
Electric Ship Pod Drives Market Size, Share, Trends, & Industry Analysis Report
By Propulsion Type (Azimuth Thrusters, Cycloidal Propellers), By Power Rating, By Installation Type, By Control System, By End User, and By Region – Market Forecast, 2025–2034
- Published Date:Jul-2025
- Pages: 130
- Format: PDF
- Report ID: PM5868
- Base Year: 2024
- Historical Data: 2020-2023
Market Overview
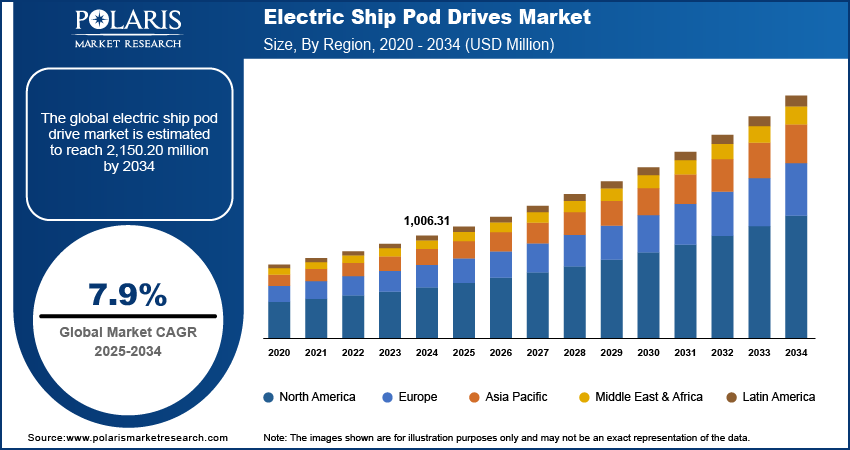
The global electric ship pod drives market size was valued at USD 1,006.31 million in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 7.9% during 2025–2034. Rising pressure to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and enhance propulsion efficiency is accelerating the adoption of electric ship pod drives across commercial and defense marine sectors.
Electric ship pod drives are systems that integrate electric motors with steerable pods, enabling 360-degree thrust and enhanced maneuverability while improving hydrodynamic efficiency. The industry’s shift toward decarbonization, driven by International Maritime Organization (IMO) regulations and regional emission control areas (ECAs) is compelling operators to explore advanced electric propulsion systems that offer both environmental and operational advantages. Pod drives reduce the mechanical complexity of traditional shaft-line systems, offering lower noise, reduced vibrations, and enhanced vessel control tight port environments and offshore operations.
Electric ship pod drives are witnessing increased integration in cruise liners, luxury yachts, research vessels, and naval ships due to their space-saving design and superior maneuverability. Their ability to enhance fuel economy and reduce maintenance downtime makes them a preferred choice for long-term fleet sustainability. Moreover, as hybrid and fully electric marine architectures gain traction, pod drives serve as a critical enabler for cleaner propulsion systems. Ongoing innovations in high-power electric motors, battery energy storage technologies, and vessel automation are expected to strengthen the market further, enabling operators to meet regulatory compliance while optimizing lifecycle costs.
To Understand More About this Research: Request a Free Sample Report
Rising focus on low-emission propulsion and increasing complexity in maritime operations propel the adoption of electric ship pod drives. Global ports and coastal fleets undergo electrification to meet stringent emission policies and sustainability targets. For instance, the United Nation’s Net-Zero Coalition aimed to cut global emissions by 45% by 2030 and achieve net-zero by 2050, with over 140 countries and numerous companies having committed to these climate targets. Electric ship pod drives integrate electric motors within steerable pods to deliver 360-degree thrust, reduce fuel use, and improve vessel control. These units support cleaner marine transport by lowering greenhouse gas output, vibration, and acoustic pollution. Their compact configuration streamlines vessel architecture and enhances operational efficiency, aligning effectively with evolving performance and design standards in both commercial and defense maritime fleets.
Urban maritime regions witness strong demand for advanced propulsion driven by growing investment in smart ports, hybrid-electric fleets, and digital navigation. Electric pod drives offer improved spatial flexibility and lower lifecycle costs, allowing shipbuilders to meet regulatory and operational demands. Port authorities and vessel operators prefer these systems for their reliability, minimal maintenance, and high precision during berthing and maneuvering. Increasing public and private funding toward clean marine technologies positions electric ship pod drives as a strategic solution for future-ready maritime infrastructure.
