
U.S. E-Fuel Market Size, Share, Trend, Industry Analysis Report
By Product (E-Diesel, E-Gasoline, Ethanol, Hydrogen, Methanol, Others), By State, By Production Method, By End User, By Region – Market Forecast, 2025–2034
- Published Date:Aug-2025
- Pages: 128
- Format: PDF
- Report ID: PM6256
- Base Year: 2024
- Historical Data: 2020-2023
Overview
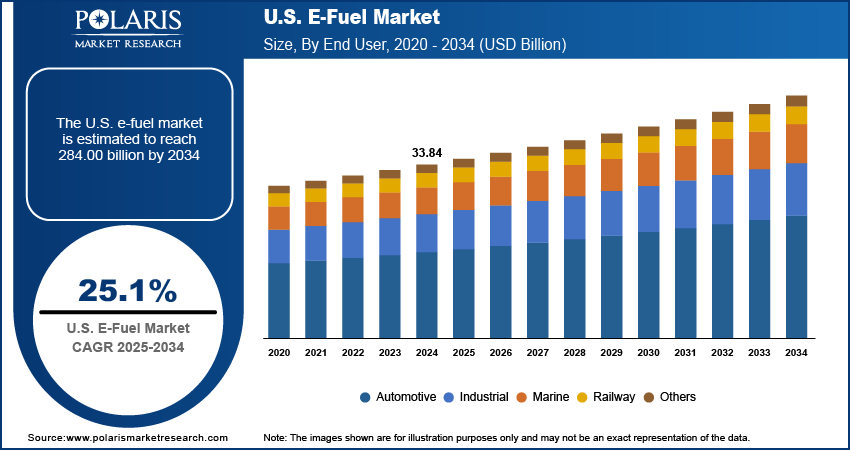
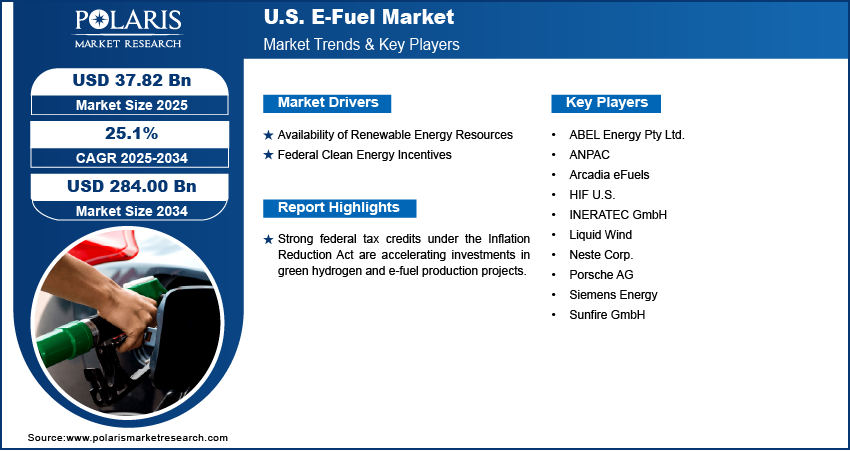
The U.S. e-fuel market size was valued at USD 33.84 billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 25.1% from 2025 to 2034. Government programs such as the Inflation Reduction Act offer tax credits and funding for clean hydrogen and carbon capture. These incentives are directly reducing capital costs for e-fuel projects, encouraging early commercialization and accelerating private-sector investment in production value chains.
Key Insights
- The ethanol segment held ~32% of the market share in 2024, driven by integration into existing fuel systems and regulatory blending requirements.
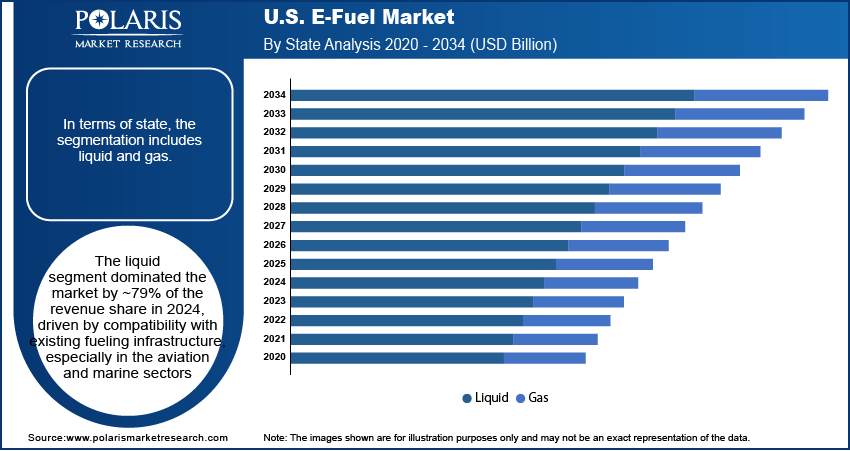
- The liquid segment captured ~79% of the revenue share in 2024, due to seamless compatibility with current fuel storage, transport, and dispensing infrastructure.
