
U.S. Food Waste Management Market Size, Share, & Industry Analysis Report
By Waste Type (Cereals, Dairy Products, Fruits & Vegetables), By Process, By Source, and By Application – Market Forecast, 2025–2034
- Published Date:Sep-2025
- Pages: 126
- Format: PDF
- Report ID: PM6433
- Base Year: 2024
- Historical Data: 2020-2023
Overview
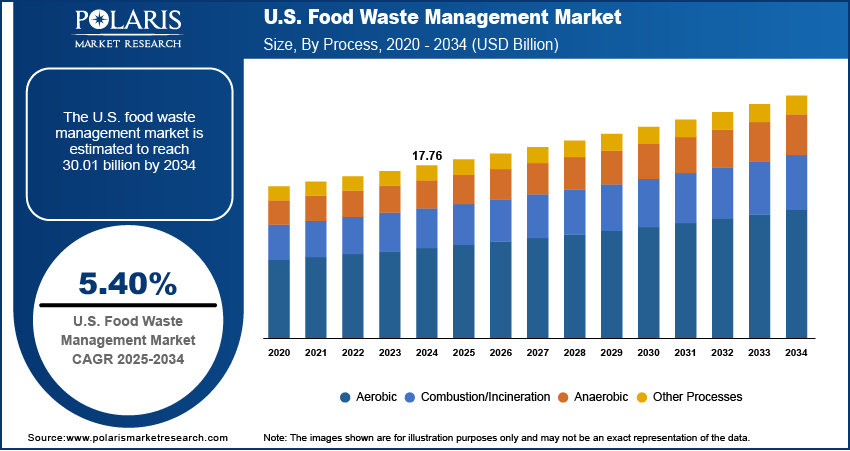
The U.S. food waste management market size was valued at USD 17.76 billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 5.40% from 2025–2034. Key factors driving demand include strict environmental regulations, growing subsidies and incentives for sustainable waste management solutions, rising concern over food wastage, and advancements in waste treatment technologies.
Key Insights
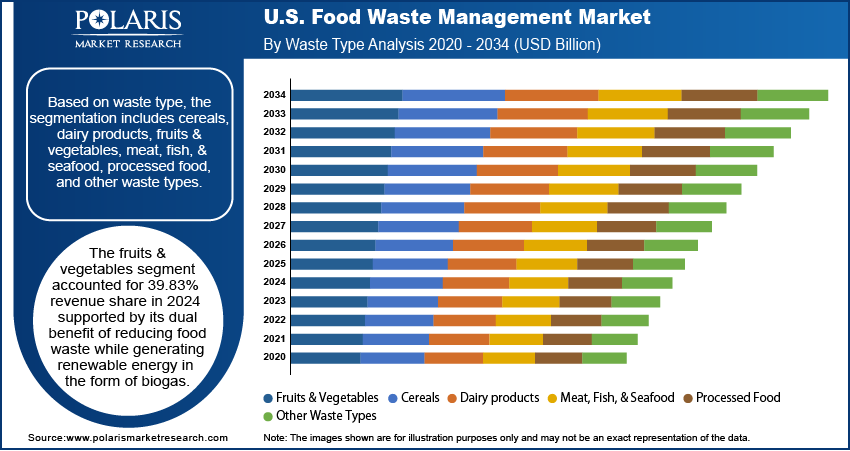
- The fruits and vegetables segment held a 39.83% revenue share in 2024, driven by its high perishability and substantial contribution to overall organic waste volumes.
- The anaerobic digestion segment is projected to grow at a 5.7% CAGR, favored for its dual ability to manage waste and produce renewable biogas.
- The municipalities and households segment accounted for a 37.47% revenue share, representing the largest source of food waste generation in the country.
- The fertilizers segment is anticipated to grow at a 5.7% CAGR, supported by rising demand for nutrient-rich organic soil amendments in agriculture.
Industry Dynamics
- Growing recognition of food waste's economic and environmental impact is driving greater policy and consumer focus on waste reduction and management solutions in the U.S.
- Advanced technologies such as anaerobic digestion and waste-to-energy conversion are enabling more efficient and sustainable transformation of food byproducts into valuable resources.
- High upfront capital and operational costs for advanced processing facilities, such as anaerobic digesters, create a barrier to widespread adoption and scalability.
- Rising demand for renewable natural gas and organic fertilizers offers a substantial revenue stream by converting waste into valuable, marketable products.
Market Statistics
- 2024 Market Size: USD 17.76 billion
- 2034 Projected Market Size: USD 30.01 billion
- CAGR (2025-2034): 5.40%
AI Impact on the U.S. Food Waste Management Market
- AI optimizes supply chains by predicting demand, thereby reducing overproduction and spoilage from farm to store.
- Smart sorting systems use cameras to identify and divert imperfect but edible produce instantly.
- It powers apps that connect consumers with discounted surplus food from restaurants and grocery stores.
- AI analyzes waste data to pinpoint inefficiencies, helping businesses cut costs and improve sustainability reporting.
