
E-Fuel Market Size, Share, Trend, Industry Analysis Report
By Product (E-Diesel, E-Gasoline, Ethanol, Hydrogen, Methanol, Others), By State, By Production Method, By End User, By Region – Market Forecast, 2025–2034
- Published Date:Aug-2025
- Pages: 129
- Format: PDF
- Report ID: PM3873
- Base Year: 2024
- Historical Data: 2020-2023
Overview
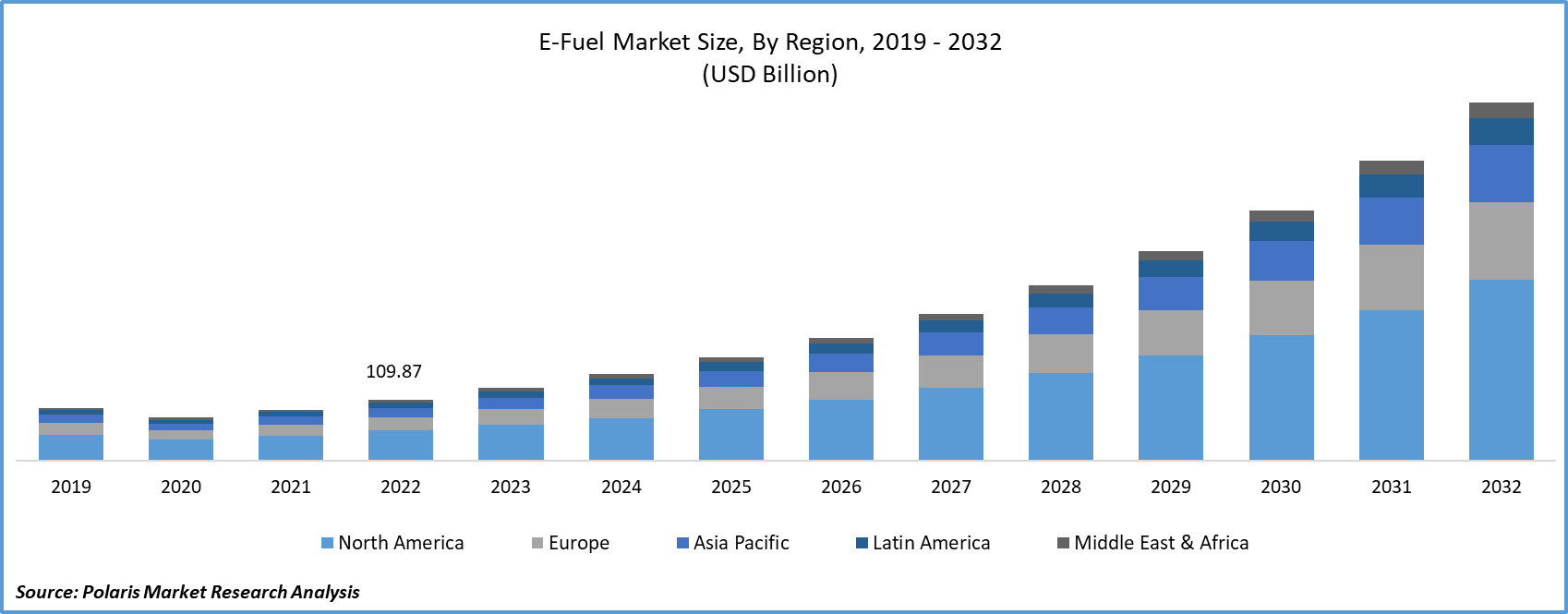
The global e-fuel market size was valued at USD 132.32 billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 24.5% from 2025 to 2034. Supportive policy measures such as carbon taxes, fuel blending mandates, and net-zero roadmaps are encouraging investments in e-fuel technologies. These regulations are accelerating commercial adoption by creating economic incentives and regulatory pressure on fossil fuel-dependent industries.
Key Insights
- The ethanol segment held ~42% of the market share in 2024, driven by its compatibility with existing engines and fuel infrastructure.
