
U.S. Antifungal Drugs Market Size, Share, Trend, Industry Analysis Report
By Drug Class (Azoles, Echinocandins, Polyenes, Allylamines, Others), By Indication, By Dosage Form, By Distribution Channel – Market Forecast, 2025–2034
- Published Date:Jul-2025
- Pages: 128
- Format: PDF
- Report ID: PM6046
- Base Year: 2024
- Historical Data: 2020-2023
Overview
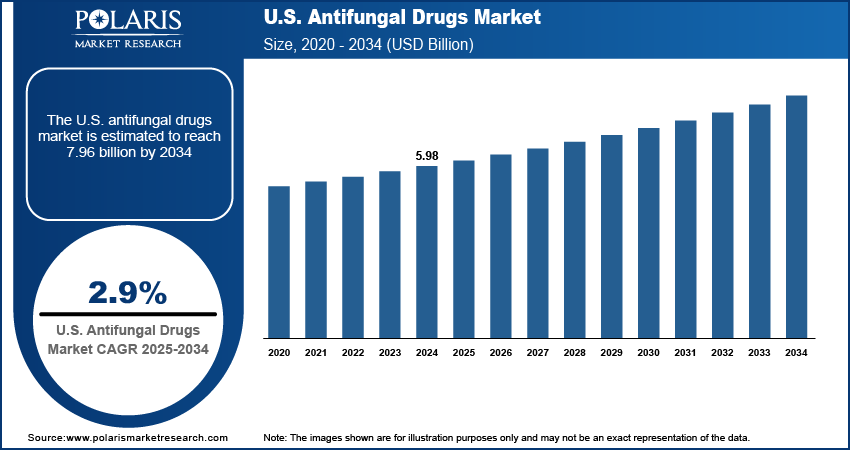
The U.S. antifungal drugs market size was valued at USD 5.98 billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 2.9% from 2025 to 2034. A large population undergoing chemotherapy, organ transplants, and autoimmune treatments increases vulnerability to opportunistic fungal infections. The growing base of immunocompromised individuals is significantly boosting the demand for effective antifungal therapies in both inpatient and outpatient settings.
Key Insights
- Azoles drug segment accounted for ~48% of the revenue share in 2024 due to their broad-spectrum efficacy.
- Candidiasis segment held the largest revenue share in 2024 due to its widespread occurrence across various patient populations.
- The oral dosage form accounted for the largest revenue share in 2024 due to due to ease of use, broad application range, and strong patient adherence.
- The hospital pharmacies segment accounted for the largest revenue share in 2024 due to the high concentration of severe fungal infection treatments administered in clinical settings.
Industry Dynamics
- The growing population of immunocompromised individuals in the U.S. is playing a major role in driving demand for antifungal drugs.
- The U.S. healthcare system is facing a steady rise in hospital-acquired fungal infections, particularly among critically ill patients.
- Consumer preference for over-the-counter (OTC) and topical antifungal solutions for conditions such as athlete’s foot and ringworm is driving retail segment growth.
- High cost of the product hinders the U.S. antifungal drugs market growth.
Market Statistics
- 2024 Market Size: USD 5.98 billion
- 2034 Projected Market Size: USD 7.96 billion
- CAGR (2025–2034): 2.9%
The U.S. antifungal drugs market involves the development, production, and distribution of medications used to treat fungal infections in humans. These drugs target infections caused by fungi such as Candida, Aspergillus, and Cryptococcus, addressing both superficial and systemic infections. Frequent use of invasive devices such as catheters and ventilators in the U.S. hospitals is contributing to a rise in incidence of fungal infections such as candidemia. Hospitals are expanding antifungal drug use as part of infection control and patient safety protocols.
To Understand More About this Research: Request a Free Sample Report
Well-developed healthcare systems, coupled with widespread insurance coverage and supportive reimbursement models, are making advanced antifungal therapies more accessible to patients, encouraging higher treatment adoption and sustained pharmaceutical sales. Moreover, ongoing research, fast-track approvals, and the introduction of improved drug formulations are enhancing treatment efficacy and safety profiles. In the U.S., pharmaceutical companies are leading in launching next-generation antifungals targeting resistant fungal strains.