Industry Dynamics
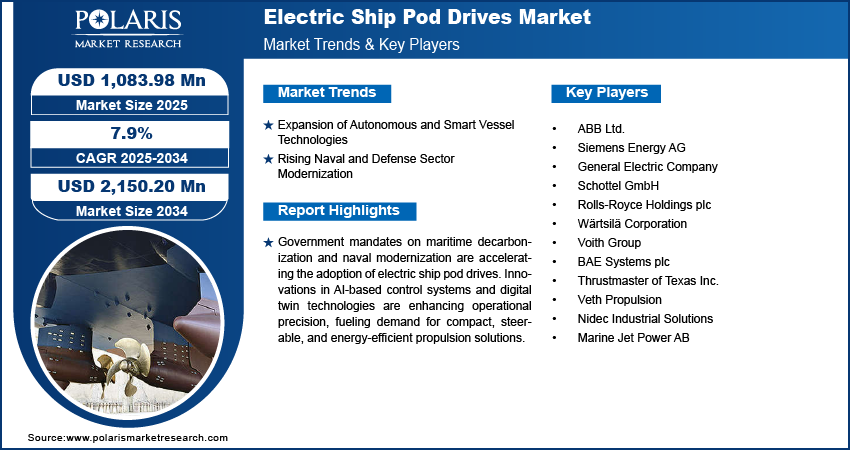
Expansion of Autonomous and Smart Vessel Technologies
The ongoing transformation of the maritime industry toward smart and autonomous vessels is a significant driver for the adoption of electric ship pod drives. As an example, in May 2025, Yara International launched the world's first fully electric and autonomous containership, completed three years in service. The vessel integrates advanced electric pod drives, enabling enhanced maneuverability, zero-emission propulsion, and a significant step forward in sustainable short-sea shipping solutions. These integrated propulsion systems provide 360-degree maneuverability, enabling vessels to achieve superior handling and responsiveness that is critical for autonomous navigation. Their steerable design allows precise course correction and real-time adjustments, making them highly suitable for advanced dynamic positioning systems. Maritime operations continue to advance toward higher levels of automation, making electric pod drives a key enabler in this transition. Their ability to integrate smoothly with onboard navigation systems, GPS, and motion sensors ensures precise vessel control with minimal manual input.
Furthermore, electric pod drives contribute to enhanced operational intelligence by supporting remote diagnostics, condition monitoring, and predictive maintenance. Their compatibility with digital infrastructure allows operators to collect and analyze propulsion performance data, which improves decision-making and reduces downtime. This level of system integration aligns with the growing deployment of AI-based control systems in next-generation vessels, ensuring consistent and autonomous operations even in complex maritime environments. Regulatory bodies and commercial operators are placing greater emphasis on enhancing the safety, efficiency, and environmental performance of autonomous fleets. Thus, electric pod drives are positioned to play a pivotal role in delivering reliable and future-ready vessel solutions.
Rising Naval and Defense Sector Modernization
Rising modernization efforts in the naval and defense sector are significantly driving the demand for electric ship pod drives among countries upgrading their maritime combat and surveillance capabilities. Defense organizations across major economies are focusing on low-noise, low-emission, and high-performance propulsion systems to gain a competitive edge in underwater stealth and maneuverability. For instance, in November 2024, India and the UK signed a collaborative agreement to develop electric propulsion systems for naval ships, aiming to strengthen maritime sustainability and defense capabilities. The partnership supports joint research, innovation, and technology sharing in green naval solutions. Pod drives are growing significantly due to their electric propulsion mechanism, inherently produce minimal acoustic signatures, thereby improving a vessel’s ability to avoid detection by enemy sonar. This feature is valuable in submarine and patrol ship applications where stealth is essential for both defensive and offensive operations. Moreover, their high-precision thrust vectoring capability enhances agility, enabling superior directional control during complex missions in constrained or hostile environments.
