in 2024, due to the ease of administration, patient compliance, and effectiveness in treating both superficial and systemic infections. Tablets and capsules are widely used in outpatient care, particularly for long-term treatments such as onychomycosis or recurrent vaginal infections. Their stability, shelf-life, and availability across a range of antifungal classes make them the preferred option for healthcare providers. Oral antifungals are often the first line of treatment and are commonly prescribed in both public and private healthcare settings. The convenience of home-based therapy continues to support strong market demand.
The ointment segment is projected to grow at the fastest pace over the forecast period due to increasing demand for topical treatments of superficial infections such as athlete’s foot, ringworm, and candidal skin infections. These formulations offer localized action with minimal systemic absorption, reducing the risk of side effects. They are preferred for first-line treatment of uncomplicated cases and are widely available over-the-counter, making them accessible to a large consumer base. Rising awareness of personal hygiene and growing use of self-medication practices are boosting sales of topical antifungal ointments in both pharmacies and online platforms.
Distribution Channel Analysis
In terms of distribution channel, the segmentation includes hospital pharmacies, retail pharmacies, and others. The hospital pharmacies segment accounted for the largest revenue share in 2024, due to the high usage of antifungal drugs in managing severe systemic infections among inpatients. Conditions such as candidemia, aspergillosis, and fungal sepsis often require immediate administration of IV formulations, which are stocked and dispensed primarily through hospital channels. Healthcare professionals rely on hospital pharmacies for controlled, timely drug delivery in critical care settings. Strong demand for echinocandins and other hospital-restricted antifungals ensures consistent procurement and inventory turnover. The role of clinical pharmacists in managing dosing and drug interactions further supports hospital-based distribution.
The retail pharmacies segment is projected to witness the fastest growth during the forecast period due to increasing consumer demand for over-the-counter (OTC) antifungal treatments and rising prescription volumes for outpatient care. Conditions such as athlete’s foot, vaginal yeast infections, and oral thrush are frequently managed outside hospital settings, making retail channels a vital point of access. Convenience, widespread availability, and online pharmacy expansion are enabling consumers to obtain antifungal products without delay. Enhanced awareness about early treatment and rising use of self-care options are further contributing to strong retail pharmacy sales across urban and rural markets.
Regional Analysis
In 2024, the North America antifungal drugs market accounted for ~41% of the revenue share due to the strong presence of advanced healthcare infrastructure, frequent use of immunosuppressive therapies, and a growing elderly population. Hospitals across the region have high rates of invasive procedures, leading to increased risk of fungal infections such as candidiasis and aspergillosis. The widespread availability of prescription and over-the-counter antifungal medications, coupled with strong awareness among both patients and healthcare providers, is driving consistent market expansion. Investments in research and drug development continue to support the introduction of new antifungal formulations.
U.S. Antifungal Drugs Market Insights
In 2024, the U.S. accounted for a significant revenue share due to its high incidence of hospital-acquired fungal infections and a large immunocompromised patient base. Widespread use of chemotherapy, organ transplantation, and intensive care support contributes to elevated fungal infection risk. The availability of advanced diagnostic services enables faster identification of fungal strains, improving treatment outcomes. Leading pharmaceutical companies based in the U.S. are actively engaged in developing new antifungal agents, further driving market growth. Increased awareness about early treatment and preventive therapies is also playing a key role in expanding drug adoption nationwide.
Asia Pacific Antifungal Drugs Market Overview
The Asia Pacific market is expected to register the highest CAGR over the forecast period due to rapid improvements in healthcare access and growing awareness of fungal infections. Urbanization and rising cases of diabetes and chronic illnesses are contributing to higher vulnerability among populations. According to the International Diabetes Federation 2024 data, Japan reported ~93 million cases of diabetes, with a prevalence rate of 8.1% among adults. This translates to about 8.97 million adult diabetes cases in the country. Hospitals in emerging markets are seeing more patients undergoing surgeries and intensive therapies. These therapies increase the incidence of fungal infections, creating a strong need for antifungal treatments. Expanding pharmaceutical manufacturing capabilities and favorable government initiatives to improve healthcare infrastructure are also encouraging the introduction of new antifungal drugs. High demand for affordable generics is expected to further boost regional growth in the coming years.
China Antifungal Drugs Market Outlook
The market in China is witnessing strong growth, due to the rising rates of fungal infections linked to an aging population and expanding chronic disease burden. Increasing adoption of Western medical practices, including chemotherapy and surgical interventions, is creating a larger pool of at-risk patients. The government’s continued investments in healthcare modernization improved hospital capacity and diagnostic capabilities, enabling faster detection and treatment of fungal infections. Domestic pharmaceutical companies are increasing the production of antifungal formulations, both generic and branded, to meet the increasing demand for antifungal drugs. Rising health awareness is also influencing consumer behavior toward early treatment of superficial infections.