- The power-to-liquid segment led with ~49% share in 2024, supported by refinery integration and broad use across aviation, shipping, and heavy transport.
- The marine segment accounted for ~32% of the market in 2024, driven by IMO 2020 regulations and tightening emission standards in coastal and international waters.
Industry Dynamics
- Strong federal tax credits under the Inflation Reduction Act are accelerating investments in green hydrogen and e-fuel production projects.
- Growing partnerships between energy firms and airlines are driving demand for e-kerosene to meet sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) mandates.
- Expansion of carbon capture and renewable energy hubs enables scalable e-fuel production in regions such as the Gulf Coast and Southwest.
- High capital costs and lengthy permitting processes for infrastructure projects delay commercial-scale e-fuel deployment across the U.S.
Market Statistics
- 2024 Market Size: USD 33.84 billion
- 2034 Projected Market Size: USD 284.00 billion
- CAGR (2025–2034): 25.1%
AI Impact on U.S. E-Fuel Market
- AI tools enable e-fuel market players to enhance carbon capture, optimize production, improve supply chains, and meet compliance standards.
- They help reduce process costs and strengthen sustainability credentials.
- Due to the imposition of stringent U.S. environmental regulations, market players use AI solutions for real-time lifecycle carbon accounting and ESG reporting, which helps them meet federal and state-level clean energy mandates.
The U.S. e-fuel market refers to the industry focused on the production, distribution, and application of synthetic fuels created using renewable electricity and captured carbon dioxide or hydrogen. These fuels serve as low-emission alternatives to conventional fossil fuels in sectors such as aviation, shipping, and heavy transport, where full electrification remains technologically or economically challenging. E-fuels include options such as e-diesel, e-kerosene, and e-methanol, produced via Power-to-Liquid (PtL) or Power-to-Gas (PtG) processes. Heavy-duty transport, shipping, and aviation in the U.S. require energy-dense fuels. E-fuels provide drop-in solutions without overhauling infrastructure, enabling low-emission operations in sectors where batteries or electrification remain technically or economically unviable over long distances.
Policies such as California’s Low Carbon Fuel Standard (LCFS) and potential federal carbon pricing mechanisms are increasing the cost of fossil fuels. This is boosting the competitiveness of e-fuels while incentivizing fuel producers and refiners to adopt synthetic alternatives. Moreover, Improvements in direct air capture and point-source carbon capture technologies are making CO₂ feedstock more accessible and cost-effective. These advancements enhance the commercial feasibility of synthetic fuels by reducing input costs and enabling closed-loop carbon utilization systems.
Drivers & Opportunities
Availability of Renewable Energy Resources: The U.S. benefits from a strong renewable energy base, especially in states such as Texas, California, and Arizona, where solar and wind generation is already well established. According to the California Energy Commission, in 2024, renewable sources such as solar, wind, and geothermal provided 64% of California’s in-state electricity generation. This renewable infrastructure allows for efficient and cost-effective production of green hydrogen, a core feedstock in e-fuel synthesis. Access to steady and low-cost clean electricity lowers operating costs for electrolysis and improves the financial viability of e-fuel projects. Proximity to renewable power sources also supports the creation of dedicated e-fuel production zones, reducing transmission losses and enabling vertically integrated facilities that can scale output to meet rising demand.
Federal Clean Energy Incentives: The U.S. legislation, including the Inflation Reduction Act, has introduced targeted support for emerging clean technologies such as e-fuels. These policies offer production tax credits, capital subsidies, and loan guarantees for hydrogen generation, carbon capture, and related infrastructure. Such measures are making early-stage e-fuel ventures financially attractive, reducing risk for investors, and speeding up timelines for project development. Government support is helping to foster a competitive environment where innovation can thrive, allowing domestic firms to build technological leadership and position the U.S. as a global hub for sustainable fuel solutions.