Alongside stealth benefits, electric pod drives also offer design flexibility and space optimization, which align with the evolving structural and technological needs of future naval platforms. The modular architecture and compact size of pod systems helps to free up internal space while offering reallocation for advanced weaponry, surveillance equipment, or unmanned systems integration. Defense manufacturers and naval architects are capitalizing on these attributes to create multi-mission vessels that supports hybrid functionalities such as reconnaissance, mine countermeasures, and rapid response logistics. Additionally, the global This shift underscores their growing relevance in naval fleet modernization programs worldwide.
Segmental Insights
Propulsion Type Analysis
The global segmentation, based on propulsion type, includes, azimuth thrusters, cycloidal propellers, rim drive systems, and fixed pod drives. The azimuth thrusters segment is projected to grow during the forecast period. This growth is attributed to their ability to rotate 360 degrees, offering superior maneuverability and propulsion efficiency. For instance, in March 2025, Engtek (Pte) Ltd announced to develop its zero-emissions hydrofoil is equipped with a locally developed azimuth thruster system, providing precise maneuverability and efficient electric propulsion for sustainable marine operations. These units are widely adopted in commercial vessels, tugboats, and naval ships where directional thrust and tight navigation control are essential. Their integration improves vessel handling in confined ports and dynamic offshore environments. Additionally, azimuth thrusters help reduce fuel consumption and emissions, aligning with global decarbonization goals. Their adaptability across vessel sizes strengthens their preference among shipbuilders and fleet operators.
The rim drive systems segment is projected to grow at a robust pace in the coming years, propelled by their ultra-quiet operation, compact structure, and high energy efficiency. These systems eliminate the need for gears or shafts, reducing mechanical complexity and enhancing reliability. Their suitability for submarines, research vessels, and autonomous maritime platforms is driving adoption in niche but rapidly expanding segments. The growing preference for electrically driven, low-acoustic propulsion solutions among naval and environmental research agencies is accelerating market demand for rim drive systems globally.
Power Rating Analysis
The global segmentation, based on power rating, includes, below 5MW, 5-15MW, 15-30MW, above 30MW. The 5–15 MW segment accounted for major share of the market in 2024, this growth in attributed primarily due to its application in mid-sized vessels such as ferries, offshore support vessels, and naval patrol ships. This power range offers a balance of thrust capacity, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness, making it an ideal choice for commercial and multipurpose vessels. Increasing demand for fuel-efficient and environmentally compliant propulsion systems in this category is supporting continued investment and deployment, particularly across coastal fleets and inland shipping corridors.
The 15–30 MW segment is projected to grow at a significant pace during the assessment phase, driven by electrification initiatives in heavy-duty vessels such as LNG carriers, frigates, and naval destroyers. Rising energy efficiency mandates and global decarbonization goals are encouraging operators to upgrade propulsion systems with higher power capacity and lower emissions. Furthermore, the ongoing modernization of military fleets and expansion of Arctic-capable commercial shipping require robust, high-power electric pod drives capable of handling extreme conditions and long operational cycles.
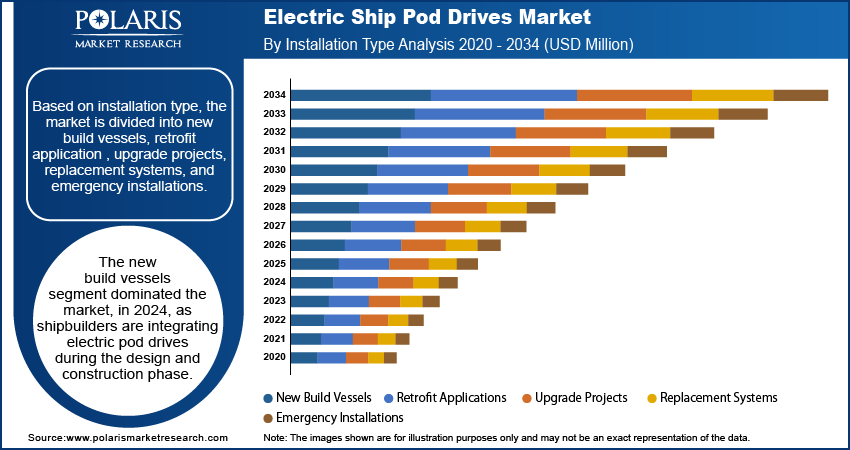
Installation Type Analysis
The global segmentation, based on propulsion type, includes, new build vessels, retrofit applications, upgrade projects, replacement systems, and emergency installations. The new build vessels segment dominated the market, in 2024, as shipbuilders are integrating electric pod drives during the design and construction phase. Early integration enables optimal positioning of propulsion systems, space-saving architecture, and compatibility with modern navigation and control systems. Global maritime regulations on emissions and noise reduction are further fueling the demand for electric ship pod drives. For instance, in January 2025, French company TEMO unveiled new modular electric pod motors designed for flexibility, lightweight performance, and ease of installation, targeting a wide range of small electric boats. The growing number of electric and hybrid vessel programs globally reinforces the preference for pre-installed pod drives in newly commissioned ships.