Europe Antifungal Drugs Market Trends
The market in Europe is expanding steadily due to a strong focus on evidence-based treatment protocols and public healthcare systems. A large aging population and rising use of immunosuppressive therapies across the region are contributing to an increase in fungal infections. Research-driven medical practices, supported by regional health agencies, encourage early diagnosis and standardized treatment of fungal diseases. Hospitals and clinics across Europe maintain consistent access to a range of antifungal drugs through centralized procurement systems. Ongoing surveillance of antimicrobial resistance and proactive development of alternative therapies are creating favorable conditions for antifungal market expansion across EU countries.
Key Players and Competitive Analysis
The competitive landscape of the antifungal drugs market is shaped by robust research pipelines, increasing partnerships, and sustained efforts toward addressing drug resistance. Industry analysis highlights a shift toward targeted antifungal therapies and improved formulations. Market expansion strategies include penetration into emerging regions, development of broad-spectrum antifungals, and launch of fixed-dose combinations. Leading players are engaging in mergers and acquisitions to enhance their antifungal portfolios, followed by focused post-merger integration to streamline R&D and regulatory workflows. Joint ventures and strategic alliances between biotech firms and pharmaceutical giants are accelerating clinical trials and commercial reach. Technology advancements in drug delivery systems, including liposomal and nanoparticle-based formulations, are improving therapeutic outcomes. Investments in diagnostics and antifungal stewardship programs are further influencing competitive positioning. The rising prevalence of systemic mycoses and multidrug-resistant fungal strains is compelling manufacturers to innovate across topical, oral, and intravenous formulations, shaping a dynamic and innovation-driven market environment.
Key Players
- Abbott
- Astellas Pharma, Inc.
- Bayer AG
- Enzon Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
- Glenmark
- GSK plc
- Merck & Co., Inc.
- Novartis AG
- Pfizer, Inc.
- Sanofi
Antifungal Drugs Industry Developments
December 2023: The FDA granted approval for the expanded indication of CRESEMBA (isavuconazonium sulfate) for pediatric patients diagnosed with invasive aspergillosis and invasive mucormycosis. This decision enhances treatment options for these serious fungal infections in children, allowing for the utilization of isavuconazonium sulfate beyond its previous limitations.
Antifungal Drugs Market Segmentation
By Drug Class Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- Azoles
- Echinocandins
- Polyenes
- Allylamines
- Others
By Indication Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- Dermatophytosis
- Aspergillosis
- Candidiasis
- Others
By Dosage Form Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- Oral Drugs
- Ointments
- Powders
- Others
By Distribution Channel Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- Hospital Pharmacies
- Retail Pharmacies
- Others
By Regional Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- North America
- U.S.
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- UK
- Italy
- Spain
- Netherlands
- Russia
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- Malaysia
- South Korea
- Indonesia
- Australia
- Vietnam
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Middle East & Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Israel
- South Africa
- Rest of Middle East & Africa
- Latin America
- Mexico
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
Antifungal Drugs Market Report Scope
|
Report Attributes |
Details |
|
Market Size in 2024 |
USD 16.31 billion |
|
Market Size in 2025 |
USD 16.89 billion |
|
Revenue Forecast by 2034 |
USD 23.22 billion |
|
CAGR |
3.6% from 2025 to 2034 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Historical Data |
2020–2023 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025–2034 |
|
Quantitative Units |
Revenue in USD billion and CAGR from 2025 to 2034 |
|
Report Coverage |
Revenue Forecast, Competitive Landscape, Growth Factors, and Industry Trends |
|
Segments Covered |
|
|
Regional Scope |
|
|
Competitive Landscape |
|
|
Report Format |
|
|
Customization |
Report customization as per your requirements with respect to countries, regions, and segmentation. |
FAQ's
The global market size was valued at USD 16.31 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow to USD 23.22 billion by 2034.
The global market is projected to register a CAGR of 3.6% during the forecast period.
In 2024, North America accounted for a ~41% share of the global antifungal drugs market revenue, due to the strong presence of advanced healthcare infrastructure, frequent use of immunosuppressive therapies, and a growing elderly population.
A few of the key players in the market are Abbott; Astellas Pharma, Inc.; Bayer AG; Enzon Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; Glenmark; GSK plc; Merck & Co., Inc.; Novartis AG; Pfizer, Inc.; and Sanofi.
The azoles drug segment accounted for ~48% of the revenue share in 2024 due to their broad-spectrum activity and established clinical effectiveness in treating both superficial and systemic fungal infections.
The candidiasis segment held the largest revenue share in 2024 due to its high prevalence among immunocompromised and hospitalized patients.