- The liquid segment dominated with ~82% revenue share in 2024, due to seamless integration with current fuel storage, transport, and dispensing systems.
- The power-to-liquid segment captured ~48% of the market in 2024, due to its ability to produce high-energy e-diesel and e-kerosene for aviation and heavy transport.
- The market in North America is projected to register a CAGR of 25.2% from 2025 to 2034, supported by federal and state-level clean fuel incentives and decarbonization policies.
- The U.S. led the North America market with ~89% share in 2024, driven by active pilot and commercial e-fuel projects supported by federal funding.
- The market in Asia Pacific generated USD 23.9 billion in 2024, fueled by rising green hydrogen investments and efforts to reduce fuel import dependence.
- China led the regional market with ~41% share in 2024, driven by strict decarbonization mandates across industry, transport, and shipping sectors.
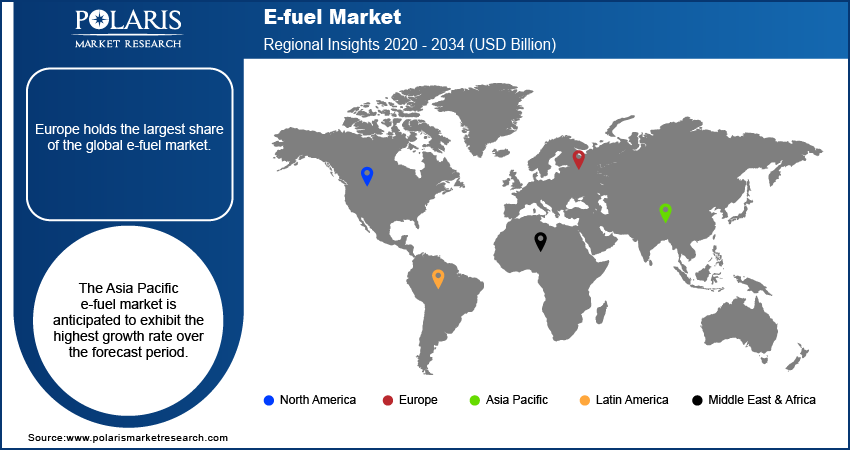
- Europe held ~49% of the global market in 2024, supported by ambitious net-zero goals, strict emissions rules, and targeted clean fuel regulations.
Industry Dynamics
- Rising fuel import dependency in China, Japan, and South Korea is driving investments in domestic e-fuel and green hydrogen production.
- Government-backed green hydrogen valleys and industrial decarbonization plans are enabling e-fuel pilot projects in key regions.
- Growing focus on clean shipping corridors boosts demand for e-ammonia and e-methanol in maritime transport.
- Underdeveloped carbon capture infrastructure and policy fragmentation delay commercial-scale e-fuel adoption across the region.
Market Statistics
- 2024 Market Size: USD 132.32 billion
- 2034 Projected Market Size: USD 1,060.06 billion
- CAGR (2025–2034): 24.5%
- Europe: Largest market in 2024
AI Impact on E-Fuel Market
- In e-fuel production, AI is used to boost operational efficiency, as it helps reduce production costs and improve scalability.
- The technology enables predictive, data-driven decision making across maintenance, logistics, and process control.
- AI-based tools help streamline regulatory compliance, a huge hurdle for nascent fuel tech.
- From startups digitizing operations to automotive giants focusing on boosting vertical e-fuel production, AI integration is projected to deliver more scalable, cost-effective, and sustainable e-fuel solutions.
The e-fuel market refers to the industry focused on the production, distribution, and application of synthetic fuels created using renewable electricity and captured carbon dioxide or hydrogen. These fuels serve as low-emission alternatives to conventional fossil fuels in sectors such as aviation, shipping, and heavy transport, where full electrification remains technologically or economically challenging. E-fuels include options like e-diesel, e-kerosene, and e-methanol, produced via Power-to-Liquid (PtL) or Power-to-Gas (PtG) processes. The market is driven by decarbonization goals, policy mandates, and innovations in renewable energy integration, positioning e-fuels as a key component of the global clean energy transition. Improvements in electrolyzer efficiency and cost reduction in green hydrogen production are enhancing the economic viability of e-fuel synthesis. These technological strides are enabling scalable e-fuel production aligned with renewable electricity generation.