The retrofit applications segment is estimated to hold a substantial market share in 2034, as shipowners seek to upgrade aging fleets with energy-efficient propulsion technologies. Retrofitting allows operators to extend vessel service life while achieving better fuel economy and reduced emissions without full-scale replacement. The push for compliance with IMO regulations and carbon intensity targets is driving demand for electric pod conversions. Additionally, modularity in modern pod systems enables streamlined retrofit installations, reducing downtime and improving the return on investment for shipping companies.
Control System Analysis
The global segmentation, based on control system, includes, manual control, semi-automatic systems, and fully automatic control. The semi-automatic systems segment is projected to grow with significant CAGR during the forecast period, by offering a practical blend of manual and automated operations. These systems let operators step in when needed while handling basic navigation tasks automatically. In March 2022, Einride introduced the world’s first remote pod operator to oversee its fleet of autonomous electric vehicles, enabling safe, human-assisted intervention when needed and advancing intelligent freight mobility. Their affordability, reduced training requirements, and operational predictability make them popular in commercial fleets, ferries, and coastal shipping. They provide a transitional solution for operators moving from manual systems toward greater automation, supporting safer and more responsive vessel control in varying marine conditions.
The fully automatic control systems segment is estimated to hold a significant market share in 2034, benefiting from the rise in smart vessel deployments and autonomous shipping pilots. These systems integrate with GPS, gyroscopes, and motion sensors to offer real-time decision-making without human input. Their adoption supports fuel optimization, course correction, and safety management across complex sea routes. Increased investment in unmanned maritime systems by naval forces and tech-driven shipping companies is reinforcing the demand for advanced, intelligent control frameworks globally.
End User Analysis
The global segmentation, based on propulsion type, includes, commercial shipping, naval defense, offshore energy, and passenger transport. The commercial shipping segment growth is driven by significant demand across global trade routes. The sector is increasingly investing in electric pod drives to improve fuel efficiency, reduce operational costs, and meet sustainability targets. Pod drives offer precise maneuverability, which is crucial for large container ships, Ro-Ro vessels, and bulk carriers navigating congested ports. Regulatory pressure to lower emissions and the economic imperative of efficient cargo transport are propelling widespread adoption in this segment.
The naval defense segment is estimated to grow at a significant CAGR from 2025-2034, driven by modernization programs across major defense economies aiming to improve stealth, agility, and tactical performance. Electric pod drives provide low acoustic signatures, vital for anti-submarine operations and covert missions. Their compact size also allows for integration with advanced surveillance, weaponry, and autonomous control systems. Increased naval procurement, defense R&D funding, and the strategic shift toward electrified naval platforms are accelerating adoption in this high-security segment.