Drivers and Opportunities
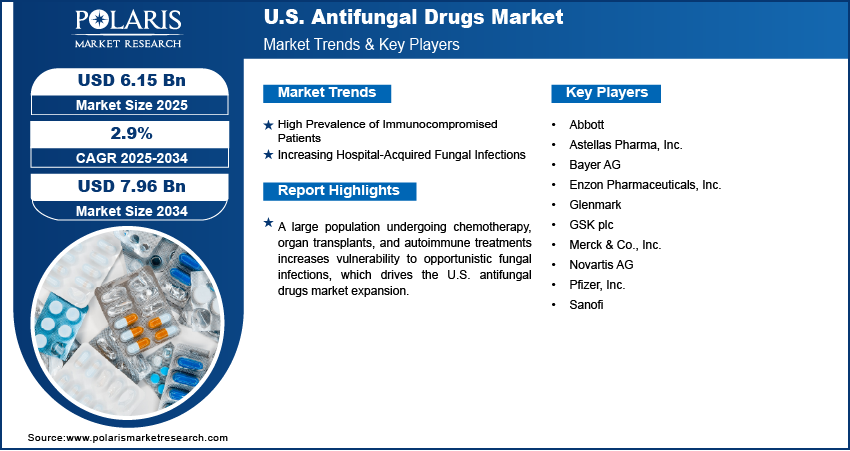
High Prevalence of Immunocompromised Patients: The growing population of immunocompromised individuals in the U.S. is playing a major role in driving the U.S. antifungal drugs market growth. Patients undergoing chemotherapy, those receiving organ or stem cell transplants, and individuals on long-term immunosuppressive therapies for autoimmune diseases are highly susceptible to fungal infections. Their weakened immune systems struggle to defend against opportunistic pathogens, such as Candida, Aspergillus, and Cryptococcus, which can lead to severe and sometimes life-threatening infections. Hospitals and clinics are increasingly relying on antifungal medications for both treatment and prophylactic use in high-risk patients. This shift is resulting in higher utilization across both inpatient and outpatient care. The need for safe, potent, and broad-spectrum antifungals is rising as physicians seek reliable options for vulnerable patient groups. Pharmaceutical firms are also investing in the development of therapies specifically tailored to this segment, further supporting the growth of the U.S. antifungal drugs market.
Increasing Hospital-Acquired Fungal Infections: The U.S. healthcare system is facing a steady rise in the incidence of hospital-acquired fungal infections, particularly among critically ill patients. The use of invasive medical equipment such as catheters, ventilators, and feeding tubes creates ideal entry points for fungal pathogens. Recent studies conducted by the National Institute of Library indicate that fungal infections are responsible for over 1.5 million fatalities each year. This alarming statistic underscores the significant impact of mycotic diseases on public health and highlights the urgent need for enhanced surveillance, diagnostics, and treatment strategies within the medical community. Extended ICU stays, frequent surgical interventions, and broad-spectrum antibiotic use further disrupt the body's microbial balance, increasing the risk of infections such as candidemia and invasive aspergillosis. Healthcare facilities are prioritizing the prevention and rapid management of these infections to reduce morbidity and mortality. Antifungal drugs are being used more aggressively as part of infection control protocols, especially in intensive care units. Hospitals are also adopting antifungal stewardship programs to ensure timely and appropriate treatment while minimizing resistance. This growing clinical need is fueling a surge in demand for fast-acting and broad-coverage antifungal medications. The trend is pushing pharmaceutical manufacturers to supply both traditional and advanced formulations suited for high-acuity hospital environments.
Segmental Insights
Drug Class Analysis
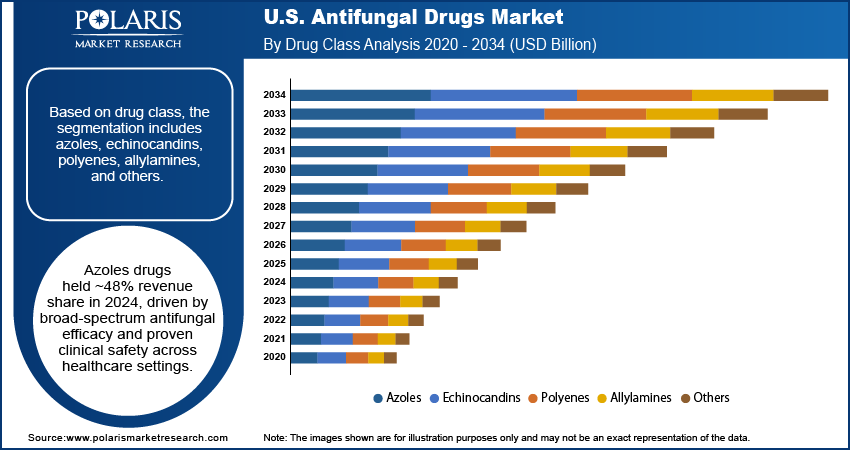
Based on drug class, the U.S. antifungal drugs market segmentation includes azoles, echinocandins, polyenes, allylamines, and others. The azoles drug segment accounted for ~48% of the revenue share in 2024 due to their broad-spectrum efficacy against both superficial and systemic fungal infections. Their established clinical safety makes them a preferred treatment across healthcare settings. Physicians often prescribe azoles for infections such as candidiasis and dermatophytosis due to their convenient oral and topical formulations. Longstanding market presence and inclusion in standard treatment guidelines continue to support their high usage. Generic availability also makes azoles cost-effective, further strengthening their demand among public and private healthcare providers. Consistent use in outpatient settings contributes to their sustained market leadership.
