
Intracranial Aneurysm Market Size, Share, & Industry Analysis Report
: By Type (Surgical Clipping, Endovascular Coiling, Flow Diverters, and Others), By End-Use, and By Region– Market Forecast, 2025–2034
- Published Date:Jun-2025
- Pages: 130
- Format: PDF
- Report ID: PM1805
- Base Year: 2024
- Historical Data: 2020-2023
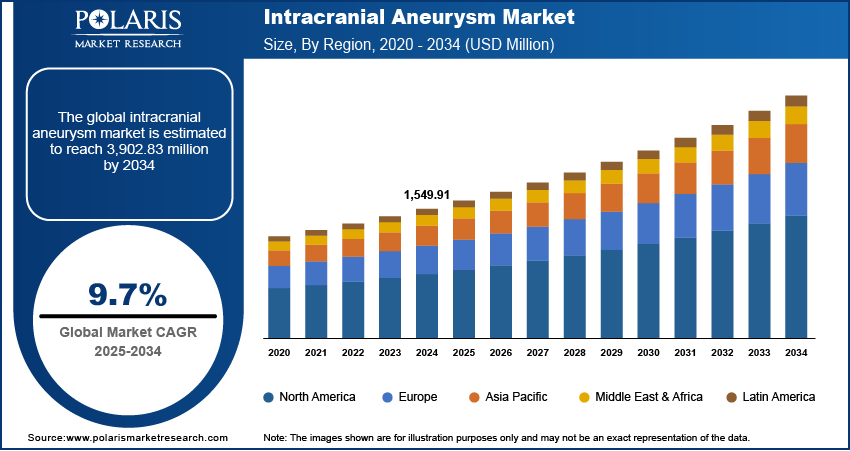
The intracranial aneurysm market size was valued at USD 1,549.91 million in 2024, exhibiting a CAGR of 9.7% during 2025–2034. The intracranial aneurysm market is driven by rising prevalence, advanced imaging technologies, increasing awareness, minimally invasive treatment demand, and growing elderly population prone to cerebrovascular disorders requiring prompt diagnosis and intervention.
Market Overview:
The intracranial aneurysm market focuses on the development, production, and application of medical therapies and devices used to diagnose and treat brain aneurysms. An intracranial aneurysm, also known as a cerebral or brain aneurysm, is a bulge or weak area in the wall of an artery in the brain, causing abnormal widening and ballooning. These aneurysms can rupture, leading to subarachnoid hemorrhage or stroke, making timely diagnosis and treatment crucial.
This market has seen significant growth due to increased awareness of the importance of early detection, advancements in neurovascular imaging technology, and a growing preference for minimally invasive treatment methods. Key trends include the rising adoption of flow-diverting stents and endovascular coiling, which offer faster recovery times and fewer complications compared to traditional surgical approaches.
The increasing prevalence of neurological disorders and intracranial aneurysms worldwide is a primary driver of this market expansion. Additionally, the rising global geriatric population, which is more susceptible to developing aneurysms, further contributes to growth. Technological advancements in medical devices, such as improved embolization coils and flow diverters, along with a growing inclination towards minimally invasive procedures, also bolster market development. Increased awareness and enhanced diagnostic techniques facilitate earlier detection and treatment, further driving growth in the intracranial aneurysm market.
To Understand More About this Research: Request a Free Sample Report
Industry Dynamics:
Increasing Prevalence of Intracranial Aneurysms
The rising prevalence of intracranial aneurysms globally is a significant driver. According to a study published in the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) in 2021, the estimated prevalence of unruptured intracranial aneurysms ranges from 3.2% to 7% in the general adult population. This substantial prevalence indicates a large pool of individuals requiring diagnosis and potential treatment, thereby fueling the demand for diagnostic tools and therapeutic interventions. Furthermore, factors such as genetic predisposition, hypertension drugs, and smoking contribute to the increased occurrence of these conditions across different age groups. Consequently, the high and increasing prevalence of intracranial aneurysms directly contributes to the growth by expanding the patient base and the need for effective management strategies.