Many sectors such as aviation, marine, and heavy-duty transport face limitations in adopting battery-based electrification. E-fuels offer a viable low-carbon alternative by enabling existing internal combustion engines to meet sustainability targets without major infrastructure overhauls. Moreover, e-fuels provide a storage solution for excess renewable electricity during peak production periods. Converting surplus solar and wind energy into liquid fuels ensures grid stability while creating a storable and transportable energy vector.
Drivers & Opportunities
Government Regulations and Carbon Pricing: Government policies are playing a key role in driving the e-fuel market forward. Carbon taxes are making traditional fossil fuels more expensive, creating a cost advantage for low-emission alternatives such as e-fuels. Blending mandates require a certain percentage of renewable or synthetic fuels to be mixed with conventional fuels, directly increasing e-fuel demand. National and international net-zero goals are further pushing industries to explore cleaner fuel sources. These regulations are encouraging investments in e-fuel production technologies and also pushing end-users to adopt them. According to the International Energy Agency, in November 2024, global investment in e-fuel production capacity surpassed USD 12 billion, supported by net-zero commitments from more than 30 countries and growing industry adoption in aviation and shipping. The combined effect of economic incentives and regulatory pressure is accelerating the commercial rollout of e-fuels.
Support from Automotive and Aviation OEMs: Automotive and aviation manufacturers are actively exploring partnerships with e-fuel producers to meet sustainability goals without overhauling their existing technologies. These collaborations focus on developing drop-in fuels that work with current engines and fueling infrastructure, reducing the need for costly redesigns. OEMs are conducting joint pilot programs, testing fuel compatibility, and supporting scale-up efforts to ensure smooth integration into their supply chains. The ability to lower lifecycle emissions while maintaining operational consistency makes e-fuels an attractive option. These industry alliances are validating the commercial potential of e-fuels and helping them bring to market faster through shared resources, innovation, and aligned decarbonization efforts.

Segmental Insights
Product Analysis
Based on product, the segmentation includes e-diesel, e-gasoline, ethanol, hydrogen, methanol, and others. The ethanol segment dominated the market with ~42% of the revenue share in 2024 due to its established compatibility with existing internal combustion engines and fueling infrastructure. Its widespread use in fuel blends, particularly in countries with ethanol mandates, makes it commercially viable and logistically efficient. The availability of biomass and carbon-neutral production routes further supports ethanol’s leadership. Strong support from both regulatory frameworks and industry stakeholders has helped position ethanol as a near-term scalable solution for reducing emissions in road transport, especially in regions focusing on low-carbon fuel alternatives to achieve their climate targets.
The e-gasoline segment is expected to register the highest CAGR of 25.0% from 2025 to 2034 due to increasing demand for low-emission fuels that seamlessly integrate into existing vehicle fleets. Its ability to serve as a direct replacement for traditional gasoline makes it an attractive option, especially in regions where full electrification is delayed. Growing investments in synthetic fuel pilot projects and policy incentives targeting passenger vehicle emissions are also fueling this segment’s momentum. OEM collaborations and improved electrolyzer efficiency are expected to lower production costs, making e-gasoline more competitive and accessible over the next decade.
State Analysis
In terms of state, the segmentation includes liquid and gas. The liquid segment dominated the market by ~82% of the revenue share in 2024 due to its compatibility with current storage, transport, and fueling systems. Their energy density and ease of integration into existing supply chains allow minimal disruption for downstream users. Liquid e-diesel, methanol, and ethanol are being prioritized across transport and industrial applications, particularly in heavy-duty and maritime sectors where alternatives like electrification are less feasible. Strong infrastructure readiness and widespread familiarity across end-use sectors have further cemented liquid e-fuels as the most commercially advanced state in the market.