The echinocandins drug segment is projected to register the highest CAGR from 2025 to 2034 due to their potent activity against resistant Candida and Aspergillus strains, especially in hospitalized patients. These drugs are commonly administered intravenously, making them ideal for critical care environments where invasive fungal infections are prevalent. Their low toxicity and selective mechanism targeting fungal cell walls offer an advantage over other systemic antifungals. Hospitals are increasingly using echinocandins as first-line or rescue therapies in patients who fail azole treatments. Ongoing clinical adoption, combined with new product introductions, is expected to expand their use in severe fungal infections and drive rapid market expansion over the forecast period.
Indication Analysis
In terms of indication, the U.S. antifungal drugs market segmentation includes dermatophytosis, aspergillosis, candidiasis, and others. The candidiasis segment held the largest revenue share in 2024 due to its widespread occurrence across various patient populations. This infection ranges from mild mucocutaneous forms to serious bloodstream infections, particularly in individuals having weakened immunity. Use of invasive devices, antibiotics, and intensive care procedures increases the risk of Candida infections. Hospitals routinely administer antifungal prophylaxis or treatment to manage these cases, creating strong demand for drugs such as fluconazole and echinocandins. The availability of multiple treatment options across different delivery routes such as oral, topical, and intravenous makes candidiasis management accessible in diverse care settings. High prevalence and recurrence rates reinforce its dominance in the indication landscape.
The aspergillosis segment is expected to register a significant CAGR during the forecast period, due to increasing detection in immunosuppressed patients, including those undergoing chemotherapy or organ transplantation. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment are critical, often requiring potent antifungal agents such as voriconazole or liposomal amphotericin B. Rising awareness among clinicians and improved diagnostic tools have enhanced detection rates, leading to faster treatment initiation. Hospitals are adopting antifungal strategies that prioritize aspergillosis management in high-risk departments such as oncology and critical care. Increased clinical focus on fungal prophylaxis and advancements in antifungal formulations tailored for invasive fungal infections are contributing to the segment growth.
Dosage Form Analysis
In terms of dosage form, the U.S. antifungal drugs market segmentation includes oral drugs, ointments, powders, and others. The oral drugs segment accounted for the largest revenue share in 2024 due to the ease of use, broad application range, and strong patient adherence. These formulations are widely prescribed in outpatient settings for common fungal conditions such as vaginal candidiasis, onychomycosis, and tinea infections. Azole-based oral drugs are especially popular for their affordability, availability, and clinical effectiveness. Physicians prefer oral dosing for long-term treatments, as compliance and convenience are the most important factors. Increased access through retail pharmacies and online channels also supports their leading position. Many patients opt for oral medication as a first-line therapy, which reinforces its demand and market share across both branded and generic categories.
The ointments segment is projected to witness the highest growth rate during the forecast period, driven by rising demand for topical treatment of superficial fungal infections such as athlete’s foot and ringworm. These formulations provide targeted action with minimal systemic effects, making them suitable for self-care and over-the-counter use. Dermatologists often prescribe ointments for localized skin infections due to their ease of application and fast relief. Consumer preference for noninvasive and accessible solutions continues to boost ointment sales through retail and digital platforms. Expanding product lines and awareness campaigns promoting early treatment help drive faster adoption across urban and rural regions in the U.S.