Advancements in Neurovascular Imaging Technologies
Technological advancements in neurovascular imaging play a crucial role. Improved imaging modalities, such as magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) and computed tomography angiography (CTA), allow for more accurate and non-invasive detection of intracranial aneurysms. A research article published in PubMed in 2022 highlighted the enhanced sensitivity and specificity of high-resolution MRA in identifying even small-sized aneurysms. These advancements enable earlier diagnosis, which is critical for preventing rupture and improving patient outcomes. The ability to visualize cerebral vasculature with greater precision facilitates better treatment planning and brain monitoring, thereby increasing the adoption of these advanced imaging techniques. As diagnostic capabilities continue to evolve, they serve as a significant driver by enhancing detection rates and guiding therapeutic decisions.
Growing Preference for Minimally Invasive Treatments
The increasing preference for minimally invasive treatment options is another key driver. Endovascular techniques, such as coil embolization and flow diversion, offer significant advantages over traditional open surgical clipping, including shorter hospital stays, reduced recovery times, and lower risk of complications. A study published by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) in 2023 reported a significant rise in the utilization of endovascular coiling as the primary treatment modality for intracranial aneurysms due to its favorable safety profile and efficacy in many cases. This shift towards minimally invasive surgery and procedures is driven by patient demand for less invasive options and the continuous development of innovative endovascular devices. The growing acceptance and application of these advanced treatment methods are substantially contributing to the expansion by offering effective and less invasive solutions.
Segmental Insights:
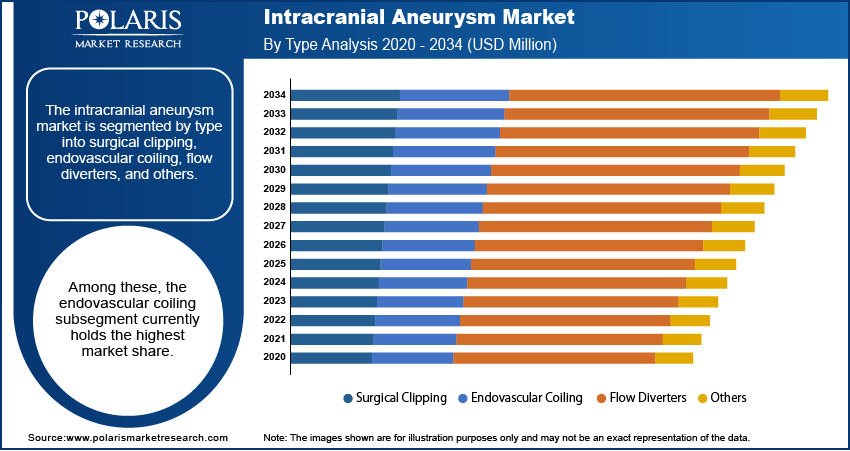
Market Assessment By Type
The endovascular coiling subsegment is expected to hold the largest market share during the forecast period. This can be attributed to several factors, including the increasing adoption of minimally invasive procedures and continuous advancements in coil technology. Endovascular coiling provides a less invasive alternative to traditional surgical clipping, leading to shorter hospital stays, quicker recovery times, and potentially fewer complications.
On the other hand, the flow diverters subsegment is showing the highest growth rate. Flow diverters are a relatively new technology designed to treat specific types of intracranial aneurysms, particularly large and wide-necked ones, by redirecting blood flow away from the aneurysm sac. The growing clinical evidence supporting the long-term efficacy and safety of flow diverters—along with their ability to address complex aneurysm shapes that may be difficult for other endovascular techniques—is driving their rapid adoption. As more neurovascular specialists gain experience with flow diverters and as the technology continues to evolve, their usage is expected to increase.
Market Evaluation By End-Use
The hospital's subsegment accounts for the largest share during the forecast period. This is primarily due to the fact that hospitals are typically equipped with the advanced neuroimaging and neurosurgical infrastructure required for the diagnosis and comprehensive management of intracranial aneurysms, including both surgical and endovascular treatments. Furthermore, hospitals often handle the majority of complex and emergency cases related to ruptured aneurysms, contributing significantly to their dominant position.