The gas segment is expected to register a CAGR of 24.3% from 2025 to 2034, driven by rising interest in green hydrogen and synthetic methane. These fuels are gaining traction for their role in decarbonizing hard-to-abate sectors such as power generation and high-heat industrial processes. Technological improvements in electrolyzers and carbon capture systems are reducing production costs, making gas-phase e-fuels more viable. Supportive government programs and investments in hydrogen infrastructure are accelerating deployment, particularly in countries aiming to build hydrogen-based energy ecosystems. Increasing cross-border partnerships and pilot-scale deployments are expected to support long-term scalability.
Production Method Analysis
In terms of production method, the segmentation includes power-to-liquid, power-to-gas, and gas-to-liquid. The power-to-liquid segment held the largest revenue share of ~48% in 2024 due to its ability to produce high-density liquid e-fuels such as e-kerosene and e-diesel, which are crucial for long-haul transport and aviation. The scalability of these processes and compatibility with existing liquid fuel infrastructure have attracted significant commercial and governmental interest. Major pilot plants are operational or under construction, particularly in regions rich in renewable energy resources. Integration of carbon capture technologies and improvements in fuel synthesis efficiency are further supporting cost reductions and scalability, reinforcing the leadership position of power-to-liquid in the current market landscape.
The gas-to-liquid segment is expected to register the highest CAGR of 25.0% from 2025 to 2034, fueled by its ability to convert synthetic gas into versatile liquid fuels using Fischer-Tropsch and similar processes. Rising interest in decentralized fuel production and the flexibility to use biogas or green hydrogen as feedstocks are key enablers. Strategic government support and partnerships are accelerating the deployment of modular GTL plants. Their potential to create drop-in fuels for aviation, marine, and military use is drawing investment. Lower lifecycle emissions and the ability to scale across different geographies make GTL a promising pathway for long-term fuel sustainability.
End User Analysis
In terms of end user, the segmentation includes automotive, industrial, marine, railway, and others. The marine segment held ~27.5% of the revenue share in 2024 due to mounting regulatory pressure from the International Maritime Organization (IMO) to cut greenhouse gas emissions. Large vessel operators are increasingly turning to e-methanol and e-diesel as viable options to meet compliance goals without retrofitting engines. Global shipping companies are investing in green fuel procurement strategies to future-proof operations and maintain trade competitiveness. The scale of marine fuel consumption, combined with emerging port infrastructure for e-fuel bunkering, is reinforcing demand across cargo and passenger shipping fleets.
The automotive segment is expected to register the highest CAGR of 24.8% from 2025 to 2034 due to rising interest in decarbonizing existing internal combustion vehicle fleets. E-gasoline and e-diesel are being seen as transitional solutions, especially in markets with slow electric vehicle (EV) adoption. Government blending mandates, OEM endorsements, and infrastructure compatibility are facilitating faster rollout. Consumers are showing interest in sustainable fuel alternatives that require no vehicle modification. Pilot programs and subsidies in regions with ambitious emissions targets are encouraging wider adoption, making the automotive segment a key driver of e-fuel demand growth through the next decade.
.webp)
Regional Analysis
The North America e-fuel market is expected to register a CAGR of 25.2% from 2025 to 2034, due to expanding federal and state-level support for low-carbon fuels and clean energy standards. Strong commitments from energy majors and fuel distributors toward decarbonization are catalyzing the development of commercial-scale e-fuel projects. Investments in carbon capture and electrolyzer infrastructure are further streamlining the production of synthetic fuels. Additionally, rising corporate interest in sustainable aviation and maritime fuel alternatives is opening new revenue streams for e-fuel producers. The region’s technology readiness and supportive regulatory frameworks are reinforcing its leadership in early-stage commercialization.