Food waste management involves the systematic collection, processing, recycling, and disposal of food waste to reduce environmental impact and promote sustainability throughout the supply chain. In the U.S., the market is driven by the presence of strict environmental regulations that mandate responsible waste handling practices. Federal and state-level policies enforce compliance with landfill diversion targets, emissions reduction, and sustainable disposal methods, compelling industries, food service providers, and households to adopt structured waste management solutions. According to an August 2025 US EPA report, the agency regulates household, industrial, and manufacturing solid and hazardous wastes under the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act. These regulations minimize the harmful effects of waste accumulation and also promote the use of advanced technologies such as composting, anaerobic digestion, and recycling, thereby ensuring a structured approach toward achieving long-term ecological balance.
Rising subsidies and incentives for sustainable waste management solutions, with broader penetration across sectors, fuel the U.S. food waste management market. Government-sponsored financial aid, tax benefits, or commercial loan-type aids help increase flexibility in the politics of waste and costs associated with investing in better waste-treatment technology and infrastructure. An example is a USD 10.2 million fund from the U.S. Department of Agriculture in 2022 to pilot projects on strategies to address food waste and to expand composting. These projects contribute to the process of reconstructing the traditional waste collection, processing, and disposal framework in a linear model to a circular, renewable resource recovery paradigm. Additionally, many stakeholders are now adopting food waste as a resource for renewable energy, bio-fertilizer, alternative packaging, etc. This policy is gaining interest as a source of backing for sustainable waste management, highlighting greater traction in the U.S. food waste management market.
Drivers & Opportunities
Rising Concern Over Food Wastage: The increasing focus on food waste is contributing to the U.S. food waste management market, reflecting how awareness of the economic, environmental, and social costs of food waste is growing. A US FDA report published in January 2025 estimates that 30 to 40% of the U.S. food supply is wasted each year. Food waste is increasingly recognized by consumers, businesses, and policymakers alike for its negative impacts on the natural resources needed to produce food, greenhouse gas emissions associated with food waste, and landfills full of unnecessary food waste. The demand for systems that collect, recycle, and redistribute food to eliminate waste at various points in the supply chain is growing in parallel with increasing awareness. Therefore, both public and private entities are making consistent investments in structured waste management programs to support sustainability goals through increased efficiencies and reduced disposal costs.
Advancements in Waste Treatment Technologies: New waste treatment technologies boost the U.S. food waste management sector with more effective, scalable, and sustainable food byproduct management. Technologies such as anaerobic digestion, waste-to-energy, and bio-fertilizer are creating strategies to convert wasted food into tangible resources. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. Department of Energy and NREL selected 20 communities for the Waste-to-Energy Technical Assistance Program. The initiative supports the conversion of various organic wastes such as food, bio solids, manure, and industrial residues into energy, reducing landfill use and promoting renewable resource recovery. The improvements in waste management technologies provide more efficient processing while also neutralizing environmental impacts, as demonstrated by the shift towards renewable energy and circular economy system practices that the U.S. is prioritizing. Furthermore, investment in new technologies such as automation and digital tools in waste collection and processing improves traceability, accuracy, and cost savings, encouraging businesses and municipalities to adopt innovative solutions over traditional waste disposal methods. Therefore, as these technologies advance, they are able to help shape the long-term sustainability of the U.S. food waste management sector.

Segmental Insights
Waste Type Analysis
Based on waste type, the segmentation includes cereals, dairy products, fruits & vegetables, meat, fish, & seafood, processed food, and other waste types. The fruits & vegetables segment accounted for 39.83% revenue share in 2024 supported by its dual benefit of reducing food waste while generating renewable energy in the form of biogas. This process aligns strongly with the U.S. focus on sustainability and clean energy transitions, making it an attractive solution for both municipalities and industries. Unlike traditional disposal methods, anaerobic treatment offers scalability and efficiency while minimizing greenhouse gas emissions. Its ability to convert high-moisture organic food waste into usable energy and bio-fertilizers further enhances its adoption, positioning it as an essential growth driver in the country’s evolving waste management landscape.
Process Analysis
In terms of process, the segmentation includes anaerobic, aerobic, combustion/incineration, other processes. The anaerobic segment is expected to witness fastest growth at a CAGR of 5.7% during the forecast period due to the unique ability to lower food waste and generate renewable energy in the form of biogas. This process aligns closely with the U.S. direction towards sustainability and clean energy transitions, which is why municipalities and industry prefer it. While disposal is traditional, anaerobic treatment scales up to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by eliminating excess organic waste rather than acting only as a treatment process. Another feature is the ability to convert high-moisture organic food waste into usable energy and bio-fertilizers. Therefore, anaerobic treatment is expected to be a major component in the enhanced growth and change of the waste management landscape in the U.S.
Source Analysis
The segmentation, based on source, includes primary food producers, food manufacturers, food distributors & suppliers, food service providers, and municipalities & households. The municipalities & households segment held 37.47% revenue share in 2024 as consumer-level waste adds to the total volume generated nationwide. Improper portioning, lack of awareness, and poor food storage practices continue to be major contributors to the increasing household waste. Local governments play a crucial role in the effective management of this segment by implementing structured collection systems, recycling programs, and public awareness initiatives. Moreover, the large portion of waste disposal at the household level highlights the importance of residential involvement in reducing landfill dependence and recognizing the effective implementation of circular economy principles in the U.S.
