
Electric Construction Equipment Market Size, Share, Trends, Industry Analysis Report
By Equipment (Excavators, Loaders, Bulldozers), By Battery Capacity, By Battery Technology, By Power Source, By End-Use Industry, By Region – Market Forecast, 2025–2034
- Published Date:Jul-2025
- Pages: 129
- Format: PDF
- Report ID: PM5984
- Base Year: 2024
- Historical Data: 2020-2023
Overview
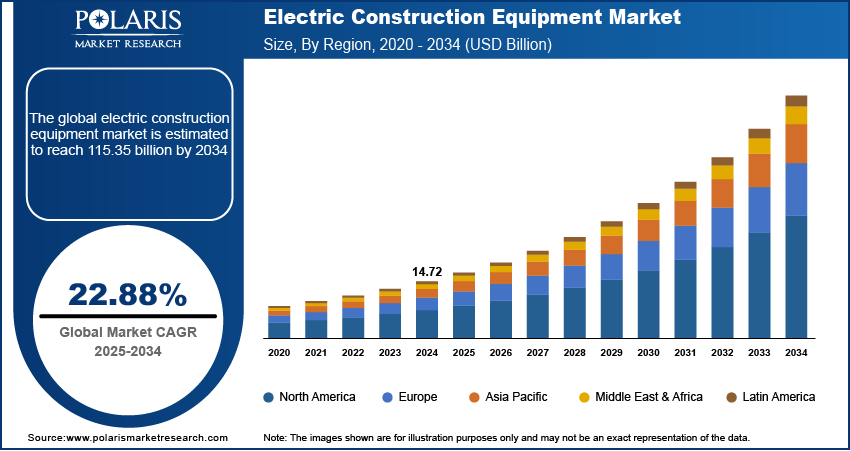
The global electric construction equipment market size was valued at USD 14.72 billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 22.88% from 2025 to 2034. Key factors driving demand for electric construction equipment include expanding urbanization worldwide, stringent carbon emission norms, and increasing fuel costs.
Key Insight
- The excavators segment accounted for a major market share in 2024.
- The 50 kWh to 200 kWh segment accounted for 42.87% of revenue share in 2024.
- The lithium-ion segment dominated the market share in 2024, accounting for a 73.21% share.
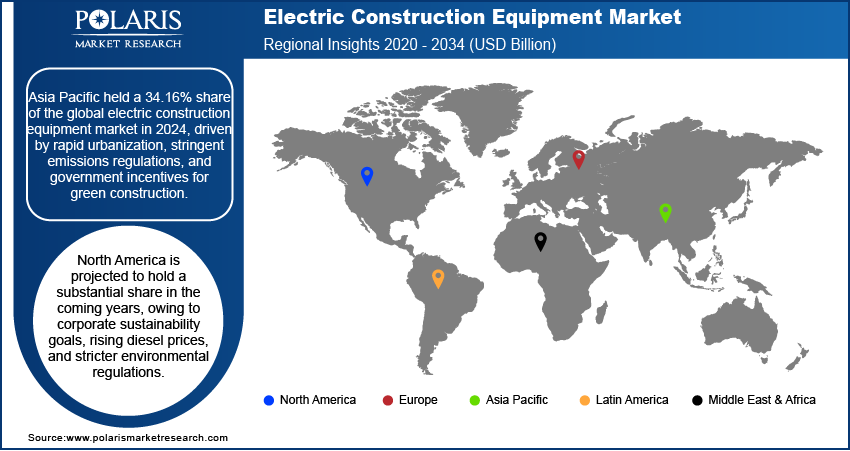
- Asia Pacific accounted for a 34.16% share of the global electric construction equipment market in 2024.
- China held a substantial revenue share in the Asia Pacific electric construction equipment landscape in 2024.
- The market in Europe is projected to grow at a rapid pace in the coming years.
- Countries such as Germany, France, and the UK are implementing strict regulations on diesel engines in urban construction zones, prompting contractors to shift toward electric alternatives.
Electric construction equipment refers to heavy machinery and vehicles used in construction projects that are powered by electric motors instead of traditional internal combustion engines. These machines, such as excavators, wheel loaders, bulldozers, and forklifts, draw energy primarily from rechargeable lithium-ion battery packs. The shift to electric power in construction machinery is driven by the industry's need to reduce carbon emissions, noise pollution, and operating costs, while meeting increasingly strict environmental regulations and sustainability goals. Electric construction equipment operates with zero tailpipe emissions, making it particularly suitable for use in urban environments, residential areas, tunnels, and indoor projects where air quality and noise are major concerns.