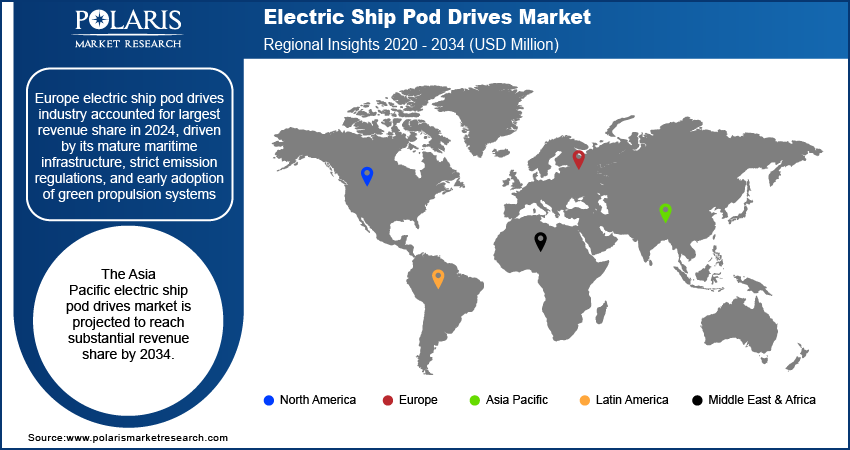
Regional Analysis
Europe electric ship pod drives industry accounted for largest revenue share in 2024, driven by its mature maritime infrastructure, strict emission regulations, and early adoption of green propulsion systems. For example, the European Union announced an ambitious emission reduction target, aiming for climate neutrality by 2050. An important part of this initiative is the "Fit for 55" package that aims to cut emissions by at least 55% by 2030 compared to 1990 levels. Countries including Norway, Germany, and the Netherlands have been at the forefront of adopting hybrid and fully electric propulsion technologies, with widespread deployment in passenger ferries, offshore support vessels, and naval fleets. The EU’s Fit for 55 and Green Deal initiatives mandate aggressive carbon reduction targets for maritime operations, compelling operators to invest in low-emission technologies such as electric pod drives. Moreover, Europe’s robust shipbuilding sector and advanced research capabilities are accelerating innovation in pod-based propulsion systems. Integration with dynamic positioning, improved maneuverability in congested ports, and modular flexibility for retrofits have further elevated adoption levels across both commercial and defense segments.
Germany Electric Ship Pod Drives Market Insight
The Germany dominated the regional market in 2024. This dominance is attributed to its strategic investments in zero-emission shipbuilding, naval modernization, and port electrification. The nation’s National Hydrogen Strategy and federal support for alternative marine fuels complement electric propulsion systems for inland waterways and coastal operations. German shipyards are focusing on modular vessel architecture that accommodates pod drive integration, enhancing operational flexibility and vessel customization. Maritime cluster initiatives and collaborative research projects between shipbuilders, universities, and component manufacturers are also supporting the scale-up of advanced pod technologies. As the demand for climate-compliant propulsion intensifies, Germany continues to serve as a hub for innovation and deployment.
Asia Pacific Electric Ship Pod Drives Market Trend
The Asia Pacific electric ship pod drives market is projected to reach substantial revenue share by 2034. The growth is fueled by expanding naval procurement programs, regional fleet modernization, and investments in smart port infrastructure. Countries such as China, South Korea, and Japan are focusing towards the integration of electric propulsion in their new build and retrofitted vessels to improve fuel efficiency, meet IMO emission norms, and enhance fleet stealth capabilities. Recently, in May 2025, NYK introduced Japan’s first electric, battery-powered workboat, marking a step forward in the nation’s efforts to decarbonize maritime operations. Additionally, China’s Belt and Road maritime expansion, along with South Korea’s Smart Shipbuilding Initiative and Japan’s Green Growth Strategy are promoting electric pod drive deployment in both domestic and international waters.
North America Electric Ship Pod Drives Market Overview
North America electric ship pod drives market accounted for substantial revenue share of the in 2024, driven by strong naval modernization efforts, federal decarbonization incentives, and rising adoption of autonomous vessel platforms. The region's demand is heavily supported by the US Navy’s focus on quiet propulsion technologies for stealth operations, multi-domain readiness, and reduced lifecycle costs. In addition, electrification programs for harbor crafts, ferries, and research vessels are progressing under state and federal sustainability goals. Infrastructure support, such as electric shore power systems and smart port development is also creating a favorable environment for electric pod drive adoption. For instance, in March 2024, U.S. Department of Transportation’s Maritime Administration (MARAD) announced a USD 450 million investment to upgrade port infrastructure, aiming to boost cargo capacity, improve supply chain efficiency, and support economic and environmental goals.
Key Players & Competitive Analysis Report
The electric ship pod drives industry is highly competition, due to increasing demand for thermal efficiency, regulatory compliance, and scalable infrastructure. Leading providers are offering modular, energy-efficient cooling systems that reduce power usage and support high-density environments. Market participants are focusing on product innovation, regional capacity expansion, and customized solutions suited for hyperscale and edge deployments. Partnerships with data center operators and technology integrators support service coverage and customer retention. Emphasis on reliability, real-time monitoring, and integration with facility management platforms contributes to strong positioning across global and regional markets.