The clinic's subsegment is anticipated to demonstrate the highest growth rate over the forecast period. This growth is driven by the increasing focus on outpatient and specialized neurovascular clinics that offer more cost-effective and accessible treatment options for certain types of unruptured aneurysms and follow-up care. The shift towards less invasive diagnostic and treatment procedures that can be performed in specialized clinic settings, along with the growing patient preference for convenient and timely access to care, is fueling the expansion of this subsegment.
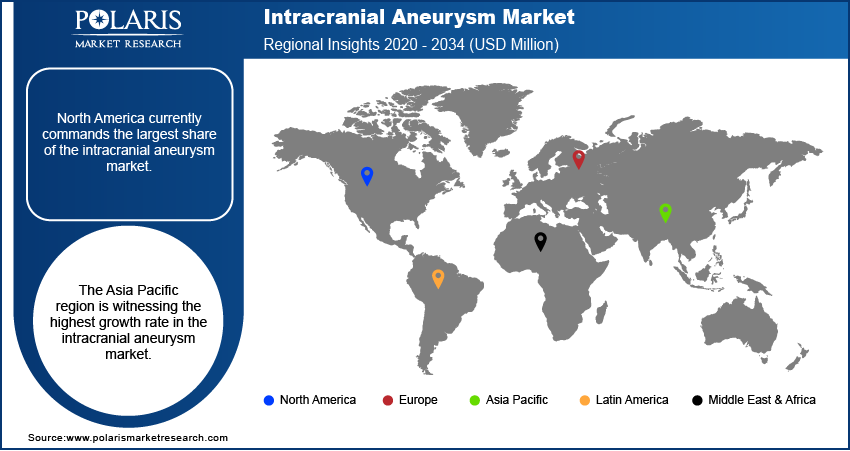
Regional Analysis
The North America intracranial aneurysm market currently commands the largest share. This can be attributed to the region's sophisticated healthcare system, the presence of leading medical device manufacturers, and favorable reimbursement policies for neurovascular procedures. Furthermore, the high awareness levels regarding neurological conditions and the widespread availability of advanced diagnostic and treatment modalities contribute to the significant market penetration in this region. The robust healthcare infrastructure and continuous technological advancements solidify North America's leading position.
The Asia Pacific intracranial aneurysm market is witnessing the highest growth rate during the forecast period. The increasing healthcare expenditure, a large and aging population susceptible to cerebrovascular diseases, and improving access to advanced neurosurgical and endovascular facilities in countries like China and India primarily drive this rapid expansion. Moreover, the rising awareness of neurological disorders and the growing adoption of minimally invasive treatment options are further accelerating the market growth in this region. The confluence of these factors positions Asia Pacific as a key growth engine.
Key Players and Competitive Insights
The competitive landscape is characterized by the presence of both well-established multinational corporations and smaller, specialized medical device companies. These players are engaged in continuous innovation, focusing on developing advanced technologies that improve treatment outcomes and patient safety. Competition is driven by factors such as product differentiation, technological advancements, strategic collaborations, and geographical expansion. Companies are investing in research and development to introduce next-generation devices with enhanced features, such as improved deliverability of embolic coils, more effective flow diversion capabilities, and safer surgical clip designs. Regulatory approvals and market access also play a crucial role in shaping the competitive environment.
List of Key Companies in Intracranial Aneurysm Industry:
- B. Braun Melsungen AG
- Integra LifeSciences Corporation (Codman Neuro)
- Johnson & Johnson (CERENOVUS)
- Kaneka Corporation
- Medtronic plc
- MicroPort Scientific Corporation
- Penumbra, Inc.
- Phenox GmbH
- Stryker Corporation
- Terumo Corporation (MicroVention Inc.)
Intracranial Aneurysm Industry Developments
- March 2025: Medtronic issued a recall for specific models of its Pipeline Vantage embolization devices used in the treatment of intracranial aneurysms. The recall was deemed serious by the FDA following reports of device malfunctions leading to patient injuries and deaths.
- May 2023: Stryker Corporation finalized its acquisition of Cerus Endovascular Ltd., a medical device company focused on neurointerventional devices for treating intracranial aneurysms.