The usage of electric construction equipment spans a wide range of applications. On construction sites, electric excavators and loaders perform tasks such as digging, earthmoving, material handling, and site preparation. Large electric construction equipment, including cable-powered excavators, is used for heavy-duty tasks on major infrastructure projects. The adoption of electric construction machinery is also accelerating the integration of advanced electronic systems and automation, creating the way for smarter, more efficient, and autonomous construction operations in the future.
To Understand More About this Research: Request a Free Sample Report
The electric construction equipment market demand is driven by the expanding urbanization across the world. World Economic Forum, in its 2022 report, stated that the share of the world’s population living in cities is expected to rise to 80% by 2050, from 55% in 2022. This rise in urbanization is prompting governments to invest in the development of roads, buildings, highways, bridges, and other infrastructure, which is fueling the high adoption of electric construction equipment, as this equipment is needed in the initial phases for earthmoving, clearing sites, and digging foundation pits.
Industry Dynamics
- Stringent carbon emission norms are driving the market growth by prompting construction companies to adopt electric construction equipment to avoid penalties.
- Increasing fuel costs are driving the demand for electric construction equipment as it operates on a battery, offering lower energy costs and greater long-term savings.
- The growing focus on developing smart cities is creating a lucrative market opportunity.
- The high cost of electric construction equipment hinders its demand.
Stringent Carbon Emission Norms: Governments and regulatory bodies worldwide are enforcing stricter regulations on greenhouse gas emissions from diesel-powered machinery, prompting construction companies to adopt electric construction equipment to avoid penalties and maintain their operational licenses. Many cities are also implementing low-emission zones, restricting the use of traditional diesel machinery and pushing contractors to adopt cleaner electric options. Additionally, businesses aiming to meet sustainability targets and improve their environmental reputation are increasingly investing in electric construction equipment to reduce their carbon footprint. Therefore, the stringent carbon emission norms are driving innovation and adoption in the industry.
Increasing Fuel Costs: Diesel-powered construction equipment is becoming increasingly expensive to operate due to rising global fuel costs. This is encouraging construction companies to adopt electric construction equipment as it operates on a battery, offering lower energy costs and greater long-term savings. Additionally, electric equipment requires less maintenance since it has fewer moving parts and no need for oil changes or exhaust system repairs, which fuels its adoption in large-scale construction projects.
Segmental Insights
Equipment Analysis
Based on equipment, the segmentation includes excavators, loaders, bulldozers, cranes, dump trucks, rollers, and others. The excavators segment accounted for a significant share in 2024 due to their widespread adoption across various construction activities such as site preparation, trenching, demolition, and material handling. Contractors and developers preferred electric excavators due to their lower emissions, reduced noise levels, and lower operating costs compared to their diesel counterparts. Several countries in Europe and North America implemented stricter emission regulations, which accelerated the demand for electric excavators in urban infrastructure and residential projects. Additionally, advancements in battery technology enabled longer operating hours and faster charging for compact and mid-sized excavators, making them more practical for daily use on construction sites.
The loaders segment is projected to grow at a robust pace in the coming years, owing to their growing demand in road construction, mining, and industrial material handling applications. Governments and private developers are increasingly investing in infrastructure modernization and green building projects, which require efficient and versatile material-moving equipment such as loaders. Manufacturers are also introducing technologically enhanced models with telematics, remote diagnostics, and automated functions, which improve operator productivity and safety, leading to high adoption rates.
Battery Capacity Analysis
In terms of battery capacity, the segmentation includes less than 50 kWh, 50 kWh to 200 kWh, and more than 200 kWh. The 50 kWh to 200 kWh segment accounted for 42.87% of revenue share in 2024 due to its optimal balance between power output and operational efficiency. Equipment within this power range offered sufficient energy to support mid-sized machines such as loaders, compact excavators, and small cranes, which dominate urban construction and infrastructure maintenance projects. Construction companies prioritized machines with this battery range as they provided longer working hours without frequent recharging, which minimized downtime on job sites. Additionally, manufacturers focused their product development around this segment as it addressed a broad range of use cases across both residential and commercial construction activities. Supportive policies in Europe and North America also encouraged contractors to shift toward equipment in this battery range to meet zero-emission goals in city zones and noise-restricted areas.
Battery Technology Analysis
In terms of battery technology, the segmentation includes lead-acid, lithium-ion, and nickel-metal hydride. The lithium-ion segment dominated the market share in 2024, accounting for a 73.21% share. This is due to its superior energy density, longer lifecycle, and faster charging capabilities compared to traditional alternatives. Construction firms favored lithium-ion-powered machines as they delivered consistent performance across a variety of operating conditions, including high-load tasks and extended usage hours. Unlike lead-acid batteries, lithium-ion units offered lower maintenance requirements and reduced overall operating costs, making them more suitable for intensive construction environments. Major manufacturers increasingly adopted this technology in compact and mid-sized equipment models, further accelerating its penetration. Regulatory pressure to reduce carbon emissions and noise pollution in urban areas also contributed to its widespread use.