Segmental Insights
Product Analysis
Based on product, the U.S. e-fuel market segmentation includes e-diesel, e-gasoline, ethanol, hydrogen, methanol, and others. The ethanol segment dominated the market with ~32% of the revenue share in 2024, due to its widespread integration into the existing fuel infrastructure and regulatory blending mandates. Ethanol production benefits from decades of domestic expertise, especially in bio-based processes, which reduces overall development time for e-fuel versions. Fuel producers are leveraging this advantage to offer e-ethanol as a low-carbon alternative without requiring major modifications to engines or distribution systems. Strong demand from the light-duty transportation sector, particularly in regions with biofuel blending standards, has pushed e-ethanol ahead of other e-fuels in terms of volume adoption and commercial maturity.
The hydrogen segment is expected to register a CAGR of 25.3% from 2025 to 2034 due to rising deployment in fuel cell vehicles, long-haul trucking, and heavy industrial applications. Federal support for clean hydrogen production, combined with falling electrolyzer costs and regional hydrogen hub development, is accelerating commercial momentum. Industries seeking deep decarbonization are increasingly turning to hydrogen for its energy density and versatility. Investment in hydrogen refueling infrastructure and growing collaborations between energy companies and transportation firms are also expected to drive the U.S. e-fuel market growth.
State Analysis
In terms of state, the U.S. e-fuel market segmentation includes liquid and gas. The liquid segment dominated the market by ~79% of the revenue share in 2024, driven by compatibility with existing fueling infrastructure, especially in aviation and marine sectors. These fuels can be stored, transported, and dispensed using conventional logistics systems, lowering adoption barriers for end users. Their high energy density makes them suitable for long-distance and high-load applications where electrification is not yet practical. Ongoing retrofitting of refineries and terminals to accommodate synthetic liquid fuels has further supported the segment’s growth. Industry preference for drop-in replacements continues to favor liquid e-fuels in near-term commercialization efforts.
The gas segment is expected to register a CAGR of 24.9% from 2025 to 2034 due to increasing demand for renewable methane and hydrogen in industrial applications and distributed energy systems. Industrial clusters and chemical producers are incorporating e-gas into processes to meet decarbonization targets. Modular gas infrastructure allows for flexible deployment in regions with constrained liquid-fuel distribution networks. Growth is also bolstered by rising investments in hydrogen pipelines and storage facilities. Utilities integrating e-gases into power generation and heating systems are further driving demand. Market participants view gas-based e-fuels as an effective solution for reducing emissions in decentralized, high-consumption environments.
Production Method Analysis
In terms of production method, the U.S. e-fuel market segmentation includes power-to-liquid, power-to-gas, and gas-to-liquid. The power-to-liquid segment held the largest revenue share of ~49% in 2024 due to its alignment with existing refining capabilities and wide applicability across multiple transport sectors. PtL pathways enable the production of synthetic hydrocarbons using captured CO₂ and renewable electricity, making them attractive for industries aiming to meet carbon-neutral targets. Projects leveraging waste CO₂ from industrial processes and renewable electricity from solar and wind have gained momentum, supported by government-backed pilot initiatives. The ability of PtL fuels to serve as drop-in alternatives for aviation and marine fuels has made this production route the most commercially mature in the U.S. e-fuel space.
The gas-to-liquid segment is expected to register the highest CAGR of 25.6% from 2025 to 2034 due to increased deployment in stranded natural gas recovery and emerging synthetic gas applications. GtL enables conversion of syngas from biomass or captured carbon sources into liquid fuels, offering a scalable path for carbon-neutral fuel production. Energy firms are piloting GtL facilities near hydrogen-rich regions and industrial CO₂ emitters, allowing for efficient feedstock access. Technological improvements in Fischer-Tropsch synthesis and reactor efficiency are reducing capital intensity, making GtL more commercially viable. The push for decentralized e-fuel hubs is further boosting GtL's long-term market potential.
End User Analysis
In terms of end user, the U.S. e-fuel market segmentation includes automotive, industrial, marine, railway, and others. The marine segment held ~32% of the revenue share in 2024 due to pressure from global regulations such as IMO 2020 and tightening emissions standards in coastal waters. Ship operators are seeking cleaner alternatives to heavy fuel oil, and synthetic fuels offer a compliant and scalable solution. Ports along both coasts are investing in bunkering infrastructure for low-carbon marine fuels. Shipping firms are adopting dual-fuel engines and retrofitting vessels to run on e-fuels, particularly in container and bulk cargo fleets. Rising fuel costs and carbon pricing are further pushing demand from this sector.