Key companies in the industry include Vertiv Holdings Co., Schneider Electric SE, STULZ GmbH, Rittal GmbH & Co. KG, Mitsubishi Electric Corporation, Eaton Corporation plc, Daikin Industries Ltd., Trane Technologies plc, Airedale International Air Conditioning Ltd., Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd., Nortek Air Solutions, and Johnson Controls International plc.
Key Players
- ABB Ltd.
- Siemens Energy AG
- General Electric Company
- Schottel GmbH
- Rolls-Royce Holdings plc
- Wärtsilä Corporation
- Voith Group
- BAE Systems plc
- Thrustmaster of Texas Inc.
- Veth Propulsion
- Nidec Industrial Solutions
- Marine Jet Power AB
Industry Developments
December 2024: ePropulsion unveiled a new pod drive, battery, and integrated AC/DC energy system aimed at enhancing electric propulsion efficiency. The launch reflects the company's focus on holistic marine electrification solutions for varied vessel applications.
November 2024: TEMO launched its new "Seaside by TEMO" range of electric pod drives (500W to 3000W) at the 2024 Metstrade Boat Show in Amsterdam. Designed for boaters and shipyards, the line focuses on compact, sustainable, and user-friendly marine mobility solutions.
February 2024: ABB announced to supply hybrid-electric propulsion technology for South America's first polar expedition cruise ship, enhancing sustainability and operational efficiency. The vessel will be showcased at the maritime exhibition in Amsterdam.
Electric Ship Pod Drives Market Segmentation
By Propulsion Type Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2020–2034)
- Azimuth Thrusters
- Cycloidal Propellers
- Rim Drive Systems
- Fixed Pod Drives
By Power Rating Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2020–2034)
- Below 5MW
- 5-15MW
- 15-30MW
- Above 30MW
By Installation Type Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2020–2034)
- New Build Vessels
- Retrofit Applications
- Upgrade Projects
- Replacement Systems
- Emergency Installations
By Control System Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2020–2034)
- Manual Control
- Semi-Automatic Systems
- Fully Automatic Control
By End User Type Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2020–2034)
- Commercial Shipping
- Naval Defense
- Offshore Energy
- Passenger Transport
By Regional Outlook (Revenue, USD Million, 2020–2034)
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- UK
- Italy
- Spain
- Netherlands
- Russia
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- Malaysia
- South Korea
- Indonesia
- Australia
- Vietnam
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Middle East & Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Israel
- South Africa
- Rest of Middle East & Africa
- Latin America
- Mexico
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
Electric Ship Pod Drives Market Report Scope
|
Report Attributes |
Details |
|
Market Size in 2024 |
USD 1,006.31 Million |
|
Market Size in 2025 |
USD 1,083.98 Million |
|
Revenue Forecast by 2034 |
USD 2,150.20 Million |
|
CAGR |
7.9% from 2025 to 2034 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Historical Data |
2020–2023 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025–2034 |
|
Quantitative Units |
Revenue in USD Million and CAGR from 2025 to 2034 |
|
Report Coverage |
Revenue Forecast, Competitive Landscape, Growth Factors, and Industry Trends |
|
Segments Covered |
|
|
Regional Scope |
|
|
Competitive Landscape |
|
|
Report Format |
|
|
Customization |
Report customization as per your requirements with respect to countries, regions, and segmentation. |
FAQ's
The global market size was valued at USD 1,006.31 million in 2024 and is projected to grow to USD 2,150.20 million by 2034.
The global market is projected to register a CAGR of 7.9% during the forecast period.
Europe dominated the market share in 2024.
A few of the key players in the market are ABB Ltd., Siemens Energy AG, General Electric Company, Schottel GmbH, Rolls-Royce Holdings plc, Wärtsilä Corporation, Voith Group, BAE Systems plc, Thrustmaster of Texas Inc., Veth Propulsion, Nidec Industrial Solutions, and Marine Jet Power AB.
The new build vessels segment dominated the market in 2024.
The semi-automatic systems segment is projected to grow with significant CAGR during the forecast period.