Application Analysis
Based on application, the segmentation includes, animal feed, fertilizers, biofuel, and power generation. The fertilizers segment is expected to witness robust growth at a CAGR of 5.7% during the forecast period as the demand for organic and sustainable agriculture continues to grow. Converting food waste into nutrient-dense compost and bio-fertilizers helps reduce chemical inputs while enhancing soil capacity. The association between organic waste recycling into fertilizers has strong momentum, with regulations that are enabling higher growth in farmer communities. Therefore, as reduction and education objectives are being met, work being done in this area has a strong opportunity to achieve sustainable agriculture.
Key Players & Competitive Analysis Report
The U.S. food waste management sector is characterized by intense competition among established waste management firms and specialized technology-driven entrants. Major players leverage competitive intelligence and strategy to capitalize on expansion opportunities driven by strict environmental regulations and increasing corporate sustainability commitments. Technological advancement in anaerobic digestion and AI-powered sorting systems is reshaping industry trends, enabling more efficient conversion of organic waste into renewable energy and compost. Strategic investments are increasingly directed toward integrated sustainable value chains that prioritize circular economy principles. Expert's insight highlights latent demand and opportunities in underserved segments, particularly among small and medium-sized businesses aiming for cost-effective waste solutions. However, supply chain disruptions and high capital requirements for advanced processing facilities remain persistent challenges. Leading vendor strategies focus on partnerships with municipalities and retailers to secure feedstock and off-take agreements for renewable natural gas, aligning with national decarbonization goals and leveraging economic and geopolitical shifts toward energy independence. Moreover, the future of industry ecosystems will depend on scalable, decentralized solutions that address both urban and industrial organic waste streams.
Major companies operating in the U.S. food waste management industry include Casella Waste Systems, Inc.; Covanta Ltd.; Divert, Inc.; Hulsey Environmental Services; Organix Recycling; Recycle Track Systems; Republic Services, Inc.; Rumpke; Shapiro Enterprises; Suez North America; Veolia North America; and Waste Management, Inc.
Key Players
- Casella Waste Systems, Inc.
- Covanta Ltd. (Covanta Holding Corporation)
- Divert, Inc.
- Hulsey Environmental Services
- Organix Recycling
- Recycle Track Systems (RTS)
- Republic Services, Inc.
- Rumpke
- Shapiro Enterprises (Skip Shapiro Enterprises)
- Suez North America
- Veolia North America
- Waste Management, Inc. (WM)
Industry Developments
- July 2025: Divert, Inc. partnered with United States Cold Storage to launch a recycling program. It will convert unsold food and beverage products into renewable energy and soil amendments, supporting circular economy principles.
- June 2023, Viridi Energy partnered with American Organic Energy to develop a major U.S. waste-to-energy project. It aims to convert 210,000 tons of annual food waste into renewable natural gas and agricultural products.
U.S. Food Waste Management Market Segmentation
By Waste Type Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- Cereals
- Dairy products
- Fruits & Vegetables
- Meat, Fish, & Seafood
- Processed Food
- Other Waste Types
By Process Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- Anaerobic
- Aerobic
- Combustion/Incineration
- Other Processes
By Source Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- Primary Food Producers
- Food Manufacturers
- Food Distributors & Suppliers
- Food Service Providers
- Municipalities & Households
By Application Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- Animal Feed
- Fertilizers
- Biofuel
- Power Generation
U.S. Food Waste Management Market Report Scope
|
Report Attributes |
Details |
|
Market Size in 2024 |
USD 17.76 Billion |
|
Market Size in 2025 |
USD 18.70 Billion |
|
Revenue Forecast by 2034 |
USD 30.01 Billion |
|
CAGR |
5.40% from 2025 to 2034 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Historical Data |
2020–2023 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025–2034 |
|
Quantitative Units |
Revenue in USD Billion and CAGR from 2025 to 2034 |
|
Report Coverage |
Revenue Forecast, Competitive Landscape, Growth Factors, and Industry Trends |
|
Segments Covered |
|
|
Competitive Landscape |
|
|
Report Format |
|
|
Customization |
Report customization as per your requirements with respect to countries, regions, and segmentation. |
FAQ's
The market size was valued at USD 17.76 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow to USD 30.01 billion by 2034.
The market is projected to register a CAGR of 5.40% during the forecast period.
A few of the key players in the market are Casella Waste Systems, Inc.; Covanta Ltd.; Divert, Inc.; Hulsey Environmental Services; Organix Recycling; Recycle Track Systems; Republic Services, Inc.; Rumpke; Shapiro Enterprises; Suez North America; Veolia North America; and Waste Management, Inc.
The fruits & vegetables segment accounted for 39.83% revenue share in 2024.
The anaerobic segment is expected to witness fastest growth at a CAGR of 5.7% during the forecast period.