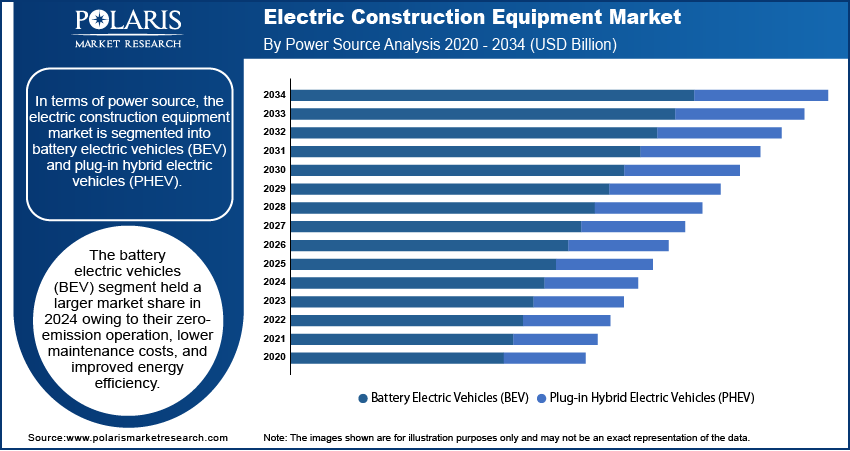
Power Source Analysis
In terms of power source, the segmentation includes battery electric vehicles (BEV) and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEV). The battery electric vehicles (BEV) segment held the largest market share in 2024 owing to their zero-emission operation, lower maintenance costs, and improved energy efficiency. Construction companies adopted BEVs at a faster rate as regulatory authorities in Europe, North America, and parts of Asia enforced stringent emission standards and promoted green construction practices. BEV-powered machinery allowed contractors to operate in noise-sensitive and emission-restricted zones without compromising performance. Manufacturers also focused on expanding their BEV product lines across various equipment types, including excavators, loaders, and compact cranes, which helped accelerate product penetration. The declining cost of lithium-ion batteries and the expansion of fast-charging infrastructure further supported the adoption of BEV models across both urban and semi-urban projects.
Regional Analysis
The Asia Pacific electric construction equipment market accounted for 34.16% of the global market share in 2024. This dominance is attributed to rapid urbanization, stringent emissions regulations, and government incentives for green construction. United Nations Human Settlements Programme, in its report, stated that the urban population in Asia is expected to grow by 50% by 20250. Countries such as India, Japan, and South Korea have invested heavily in infrastructure projects, which has driven the adoption of electric construction equipment. Additionally, rising fuel costs and the need for energy-efficient solutions in densely populated cities fueled adoption. The growing focus on smart cities and renewable energy integration further supported the shift toward electric construction equipment in the region.
China Electric Construction Equipment Market Insight
China held a substantial revenue share in the Asia Pacific electric construction equipment landscape in 2024 due to aggressive government policies to reduce pollution and achieve carbon neutrality by 2060. The country's dominance in battery production and electric vehicle (EV) technology lowered costs for electric machinery, contributing to market expansion. Major construction projects, such as those under the Belt and Road Initiative, are increasingly mandating the use of electric construction equipment. Local manufacturers, such as SANY and XCMG, further expanded their electric portfolios, supported by subsidies and stricter emissions standards in urban areas, leading to industry expansion.
North America Electric Construction Equipment Market Trends
North America is projected to hold a substantial share in the coming years, owing to corporate sustainability goals, rising diesel prices, and stricter environmental regulations. The U.S. and Canada are witnessing increased investments in renewable energy projects, which prioritize clean construction practices, leading to high adoption of electric construction equipment. Incentives such as tax credits for zero-emission equipment and partnerships between manufacturers and utility companies are also accelerating adoption. Additionally, the trend toward electrification in mining and industrial applications is boosting demand for battery-powered machinery.
U.S. Electric Construction Equipment Market Overview
The U.S. is witnessing growing demand for electric construction equipment due to federal and state-level emissions regulations, particularly in California, which has stringent air quality standards. The Biden administration’s infrastructure bill, which promotes green construction, also increased demand for construction equipment powered by battery or electricity. Advances in battery technology and charging infrastructure in the U.S. are making electric equipment more viable for heavy-duty applications. Companies such as Caterpillar and John Deere are investing in electric models to meet rising demand from both the public and private sectors.