Distribution Channel Analysis
In terms of distribution channel, the U.S. antifungal drugs market segmentation includes hospital pharmacies, retail pharmacies, and others. The hospital pharmacies segment accounted for the largest revenue share in 2024 due to the high concentration of severe fungal infection treatments administered in clinical settings. Invasive infections such as candidemia and aspergillosis often require immediate intervention with IV antifungal drugs, which are dispensed primarily through hospital pharmacies. The role of hospital pharmacists in managing dosing, drug interactions, and treatment monitoring ensures precise drug use in critical care. High patient turnover in oncology, transplant, and ICU departments sustains ongoing demand. Institutional buying patterns and formulary inclusion also contribute to large-volume purchases. Hospital-based treatment protocols continue to drive strong dependence on antifungal drugs distributed through institutional channels.
The retail pharmacies segment is projected to witness the highest growth during the forecast period, due to the increasing use of antifungal treatments for common conditions such as skin and nail infections. Consumers are opting for over-the-counter and prescription solutions that are accessible without visiting a hospital. Rising awareness of personal hygiene and early symptom management supports strong product movement in retail outlets. Pharmacies are expanding their antifungal offerings across creams, powders, and oral formulations, meeting the needs of diverse patient demographics. Growth in e-commerce and U.S. telemedicine is also facilitating direct-to-consumer antifungal sales. The shift toward convenient, self-managed care is a key factor driving faster retail pharmacy adoption.
Key Players and Competitive Analysis
The competitive landscape of the U.S. antifungal drugs market is shaped by a mix of established pharmaceutical leaders and emerging biotech firms leveraging targeted innovation. Industry analysis indicates growing investments in novel antifungal agents capable of addressing resistant fungal strains and reducing systemic toxicity. Market expansion strategies include the development of broad-spectrum formulations, lifecycle management of existing drugs, and penetration into outpatient and over-the-counter segments. Companies are actively pursuing mergers and acquisitions to strengthen product pipelines and extend market reach, often followed by post-merger integration to consolidate research, manufacturing, and regulatory operations. Strategic alliances between pharmaceutical developers and diagnostic firms are accelerating the clinical validation of new therapies. Technology advancements in drug delivery systems such as liposomal formulations and sustained-release platforms are also gaining momentum. Regulatory support for accelerated drug approvals is encouraging companies to fast-track innovation, creating a dynamic, highly competitive environment where therapeutic differentiation is becoming a key determinant of market leadership.
Key Players
- Abbott
- Astellas Pharma, Inc.
- Bayer AG
- Enzon Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
- Glenmark
- GSK plc
- Merck & Co., Inc.
- Novartis AG
- Pfizer, Inc.
- Sanofi
U.S. Antifungal Drugs Industry Developments
March 2023: Cidara Therapeutics, Inc. and Melinta Therapeutics, LLC announced that the FDA approved REZZAYO (rezafungin for injection) for treating candidemia and invasive candidiasis in adults having limited or no alternative options.
U.S. Antifungal Drugs Market Segmentation
By Drug Class Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- Azoles
- Echinocandins
- Polyenes
- Allylamines
- Others
By Indication Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- Dermatophytosis
- Aspergillosis
- Candidiasis
- Others
By Dosage Form Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- Oral Drugs
- Ointments
- Powders
- Others
By Distribution Channel Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- Hospital Pharmacies
- Retail Pharmacies
- Others
U.S. Antifungal Drugs Market Report Scope
|
Report Attributes |
Details |
|
Market Size in 2024 |
USD 5.98 billion |
|
Market Size in 2025 |
USD 6.15 billion |
|
Revenue Forecast by 2034 |
USD 7.96 billion |
|
CAGR |
2.9% from 2025 to 2034 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Historical Data |
2020–2023 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025–2034 |
|
Quantitative Units |
Revenue in USD billion and CAGR from 2025 to 2034 |
|
Report Coverage |
Revenue Forecast, Competitive Landscape, Growth Factors, and Industry Trends |
|
Segments Covered |
|
|
Competitive Landscape |
|
|
Report Format |
|
|
Customization |
Report customization as per your requirements with respect to countries, regions, and segmentation. |
FAQ's
The U.S. market size was valued at USD 5.98 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow to USD 7.96 billion by 2034.
The U.S. market is projected to register a CAGR of 2.9% during the forecast period.
A few of the key players in the market are Abbott; Astellas Pharma, Inc.; Bayer AG; Enzon Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; Glenmark; GSK plc; Merck & Co., Inc.; Novartis AG; Pfizer, Inc.; and Sanofi.
The azoles drug segment accounted for ~48% of the revenue share in 2024 due to their broad-spectrum efficacy against both superficial and systemic fungal infections, along with established clinical safety, which makes them a preferred treatment across healthcare settings.
The candidiasis segment held the largest revenue share in 2024 due to its widespread occurrence across various patient populations.