U.S. E-Fuel Market Insights
The U.S. dominated the industry in North America with ~89% of the share in 2024, due to high deployment of pilot and commercial e-fuel production facilities supported by robust funding from federal decarbonization initiatives. The Inflation Reduction Act and Low Carbon Fuel Standards in states such as California are incentivizing private sector innovation. Collaborations between refineries, renewable energy developers, and transportation OEMs are accelerating scalability. The presence of leading clean tech startups and access to low-cost renewable electricity are further enhancing the viability of e-fuel operations. Strong demand from the aviation and trucking sectors is also driving early market traction.
Asia Pacific E-Fuel Market Trends
Asia Pacific accounted for USD 23.9 billion of the revenue share in 2024 due to growing investments in green hydrogen production and rising fuel import dependency in key economies. Governments in the region are supporting domestic e-fuel capacity to reduce reliance on conventional fossil fuels. Rapid growth in air and maritime freight industries is spurring demand for low-emission alternatives. Technological collaboration between Japan, South Korea, and Southeast Asian countries is promoting the development of region-wide synthetic fuel supply chains. The presence of large industrial clusters and proactive climate commitments is enabling fast-track pilot deployment and regional market expansion.
China E-Fuel Market Overview
China led the Asia Pacific industry with ~41% of the revenue share in 2024, due to aggressive decarbonization mandates for its industrial, automotive, and shipping sectors. Large-scale renewable energy investments and advanced electrolyzer manufacturing capacity are enabling cost-effective production of synthetic fuels. The Chinese government has set a target of producing 100 million tons of e-fuels per year by 2060. State-backed enterprises are entering joint ventures to commercialize power-to-liquid technologies across industrial parks. Moreover, National hydrogen roadmaps and carbon neutrality targets are translating into capital allocation for low-carbon fuels. Demand for e-fuels is also rising across heavy-duty transportation segments as emission control regulations tighten and energy security gains policy priority.
Europe E-Fuel Market
Europe accounted for ~49% of the revenue share in 2024 due to ambitious net-zero targets, stringent emission standards, and sector-specific decarbonization policies. The FuelEU Maritime and ReFuelEU Aviation initiatives are creating strong market demand by mandating the use of sustainable fuels. National governments are funding hydrogen and CO₂ utilization technologies that directly support e-fuel development. The European Union has committed to invest USD 15.10 billion in the development and commercialization of e-fuels by 2030. Leading energy companies are building integrated production facilities in collaboration with automotive and aerospace sectors. Strategic infrastructure plans such as hydrogen corridors and e-fuel blending mandates are reinforcing market maturity and regional competitiveness in clean fuel innovation.
Germany E-Fuel Market Overview
Germany accounted for ~21% of the revenue share in 2024 due to its leadership in industrial decarbonization, green hydrogen production, and cross-sector alliances. The country’s long-standing emphasis on energy transition is resulting in large-scale public and private investment in synthetic fuel technology. Strong demand from the automotive, chemicals, and logistics industries is boosting domestic adoption. Research institutions and OEMs are actively involved in demonstrating and scaling power-to-liquid applications. Policy alignment with EU climate frameworks and support for international pilot programs solidify Germany’s role as a key technology hub for e-fuel commercialization.
Key Players & Competitive Analysis
The competitive landscape of the e-fuel market is shaped by a dynamic mix of market expansion strategies, joint ventures, and post-merger integration efforts aimed at scaling production and distribution networks. Industry analysis indicates a strong focus on strategic alliances between energy producers, technology firms, and transportation sectors to accelerate commercialization.
Companies are actively engaging in mergers and acquisitions to secure access to renewable power sources and carbon capture technologies, consolidating their position across the value chain. Technology advancements in electrolysis, synthetic fuel synthesis, and CO₂ utilization are driving differentiation in efficiency and cost performance. Cross-border collaborations and joint R&D programs are enhancing knowledge transfer and supporting regulatory alignment. Market participants are also refining their post-merger integration models to streamline operations and leverage synergies. As the regulatory environment evolves to support decarbonization, firms are investing heavily in pilot projects and early infrastructure to strengthen their long-term presence in this emerging energy domain.