Europe Electric Construction Equipment Market Assessment
The market in Europe is projected to grow at a rapid pace in the coming years, owing to the EU’s ambitious Green Deal and emissions reduction targets. Countries such as Germany, France, and the UK are imposing stringent regulations on diesel engines in urban construction zones, prompting contractors to shift toward electric alternatives. Government subsidies, carbon pricing, and corporate ESG commitments are further driving demand. Additionally, the region’s strong focus on circular economy principles and sustainable urban development is accelerating the shift to electric machinery, with manufacturers such as Volvo CE and Liebherr expanding their zero-emission offerings.
Key Players and Competitive Analysis
The electric construction equipment industry is rapidly evolving, driven by sustainability goals, stricter emissions regulations, and advancements in battery technology. Major manufacturers, such as Caterpillar Inc., Komatsu Ltd., and Hitachi Construction Machinery Co., Ltd., are investing heavily in electric excavators, loaders, and compactors to meet the growing demand for zero-emission machinery. John Deere and Volvo CE have introduced electric wheel loaders and compact excavators, targeting urban construction and indoor applications where noise and pollution restrictions are critical. Meanwhile, Liebherr Group and JCB have launched high-performance electric excavators, with JCB’s 19C-1E model becoming one of the first fully electric mini excavators in commercial use.
A few major companies operating in the electric construction equipment market include Caterpillar Inc.; Doosan Infracore Co., Ltd.; Hitachi Construction Machinery Co., Ltd.; JCB; John Deere; Komatsu Ltd.; Kubota Corporation; Liebherr Group; Sany Group; Terex Corporation; and Volvo CE.
Key Players
- Caterpillar Inc.
- Doosan Infracore Co., Ltd.
- Hitachi Construction Machinery Co., Ltd.
- JCB
- John Deere
- Komatsu Ltd.
- Kubota Corporation
- Liebherr Group
- Sany Group
- Terex Corporation
- Volvo CE
Industry Developments
June 2024: SANY Group, in collaboration with local partner DNL Machine & Equipment, launched the SY215E medium-sized electric excavator in the Netherlands.
May 2025: Volvo CE announced the launch of the largest electric excavator, EC230, in Japan at the Japan CSPI-Expo.
September 2023: Komatsu Ltd. introduced the PC200LCE-11 and 210LCE-11 models of its 20-tonne class electric excavators as rental machines in the Japanese and European regions.
Electric Construction Equipment Market Segmentation
By Equipment Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- Excavators
- Loaders
- Bulldozers
- Cranes
- Dump trucks
- Roller
- Others
By Battery Capacity Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- Less Than 50 kWh
- 50 kWh to 200 kWh
- More Than 200 kWh
By Battery Technology Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- Lead-Acid
- Lithium-Ion
- Nickel-Metal Hydride
By Power Source Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- Battery Electric Vehicles (BEV)
- Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEV)
By End-Use Industry Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- Construction
- Mining
- Material Handling
- Agriculture
- Others
By Regional Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- North America
- U.S.
- Canada
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- UK
- Italy
- Spain
- Netherlands
- Russia
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- Malaysia
- South Korea
- Indonesia
- Australia
- Vietnam
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Middle East & Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Israel
- South Africa
- Rest of Middle East & Africa
- Latin America
- Mexico
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
Electric Construction Equipment Market Report Scope
|
Report Attributes |
Details |
|
Market Size in 2024 |
USD 14.72 Billion |
|
Market Size in 2025 |
USD 18.06 Billion |
|
Revenue Forecast by 2034 |
USD 115.35 Billion |
|
CAGR |
22.88% from 2025 to 2034 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Historical Data |
2020–2023 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025–2034 |
|
Quantitative Units |
Revenue in USD Billion and CAGR from 2025 to 2034 |
|
Report Coverage |
Revenue Forecast, Competitive Landscape, Growth Factors, and Industry Trends |
|
Segments Covered |
|
|
Regional Scope |
|
|
Competitive Landscape |
|
|
Report Format |
|
|
Customization |
Report customization as per your requirements with respect to countries, regions, and segmentation. |
FAQ's
The global market size was valued at USD 14.72 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow to USD 115.35 billion by 2034.
The global market is projected to register a CAGR of 22.88% during the forecast period.
Asia Pacific dominated the market in 2024.
A few of the key players in the market are Caterpillar Inc.; Doosan Infracore Co., Ltd.; Hitachi Construction Machinery Co., Ltd.; JCB; John Deere; Komatsu Ltd.; Kubota Corporation; Liebherr Group; Sany Group; Terex Corporation; and Volvo CE.
The battery electric vehicles (BEV) segment dominated the market in 2024.
The loaders segment is expected to witness the fastest growth during the forecast period.