Intracranial Aneurysm Market Segmentation
By Type Outlook (Revenue – USD Million, 2020–2034)
- Surgical Clipping
- Endovascular Coiling
- Flow Diverters
- Others
By End-Use Outlook (Revenue – USD Million, 2020–2034)
- Hospitals
- Clinics
- Others
By Regional Outlook (Revenue-USD Million, 2020–2034)
- North America
- US
- Canada
- Mexico
- Europe
- Germany
- France
- UK
- Italy
- Spain
- Netherlands
- Russia
- Rest of Europe
- Asia Pacific
- China
- Japan
- India
- Malaysia
- South Korea
- Indonesia
- Australia
- Vietnam
- Rest of Asia Pacific
- Middle East & Africa
- Saudi Arabia
- UAE
- Israel
- South Africa
- Rest of Middle East & Africa
- Latin America
- Brazil
- Argentina
- Rest of Latin America
Intracranial Aneurysm Market Report Scope:
|
Report Attributes |
Details |
|
Market Size Value in 2024 |
USD 1,549.91 million |
|
Market Size Value in 2025 |
USD 1,696.38 million |
|
Revenue Forecast by 2034 |
USD 3,902.83 million |
|
CAGR |
9.7% from 2025 to 2034 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Historical Data |
2020–2023 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025–2034 |
|
Quantitative Units |
Revenue in USD million and CAGR from 2025 to 2034 |
|
Report Coverage |
Revenue Forecast, Market Competitive Landscape, Growth Factors, and Industry Insights |
|
Segments Covered |
|
|
Regional Scope |
|
|
Competitive Landscape |
|
|
Report Format |
|
|
Customization |
Report customization as per your requirements with respect to countries, regions, and segmentation. |
How is the report valuable for an organization?
Workflow/Innovation Strategy
The intracranial aneurysm market has been segmented into detailed segments of type and end-use. Moreover, the study provides the reader with a detailed understanding of the different segments at both the global and regional levels.
Market Entry Strategies
A successful growth and marketing strategy necessitates a multi-faceted approach. Companies should prioritize robust research and development efforts to introduce innovative and technologically advanced devices that address unmet clinical needs, such as improved safety and efficacy in treating complex aneurysms. Strategic collaborations with hospitals and key opinion leaders can facilitate product adoption and generate crucial clinical data. Educational initiatives targeting neurosurgeons and interventional neuroradiologists are essential for increasing awareness and proper utilization of new technologies.
FAQ's
The global market size was valued at USD 1,549.91 million in 2024 and is projected to grow to USD 3,902.83 million by 2034.
The market is projected to register a CAGR of 9.7% during the forecast period, 2024-2034.
North America had the largest share of the market.
Some of the major players include Medtronic plc, Stryker Corporation, Johnson & Johnson (CERENOVUS), Terumo Corporation (MicroVention Inc.), B. Braun Melsungen AG, MicroPort Scientific Corporation, Integra LifeSciences Corporation (Codman Neuro), Penumbra, Inc., Kaneka Corporation, and Phenox GmbH.
The endovascular coiling segment accounted for the largerst share in 2024.
Following are some of the trends: ? Increasing Preference for Minimally Invasive Endovascular Techniques: There's a growing trend towards using less invasive procedures like endovascular coiling and flow diversion over traditional surgical clipping due to benefits such as shorter recovery times and reduced complications. ? Technological Advancements in Neurovascular Devices: Continuous innovation in the design and materials of embolic coils, flow diverters, and stents is leading to improved safety and efficacy in aneurysm treatment. This includes the development of anti-thrombotic coatings and intrasaccular flow disruption devices.
An intracranial aneurysm, also known as a cerebral aneurysm or brain aneurysm, is a weakened and bulging area in the wall of a blood vessel in the brain. It occurs when the pressure of blood flowing through the artery pushes against a weak spot, causing it to balloon outwards. These aneurysms can vary in size and shape, with the most common type being a saccular or "berry" aneurysm, which resembles a sac attached to the artery. While many intracranial aneurysms remain small and asymptomatic, they carry the risk of rupturing, leading to bleeding in the brain (hemorrhagic stroke), a life-threatening condition.