The automotive segment is expected to register the highest CAGR of 25.4% from 2025 to 2034, as synthetic fuels gain traction in decarbonizing internal combustion engine fleets. Vehicle manufacturers and fuel suppliers are working together to validate engine compatibility and ensure performance standards. States aiming to reduce emissions from legacy vehicles are offering incentives for using low-carbon fuels, encouraging wider adoption. E-fuels serve as a practical alternative in rural and long-distance driving scenarios where EV charging infrastructure is limited. Consumer interest in carbon-neutral mobility solutions without switching vehicle platforms is also supporting the segment’s expansion across both light and heavy-duty categories.
Key Players & Competitive Analysis
The competitive landscape of the U.S. e-fuel market is shaped by dynamic industry analysis, where players actively pursue market expansion strategies to capitalize on growing demand for low-carbon fuels. Companies are forming joint ventures and entering strategic alliances to pool resources, share technology, and accelerate the commercialization of production infrastructure. Mergers and acquisitions have gained traction, allowing key stakeholders to consolidate expertise and enhance vertical integration across the e-fuel value chain. Post-merger integration efforts focus on optimizing supply networks and streamlining project delivery timelines.
Technological advancements in power-to-liquid and green hydrogen production are being leveraged to improve process efficiency and reduce lifecycle emissions. Competitive differentiation increasingly depends on the ability to secure feedstock sources, develop scalable production platforms, and meet regulatory sustainability standards. Market participants are also investing in digital tools to support real-time monitoring, carbon accounting, and supply traceability, positioning themselves for long-term viability in a rapidly evolving energy transition landscape.
Key Players
- ABEL Energy Pty Ltd.
- Arcadia eFuels
- Carbon Engineering
- HIF U.S.
- INERATEC GmbH
- Liquid Wind
- Neste Corp.
- Porsche AG
- Siemens Energy
- Sunfire GmbH
U.S. E-Fuel Industry Developments
May 2023: Infinium announced construction on its second U.S. eFuels production site, Project Roadrunner, in Reeves County, Texas. The facility aims to be the world's largest eFuels plant, producing 23,000 tonnes (7.6 million gallons) of sustainable aviation fuel (eSAF) annually for clients including American Airlines and IAG.
U.S. E-Fuel Market Segmentation
By Product Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- E-Diesel
- E-Gasoline
- Ethanol
- Hydrogen
- Methanol
- Others
By State Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- Liquid
- Gas
By Production Method Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- Power-to-Liquid
- Power-to-Gas
- Gas-to-Liquid
By End User Outlook (Revenue, USD Billion, 2020–2034)
- Automotive
- Industrial
- Marine
- Railway
- Others
U.S. E-Fuel Market Report Scope
|
Report Attributes |
Details |
|
Market Size in 2024 |
USD 33.84 billion |
|
Market Size in 2025 |
USD 37.82 billion |
|
Revenue Forecast by 2034 |
USD 284.00 billion |
|
CAGR |
25.1% from 2025 to 2034 |
|
Base Year |
2024 |
|
Historical Data |
2020–2023 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025–2034 |
|
Quantitative Units |
Revenue in USD billion and CAGR from 2025 to 2034 |
|
Report Coverage |
Revenue Forecast, Competitive Landscape, Growth Factors, and Industry Trends |
|
Segments Covered |
|
|
Competitive Landscape |
|
|
Report Format |
|
|
Customization |
Report customization as per your requirements with respect to countries, regions, and segmentation. |
FAQ's
The U.S. market size was valued at USD 33.84 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow to USD 284.00 billion by 2034.
The U.S. market is projected to register a CAGR of 25.1% during the forecast period.
A few of the key players in the market are ABEL Energy Pty Ltd., ANPAC, Arcadia eFuels, HIF U.S., INERATEC GmbH, Liquid Wind, Neste Corp., Porsche AG, Siemens Energy, and Sunfire GmbH.
The ethanol segment dominated the market in 2024 with ~32% of the revenue share due to its widespread integration into the existing fuel infrastructure and regulatory blending mandates.
The liquid segment dominated the market by ~79% of the revenue share in 2024 driven by compatibility with existing fueling infrastructure, especially in aviation and marine sectors.