Key Players
- ABEL Energy Pty Ltd.
- ANPAC
- Arcadia eFuels
- HIF Global
- INERATEC GmbH
- Liquid Wind
- Neste Corp.
- Porsche AG
- Siemens Energy
- Sunfire GmbH
E-Fuel Industry Developments
September 2025: HIF Global announced the selection of Electric Hydrogen (EH2) for supplying advanced electrolyzer systems. The company stated that the systems will be used at its e-Fuels facility in Texas.
May 2025: Arcadia eFuels received an environmental permit for its project in Vordingborg, Denmark. According to Arcadia eFuels, the company now has the approval to operate a full-scale production of electro-Sustainable Aviation Fuel (e-SAF).
June 2025: INERATEC launched ERA ONE, Europe’s largest facility for e-fuel production in Frankfurt. This plant is designed to efficiently convert renewable energy into synthetic fuels, leveraging advanced technology to facilitate the transition toward sustainable energy sources in the transportation sector.
November 2023: Liquid Wind announced a partnership with Pan-European to include plans to develop and market 10 additional eMethanol facilities in the Nordics by 2027.
March 2023: Orsted announced that it is constructing Europe’s e-fuel facility in Sweden with Siemens Energy technology, featuring 70MW PEM electrolyzers, digitalization solutions, and power systems.
E-Fuel Market Segmentation
By Product Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- E-Diesel
- E-Gasoline
- Ethanol
- Hydrogen
- Methanol
- Others
By State Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- Liquid
- Gas
By Production Method Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- Power-to-Liquid
- Power-to-Gas
- Gas-to-Liquid
By End User Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- Automotive
- Industrial
- Marine
- Railway
- Others
By Regional Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- North America
- U.S.
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- UK
- Italy
- Spain
- Netherlands
- Russia
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- Malaysia
- South Korea
- Indonesia
- Australia
- Vietnam
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Middle East & Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Israel
- South Africa
- Rest of Middle East & Africa
- Latin America
- Mexico
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
E-Fuel Market Report Scope
|
Report Attributes |
Details |
|
Market Size in 2024 |
USD 132.32 billion |
|
Market Size in 2025 |
USD 147.17 billion |
|
Revenue Forecast by 2034 |
USD 1,060.06 billion |
|
CAGR |
24.5% from 2025 to 2034 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Historical Data |
2020–2023 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025–2034 |
|
Quantitative Units |
Revenue in USD billion and CAGR from 2025 to 2034 |
|
Report Coverage |
Revenue Forecast, Competitive Landscape, Growth Factors, and Industry Trends |
|
Segments Covered |
|
|
Regional Scope |
|
|
Competitive Landscape |
|
|
Report Format |
|
|
Customization |
Report customization as per your requirements with respect to countries, regions, and segmentation. |
FAQ's
The global market size was valued at USD 132.32 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow to USD 1,060.06 billion by 2034.
The global market is projected to register a CAGR of 24.5% during the forecast period.
Europe accounted for ~49% of the revenue share in 2024 due to ambitious net-zero targets, stringent emission standards, and sector-specific decarbonization policies.
A few of the key players in the market are ABEL Energy Pty Ltd., ANPAC, Arcadia eFuels, HIF Global, INERATEC GmbH, Liquid Wind, Neste Corp., Porsche AG, Siemens Energy, and Sunfire GmbH.
The ethanol segment dominated the market with ~42% of the revenue share in 2024 due to its established compatibility with existing internal combustion engines and fueling infrastructure.
The liquid segment dominated the market by ~82% of the revenue share in 2024 due to their compatibility with current storage, transport, and fueling systems.
E-fuels, also known as electrofuels or synthetic fuels, are a class of fuels produced using renewable energy sources. The general process involves using electricity from solar, wind, or other renewable sources to produce hydrogen through electrolysis of water. This "green hydrogen" is then combined with captured carbon dioxide (CO2) to create liquid or gaseous hydrocarbon fuels.
